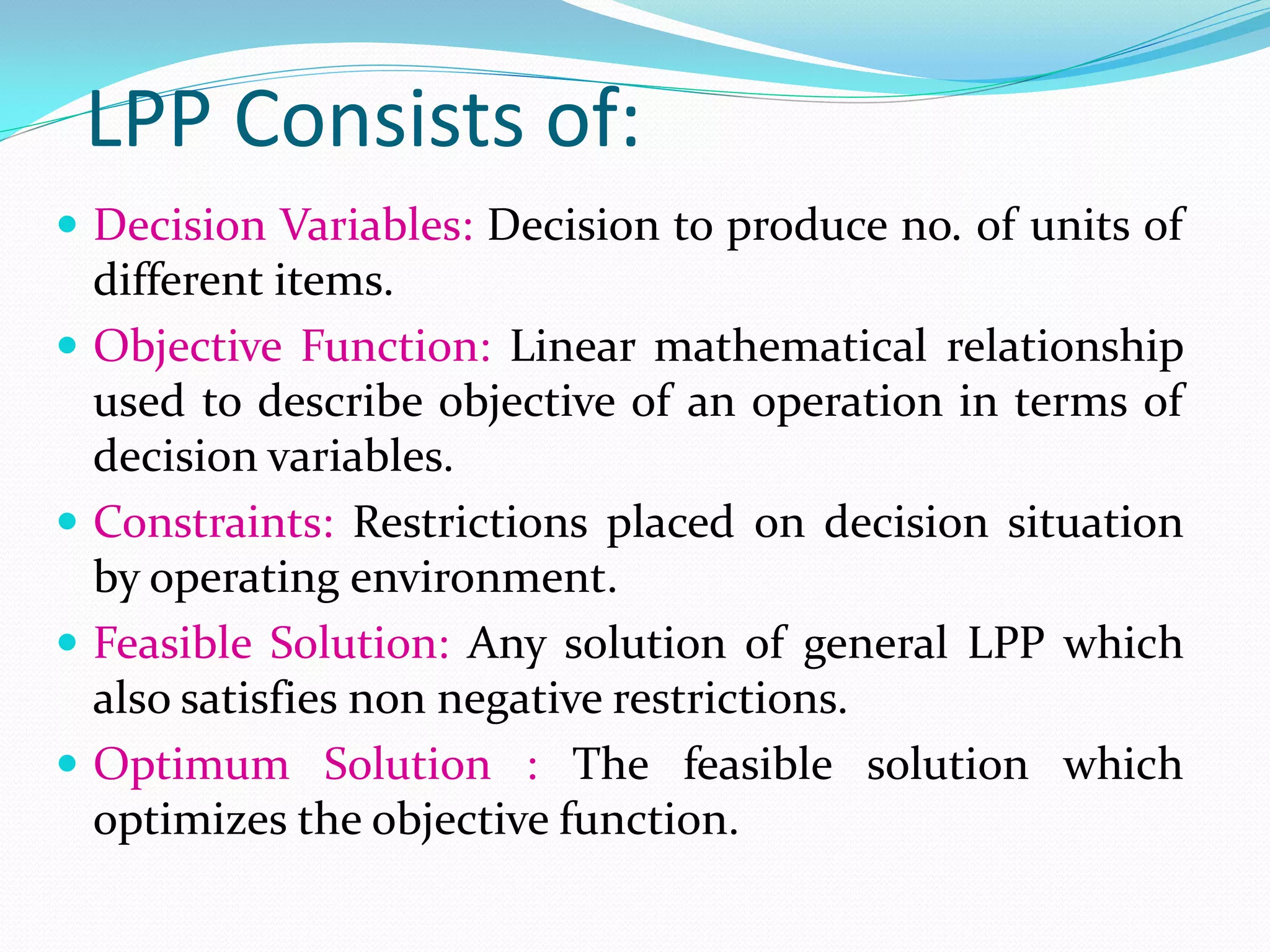
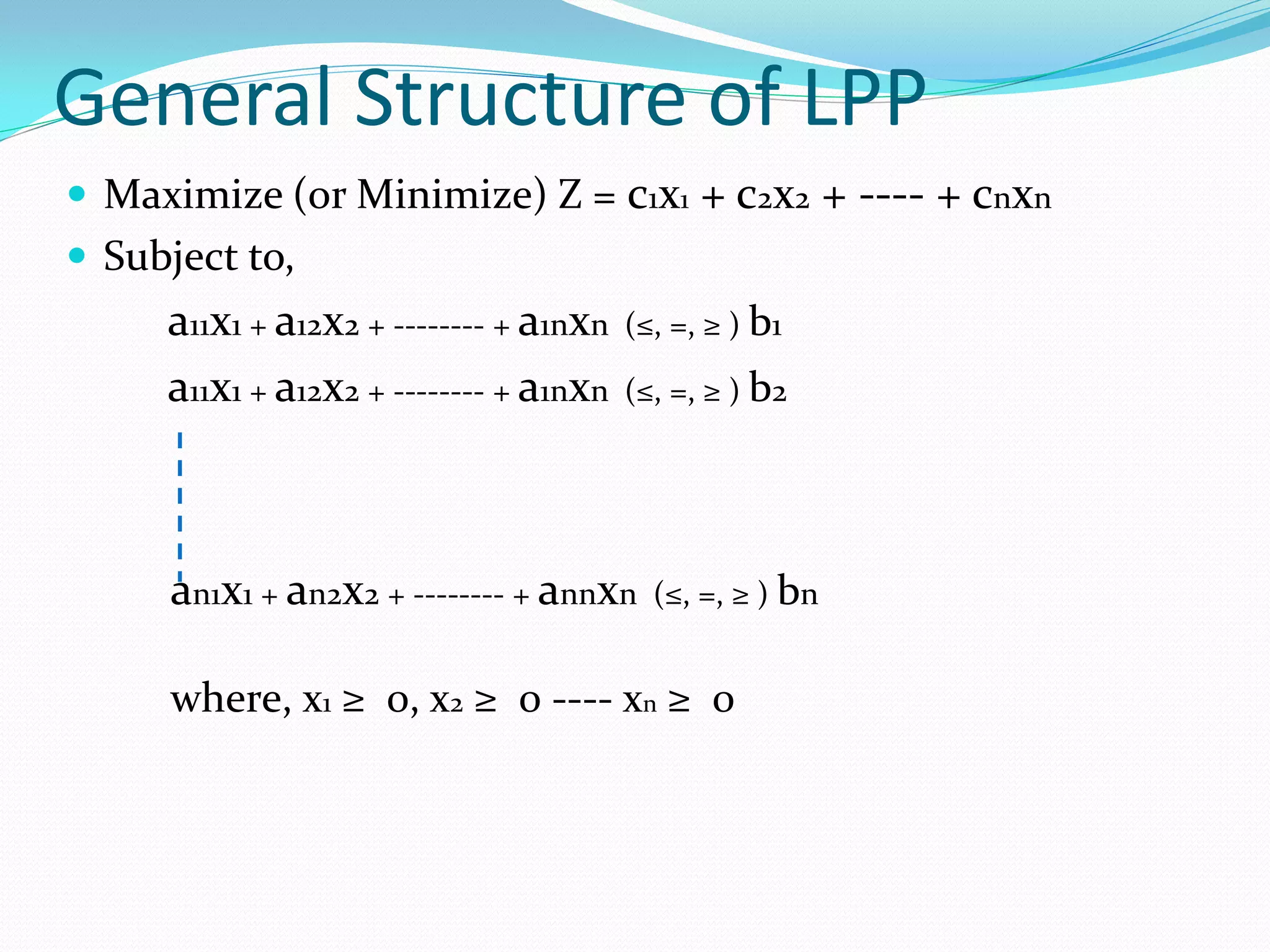
Linear programming problem (LPP) is a mathematical modeling technique used to determine optimal levels of activities given constraints and an objective to maximize or minimize. It allocates limited resources like labor, materials, machines among competing activities based on an optimality criterion. An LPP consists of decision variables, an objective function to describe the goal, constraints on the decision situation, feasible and optimal solutions.
