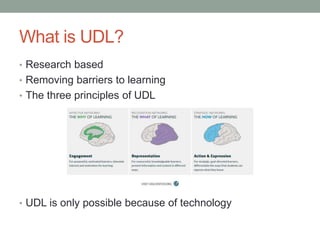
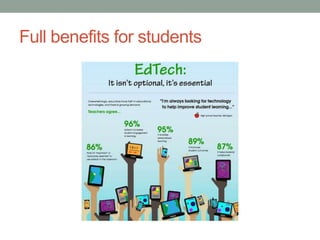
The open house presentation featured three stations about using technology and universal design for learning (UDL) principles in education. Station One introduced UDL and its benefits for diverse learners. Station Two demonstrated technology currently used in the classroom. Station Three explained why technology is important for developing 21st century skills and connecting students with other cultures, featuring an interactive lesson on intercultural classes. The goal of the presentation was to illustrate how technology and UDL can help create student-centered, lifelong learners and ensure all students have access to education.