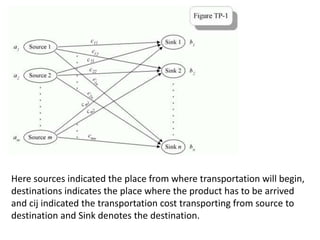
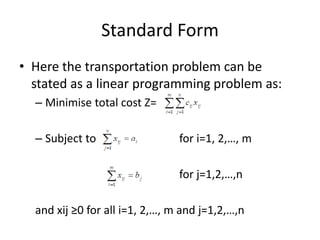
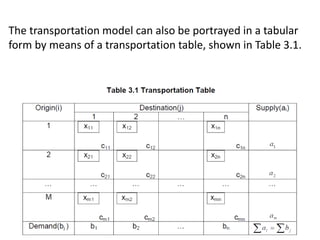
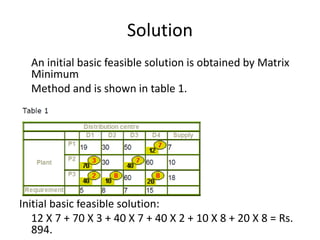
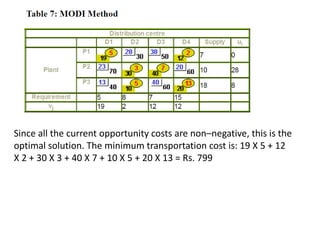
The document describes the modified distribution method (MODI) for solving transportation problems. MODI is an improvement on the stepping stone method. It involves starting with an initial basic feasible solution, calculating opportunity costs, and finding a negative opportunity cost to enter a new cell into the solution. A closed path is drawn around this cell and units are added/subtracted along the path to create a new basic feasible solution. This process repeats until all opportunity costs are non-negative, indicating an optimal solution. An example demonstrates applying MODI to find the optimal solution that minimizes transportation costs.