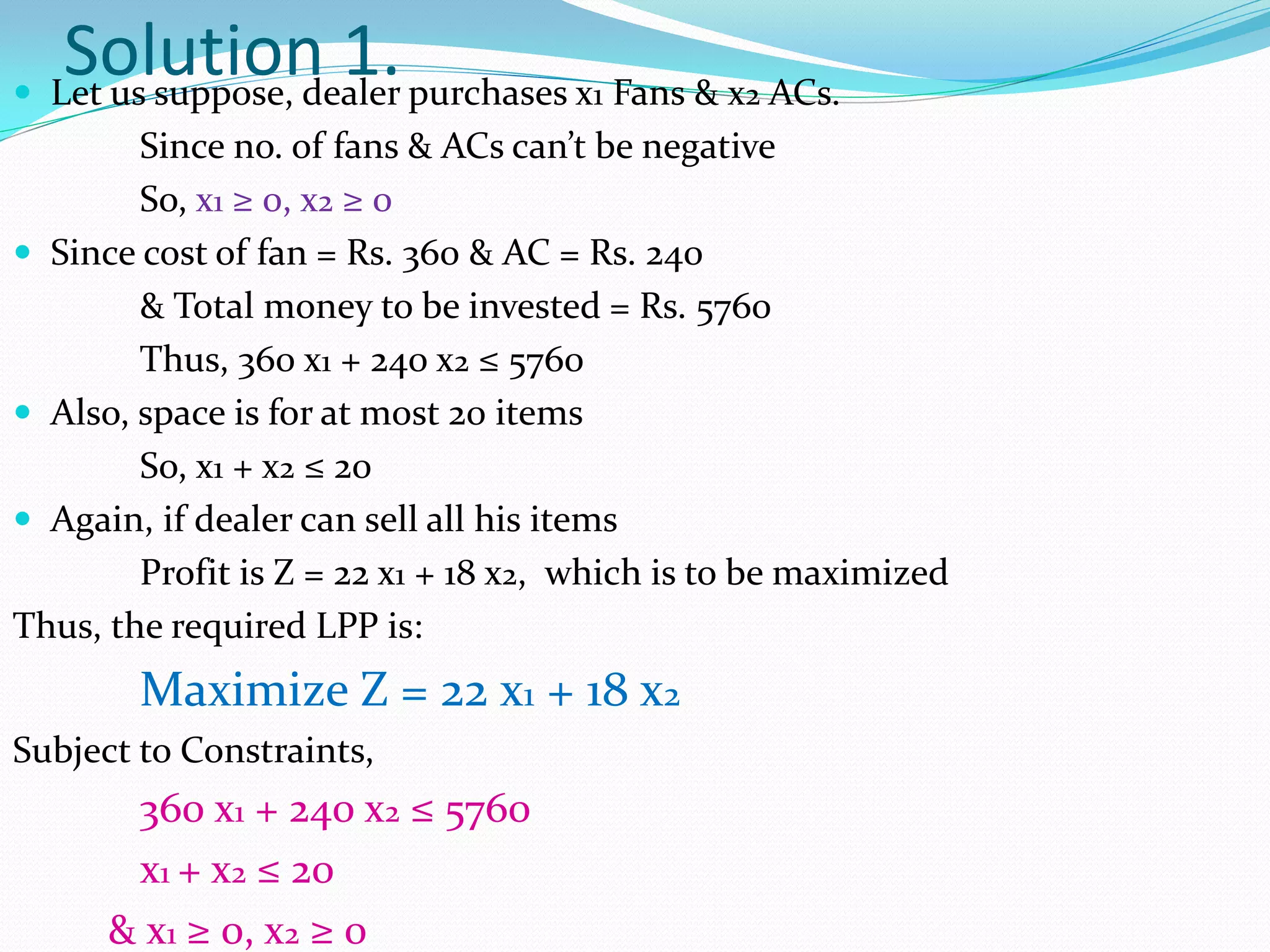
As an example, a dealer wants to maximize profits by purchasing fans and air conditioners within a Rs. 5760 budget and 20 item space limit. The LPP models this as maximizing profits from fan and AC sales subject to cost and space constraints.
