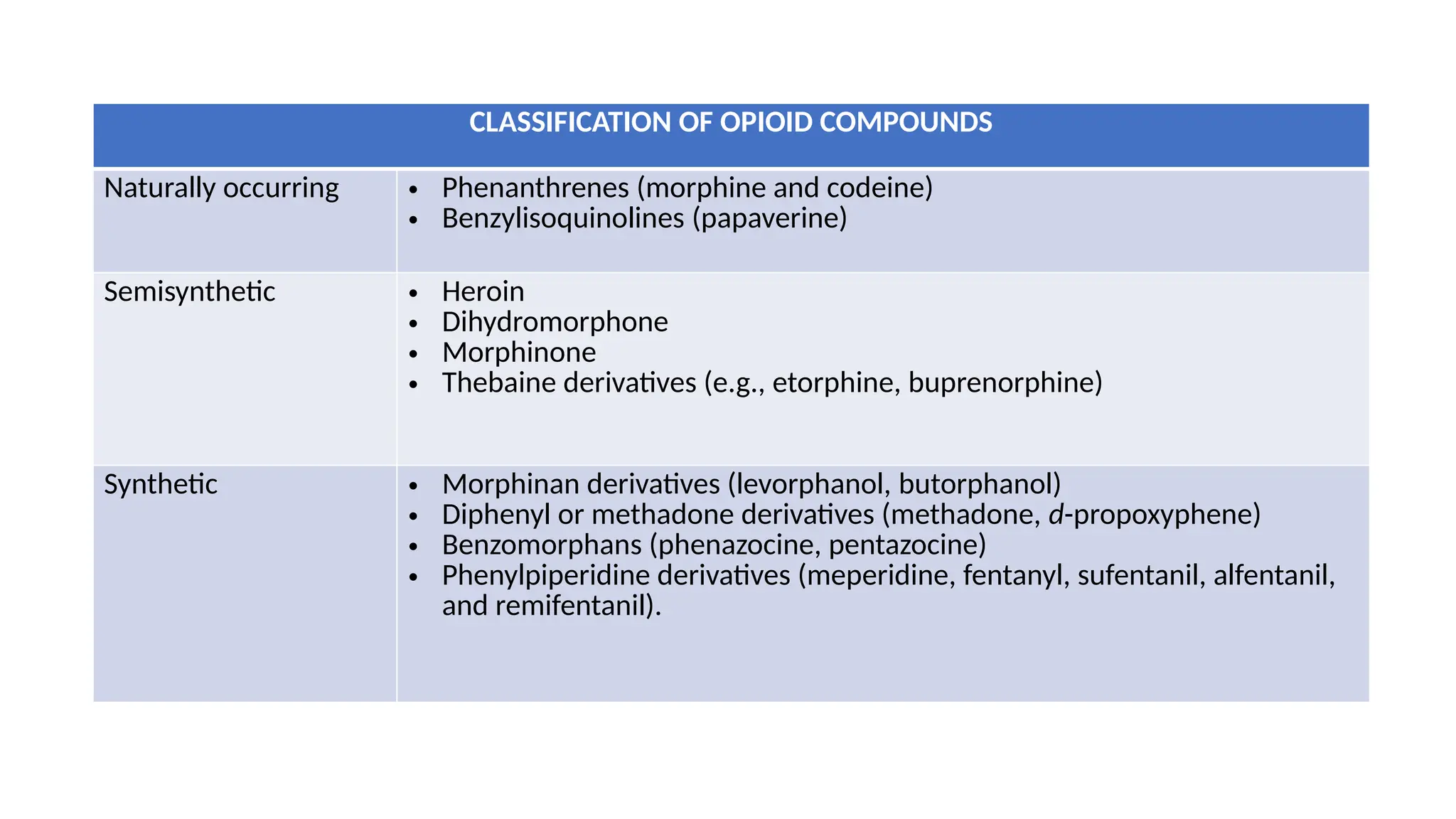
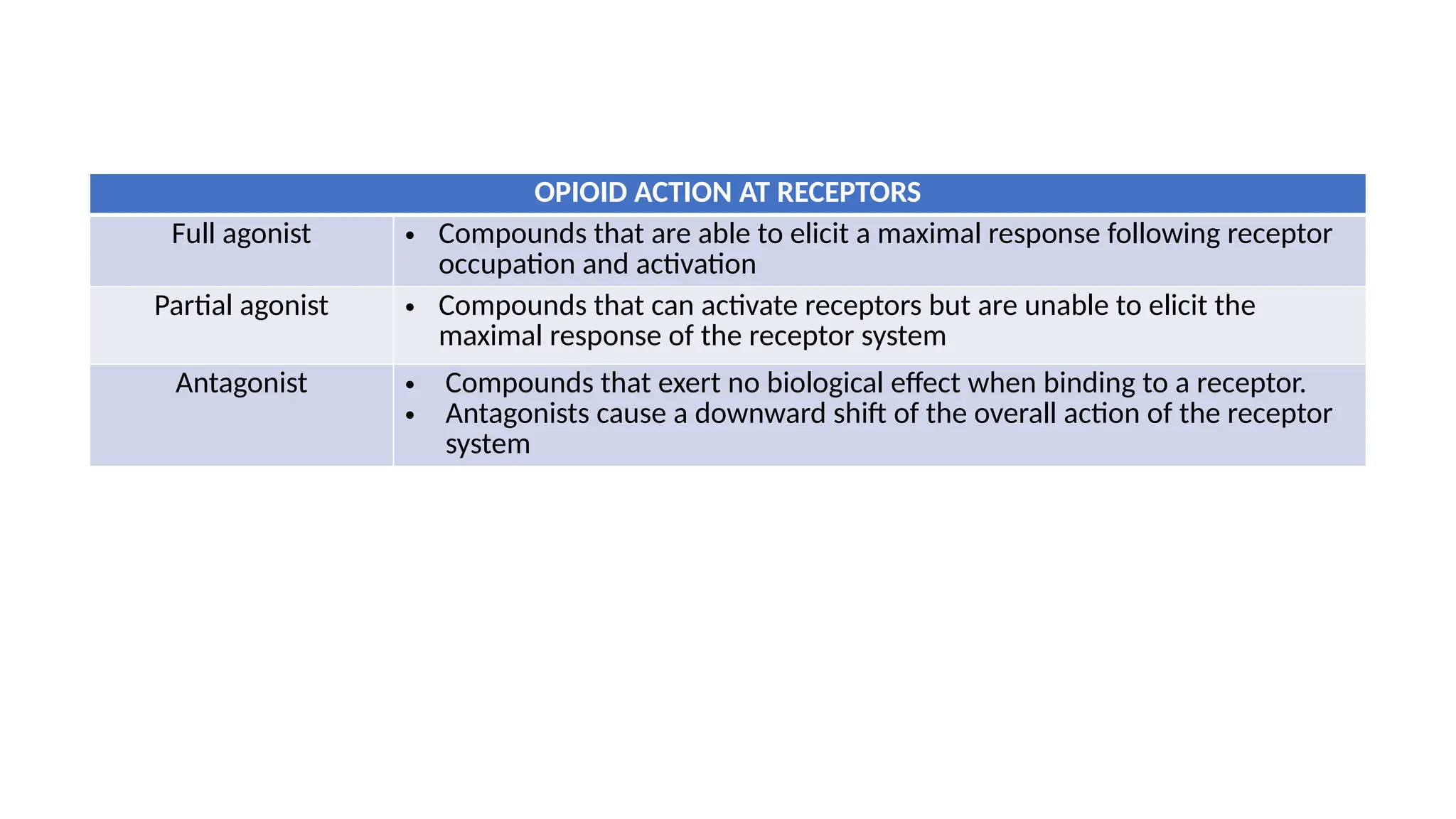
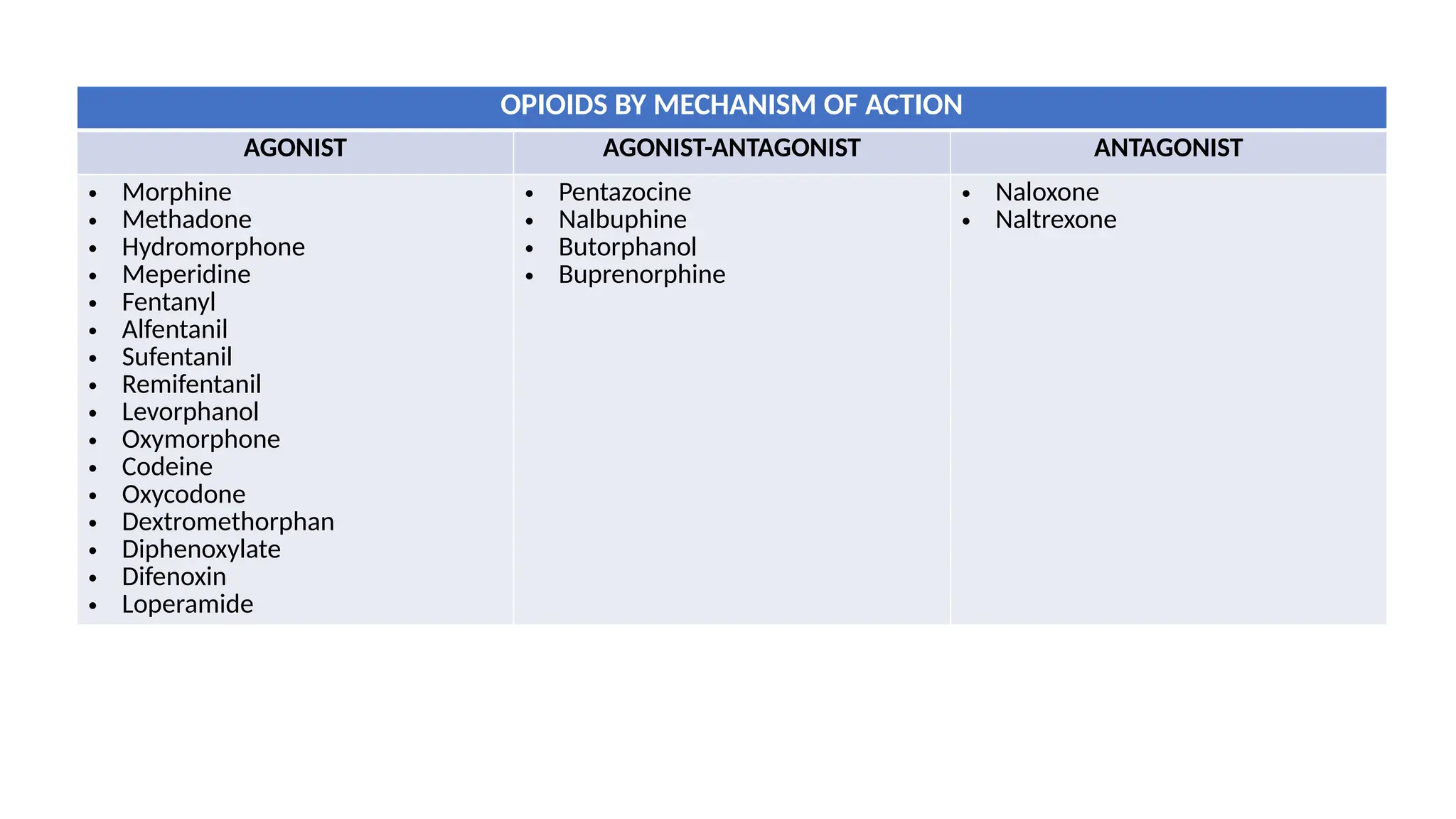
