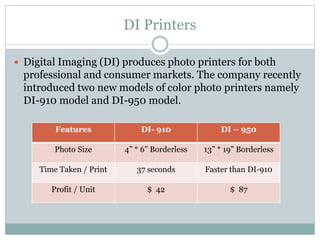
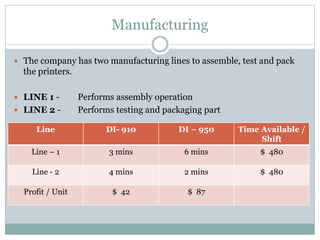
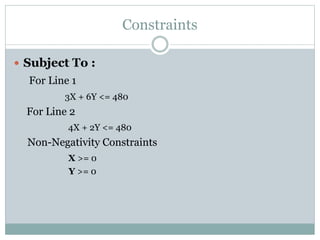
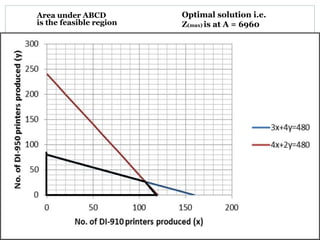
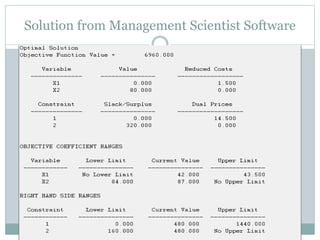
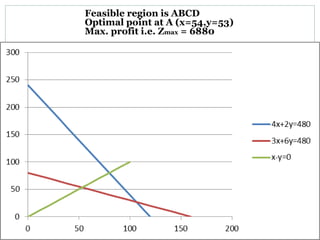
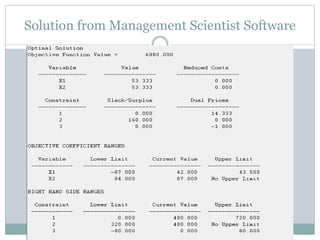
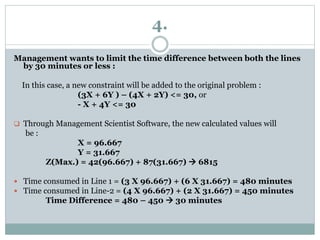
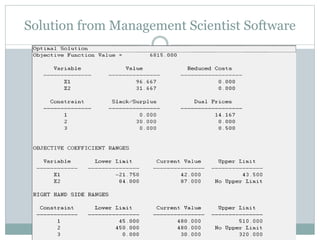
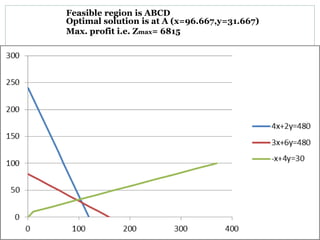
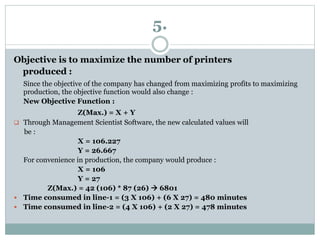
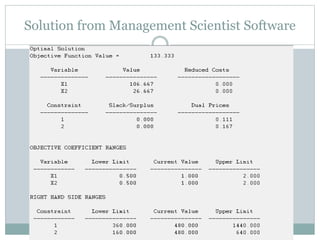
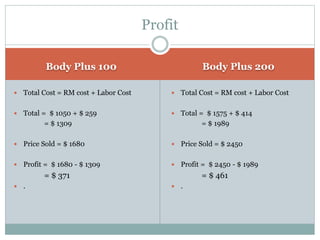
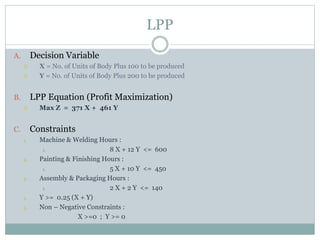
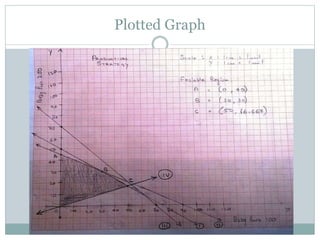
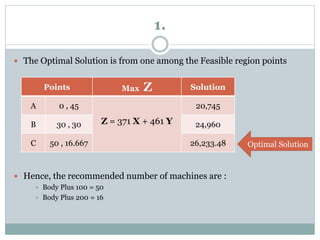
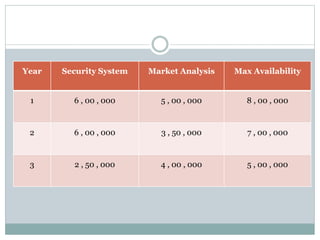
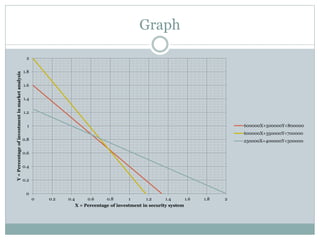
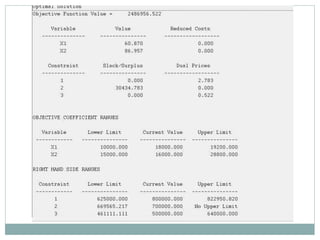
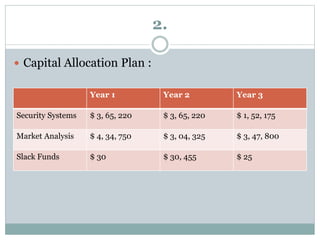
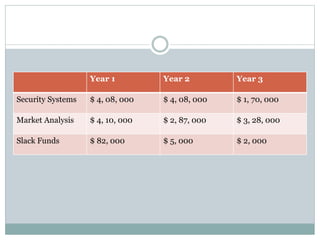
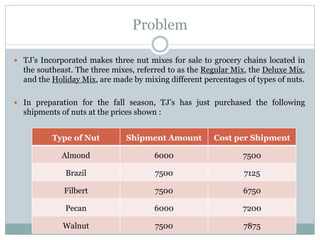
