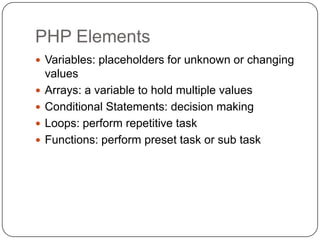
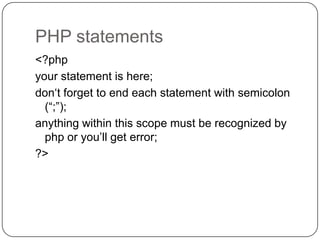
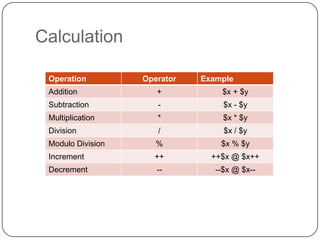
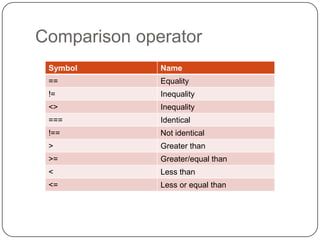
This document provides an overview of PHP and MySQL. It discusses key PHP elements like variables, arrays, conditional statements, and loops. It also covers PHP statements, naming variables, outputting values, performing calculations, working with arrays, conditional logic, and loops. The document then discusses connecting to and querying MySQL databases, and how to insert, update, delete data. It also covers building forms, getting form input, and basic file input/output in PHP.




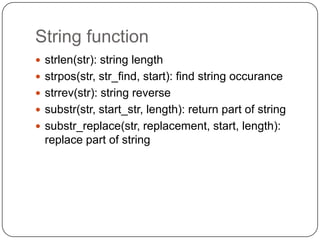
![Array
Declaration
$RGBcolor = array(“red”, “Blue”, “Green);
$mycar[] = “Rapide”;
Access
$myarray[element number]
Functions
array_pop(); array_push(); array_rand();
array_reverse; count(array); sort(array);
print_r(array)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phpmysql-120726212944-phpapp01/85/Php-my-sql-11-320.jpg)






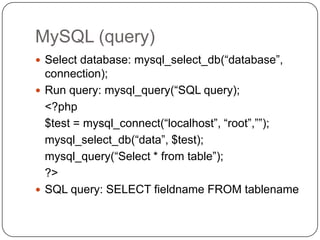
![MySQL (Display query)
mysql_fetch_array($result)
$result is array of data
Example:
<?php
$result = mysql_query(“MySQL select
query”);
while($row = mysql_fetch_array($result)) {
echo $row[„fieldname‟];
}
?>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phpmysql-120726212944-phpapp01/85/Php-my-sql-27-320.jpg)