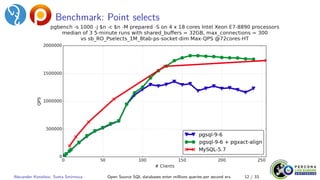
The document discusses scalability benchmarks and performance comparisons between PostgreSQL and MySQL, emphasizing improvements in version 9.6 and 5.7, respectively. It outlines issues encountered with benchmarking tools and proposes various optimizations for PostgreSQL to enhance performance, including methodologies for running tests and analyzing bottlenecks. Ultimately, both databases aim to achieve higher query processing capabilities, revealing insights into their architecture and operational efficiencies.





![sysbench with prepared statements: try 1
▶ Problem: NULL handling is broken in sysbench for PostgreSQL.
FATAL: failed to execute function `event': 3
(last message repeated 7 times)
FATAL: PQexecPrepared() failed: 7 ERROR: invalid input syntax for integer: ""
▶ Fix. Pull request was merged by Alexey Kopytov.
/* Convert SysBench bind structures to PgSQL data */
for (i = 0; i < (unsigned)pgstmt->nparams; i++)
{
- if (stmt->bound_param[i].is_null)
+ if (stmt->bound_param[i].is_null && *(stmt->bound_param[i].is_null))
continue;
switch (stmt->bound_param[i].type) {
Alexander Korotkov, Sveta Smirnova Open Source SQL databases enter millions queries per second era 6 / 33](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mqps-161004211401/85/Open-Source-SQL-databases-enter-millions-queries-per-second-era-6-320.jpg)