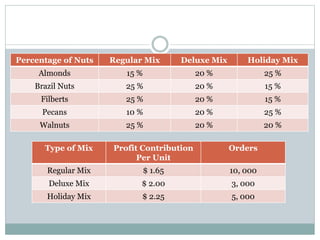
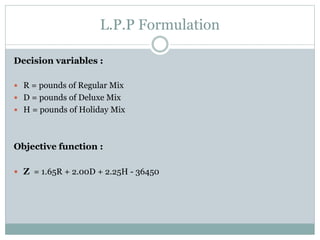
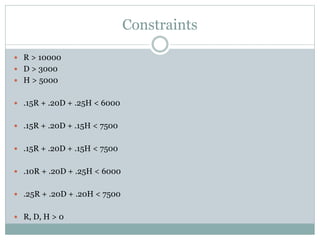
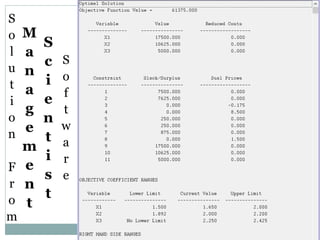
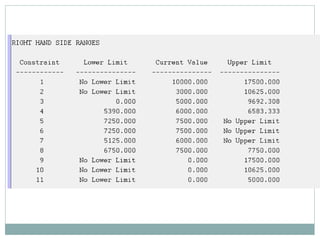
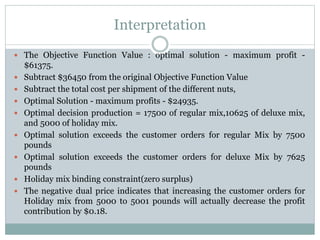
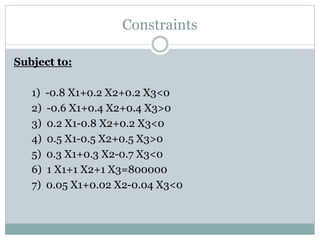
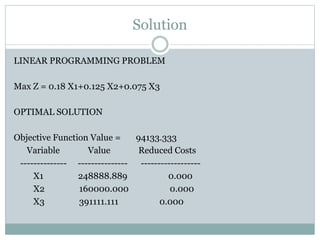
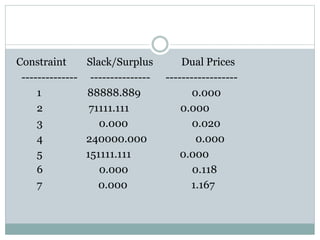
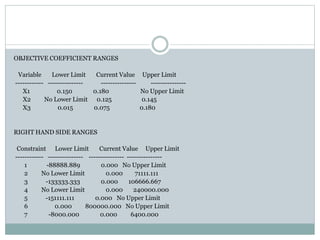
The document discusses operational research case studies for several companies including Digital Imaging which produces photo printers, Better Fitness Inc. that manufactures exercise equipment, and Hart Venture Capital which provides funding for software development projects. The case studies formulate linear programming problems to optimize objectives like profit maximization based on production constraints like available machine time and labor costs.