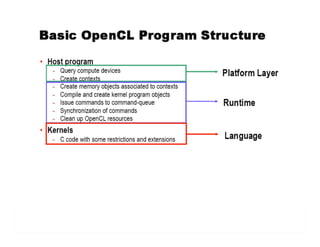
The document provides an overview of the OpenCL execution model, detailing key concepts such as kernels, programs, and the data-parallel execution model. It outlines the compilation process, including context creation, program loading, and kernel execution, supported by examples. Additionally, it emphasizes the asynchronous nature of queue operations and highlights further learning requirements for kernel function writing and argument setting.



![Data-Parallelism in OpenCL™
•Define N-dimensional computation domain (N = 1, 2 or 3)
▫ Each independent element of execution in N-D
domain is called a work-item
▫ The N-D domain defines the total number of work-
items that execute in parallel
Scalar Data-Parallel
1024 x 1024 image:
void kernel void
problem dimensions: scalar_mul(int n, dp_mul(global const float *a,
1024 x 1024 = 1 kernel const float *a, global const float *b,
execution per pixel: const float *b, global float *result)
1,048,576 total executions float *result) {
{ int id = get_global_id(0);
int i; result[id] = a[id] * b[id];
for (i=0; i<n; i++) }
result[i] = a[i] * b[i]; // execute dp_mul over “n” work-items
}
4
Fast Forward Your Development](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/openclhostprogramming080111-110108075533-phpapp02/85/OpenCL-Programming-101-4-320.jpg)





![Create Context
• Context enables operation (Queue) and memory
sharing between devices
cl_context_properties cps[3] =
{ CL_CONTEXT_PLATFORM, (cl_context_properties)(*i)(), 0 };
std::cout<<"Creating a context AMD platformn";
cl::Context context(CL_DEVICE_TYPE_CPU, cps, NULL, NULL, &err);
if (err != CL_SUCCESS)
{
std::cerr << "Context::Context() failed (" << err << ")n";
return SDK_FAILURE;
}
11
Fast Forward Your Development](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/openclhostprogramming080111-110108075533-phpapp02/85/OpenCL-Programming-101-11-320.jpg)



![Create Queue per device & Run it
• Loads the kernel program (*.cl). This does not
have to happen immediately
• Attention: enqueue() is Asynchronous call
meaning : function return does not imply Kernel
was executed or even started to execute
cl::CommandQueue queue(context, devices[0], 0, &err);
std::cout<<"Running CL programn";
err = queue.enqueueNDRangeKernel(…..)
err = queue.finish();
if (err != CL_SUCCESS) {
std::cerr << "Event::wait() failed (" << err << ")n";
}
15
Fast Forward Your Development](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/openclhostprogramming080111-110108075533-phpapp02/85/OpenCL-Programming-101-15-320.jpg)