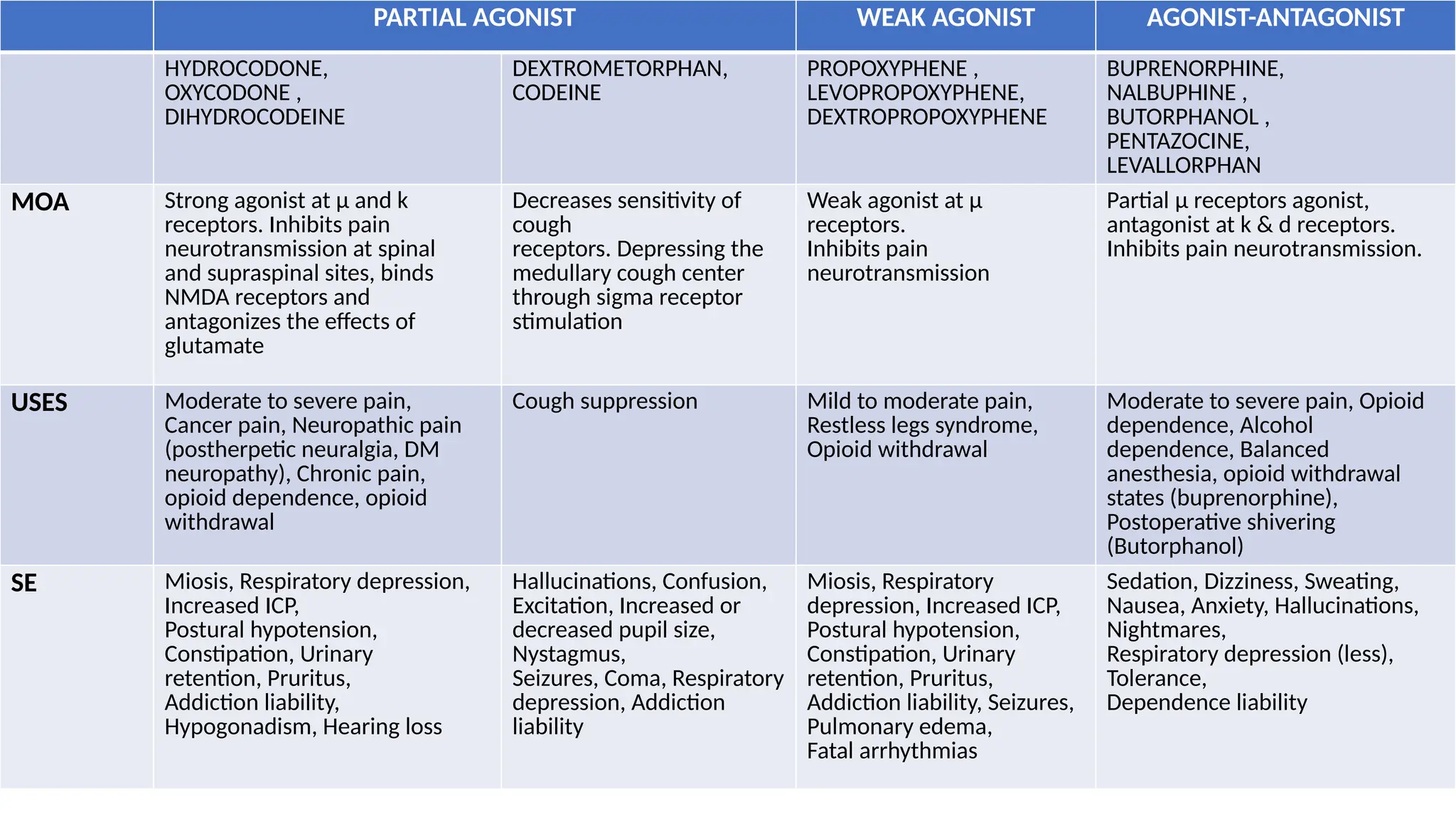
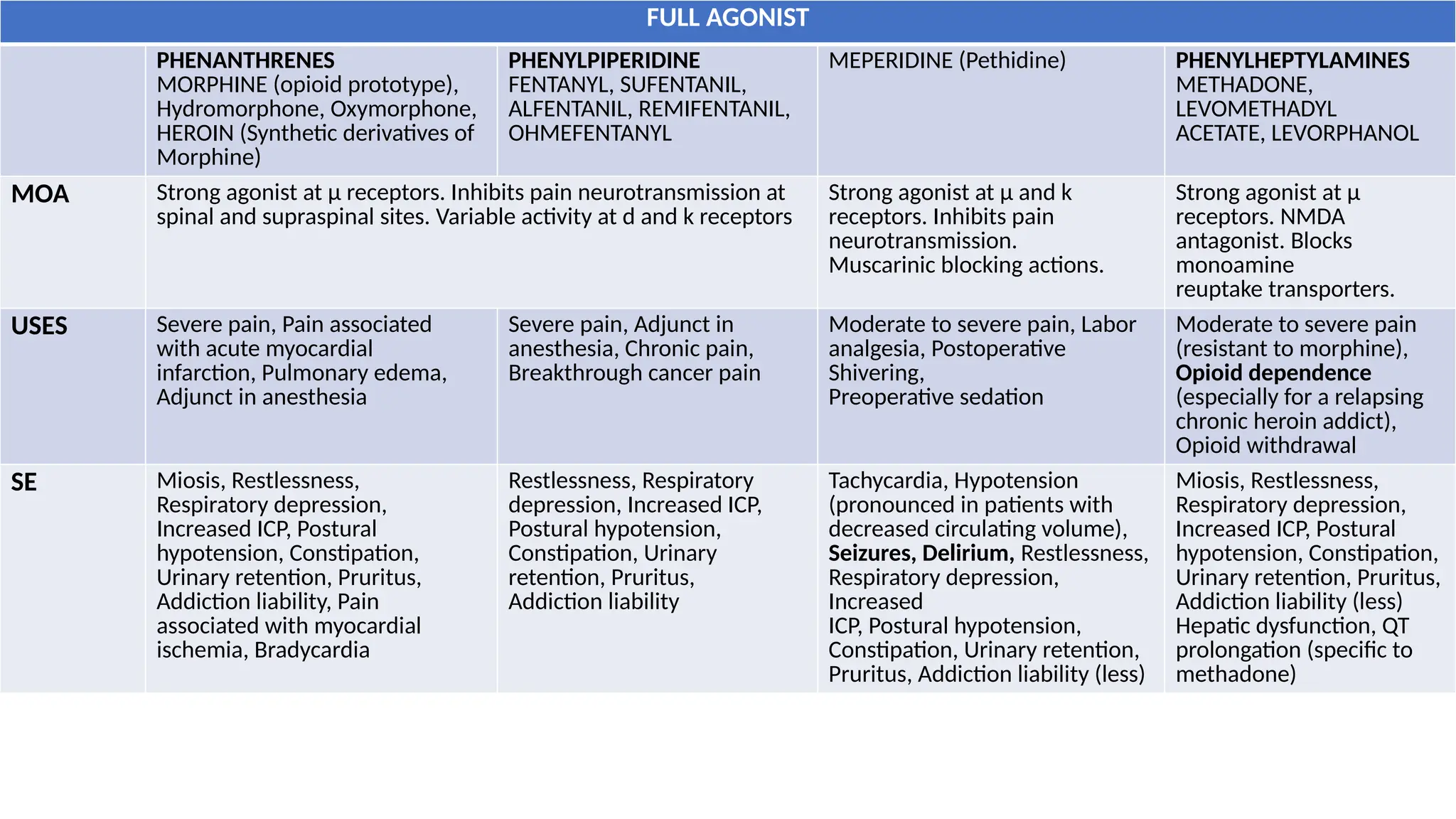
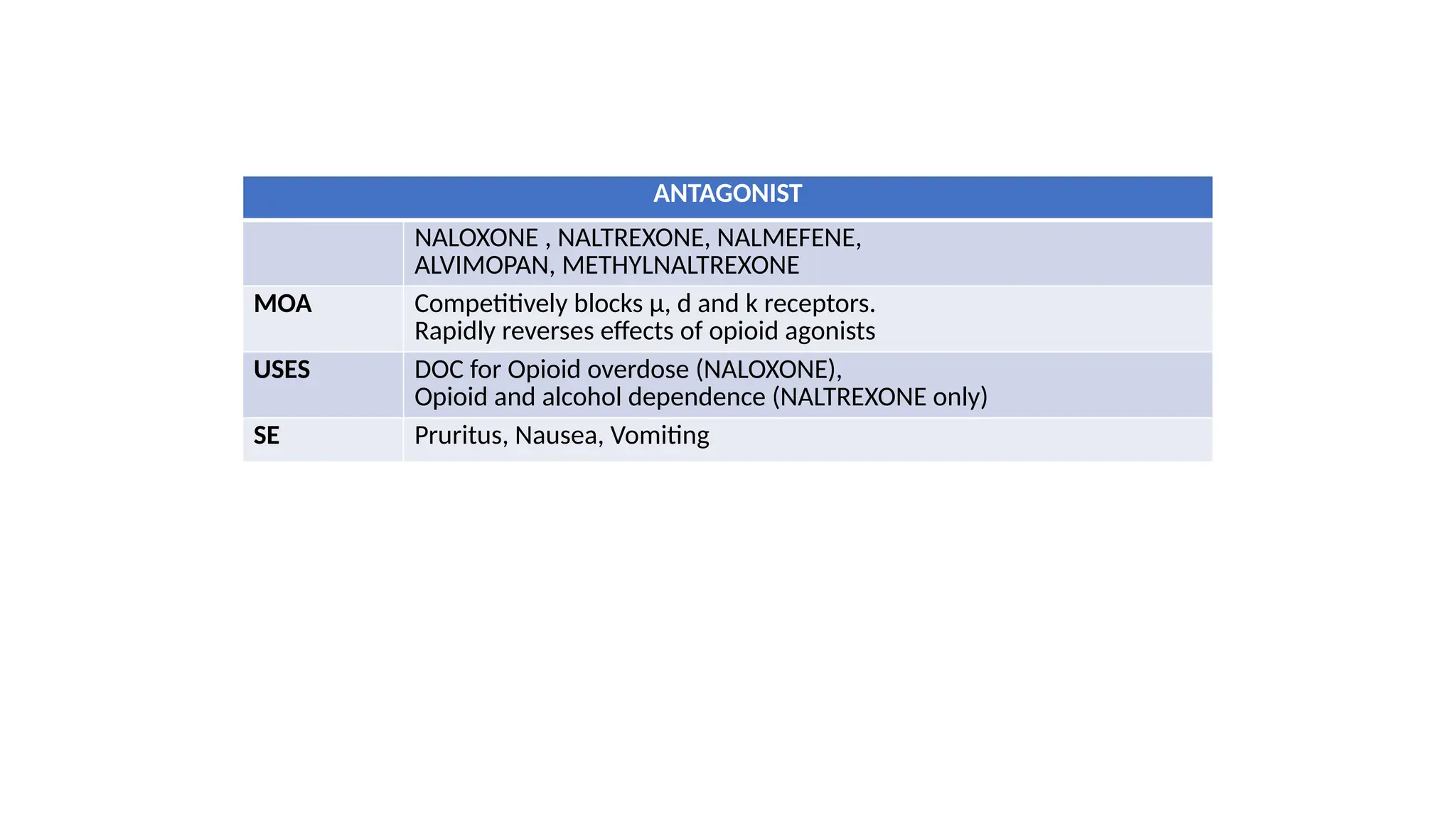
The document provides a comprehensive classification of opioid compounds, including naturally occurring, semisynthetic, and synthetic opioids, as well as their actions at opioid receptor subtypes (μ, δ, κ). It details the mechanisms of action of various opioid compounds, categorizing them as agonists, partial agonists, and antagonists along with their uses and side effects. Additionally, it highlights specific examples of opioids within each category and the health implications associated with their use.