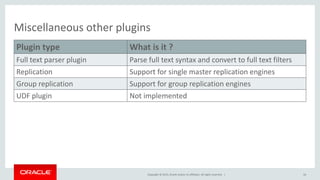
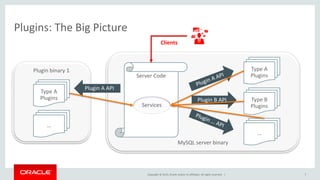
This document provides an overview of MySQL plugin development, highlighting the various types of plugins supported by the MySQL server, such as daemon, authentication, and storage engine plugins. It discusses the lifecycle of server plugins, their linking types, and the availability of sample plugins and further reading resources for developers. The content is positioned for advanced developers and includes a safe harbor statement regarding product direction.






![Copyright © 2015, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. |
A lifecycle of a plugin
Phase What triggers it ?
Initialization • INSTALL PLUGIN
• Server startup
• --plugin-load[-add] options
• mysql.plugin table
OPTIONAL: API call(s) Server events, mostly query execution
De-initialization • UNINSTALL PLUGIN
• Server shutdown
• User session end
8](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/openfest15mysqlplugindevelopment-151109070955-lva1-app6891/85/Openfest15-MySQL-Plugin-Development-8-320.jpg)