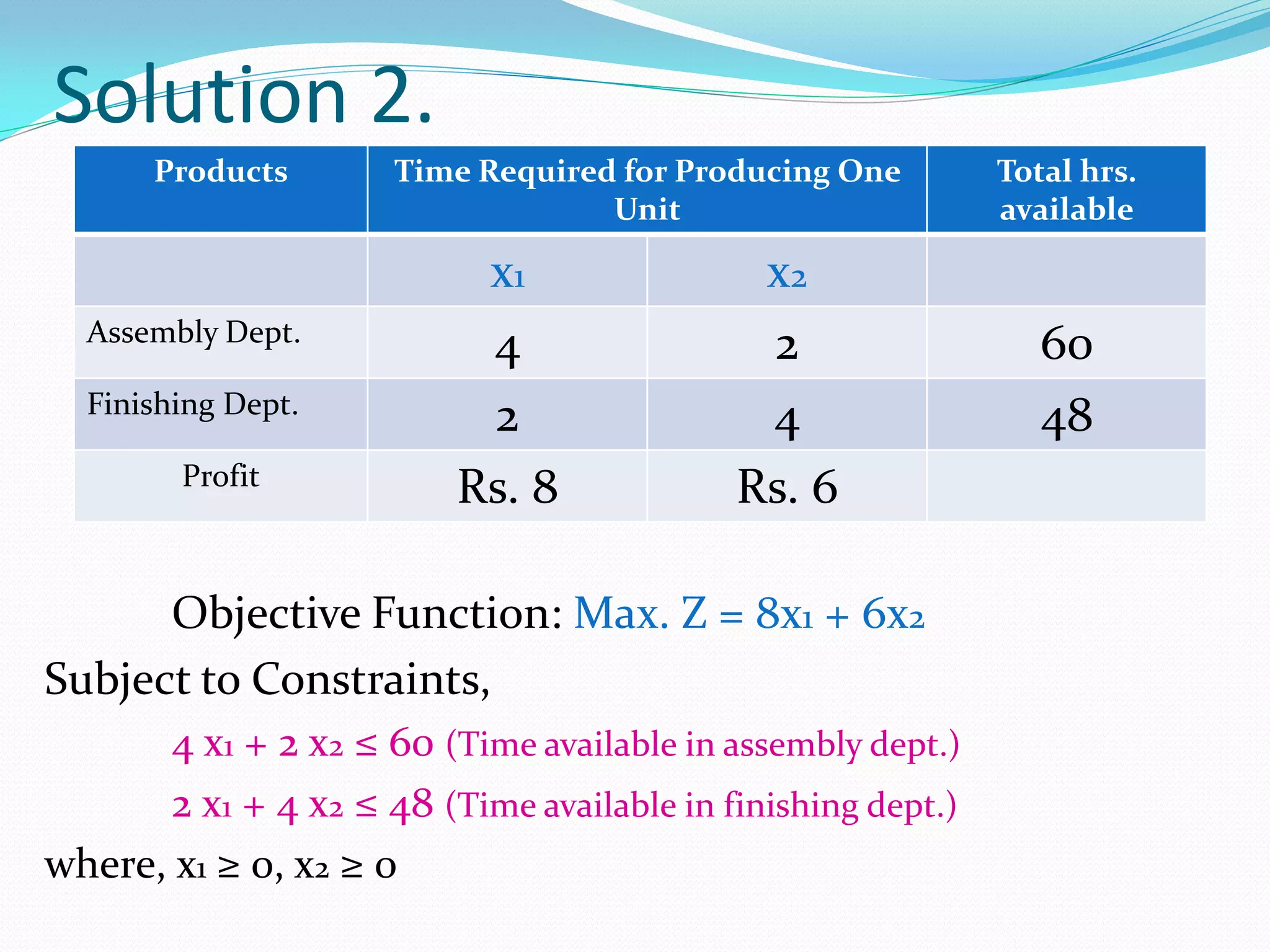
A second example models a company producing two items to maximize profit within assembly