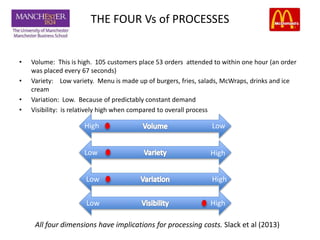
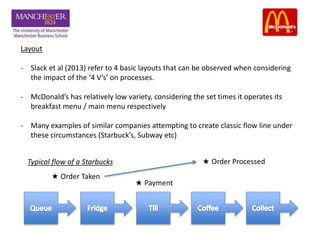
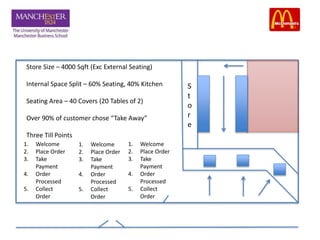
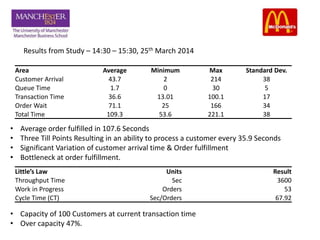
This document discusses the operational aspects of a McDonald's restaurant located in Media City, Dubai, established in 1940, which emphasizes customer experience and fast service through a global strategy called 'plan to win'. The document analyzes the restaurant's processing strategy, layout, and bottlenecks, as well as customer flow and transaction times. Recommendations are provided to enhance efficiency, improve customer navigation, and reduce pressure on service areas.