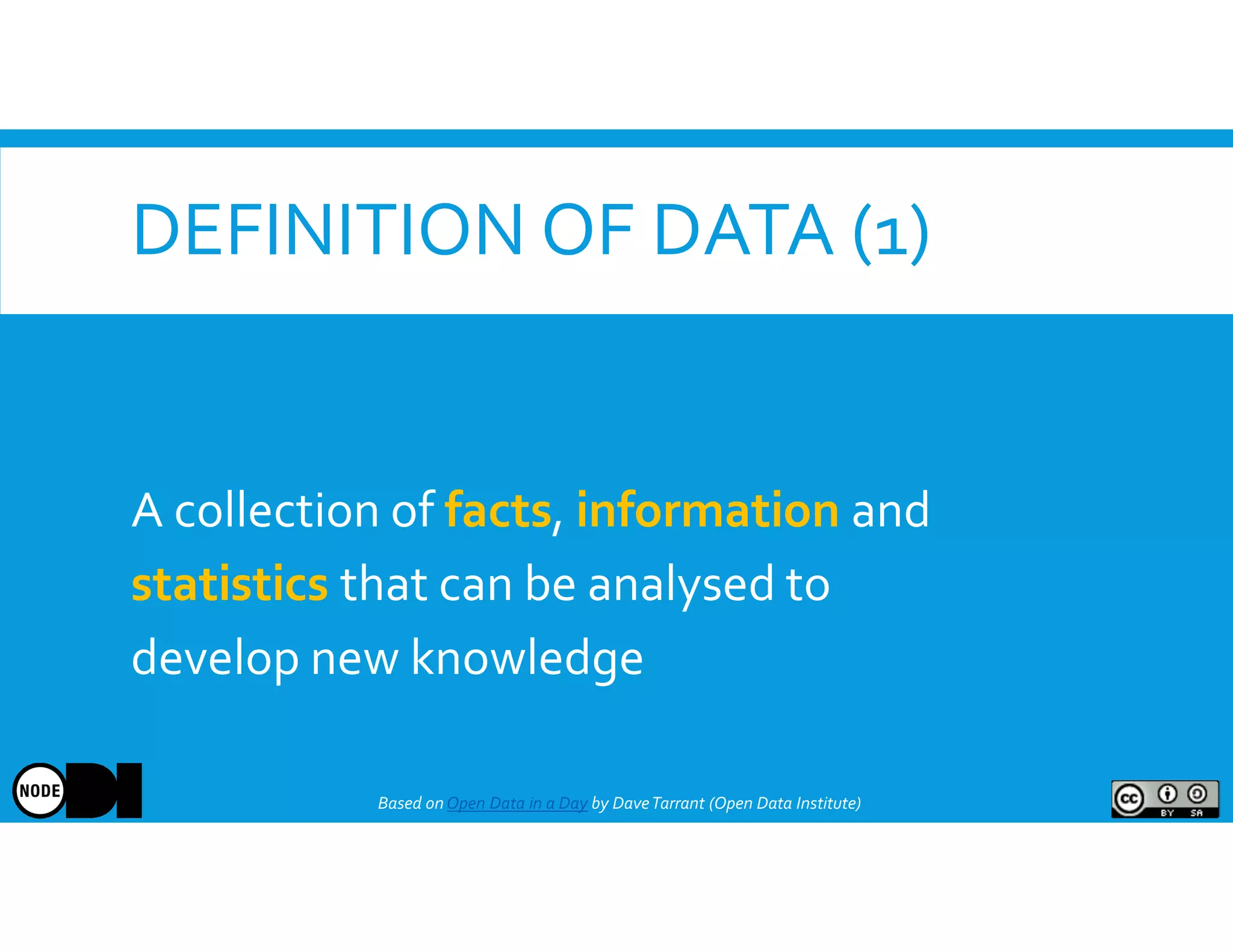
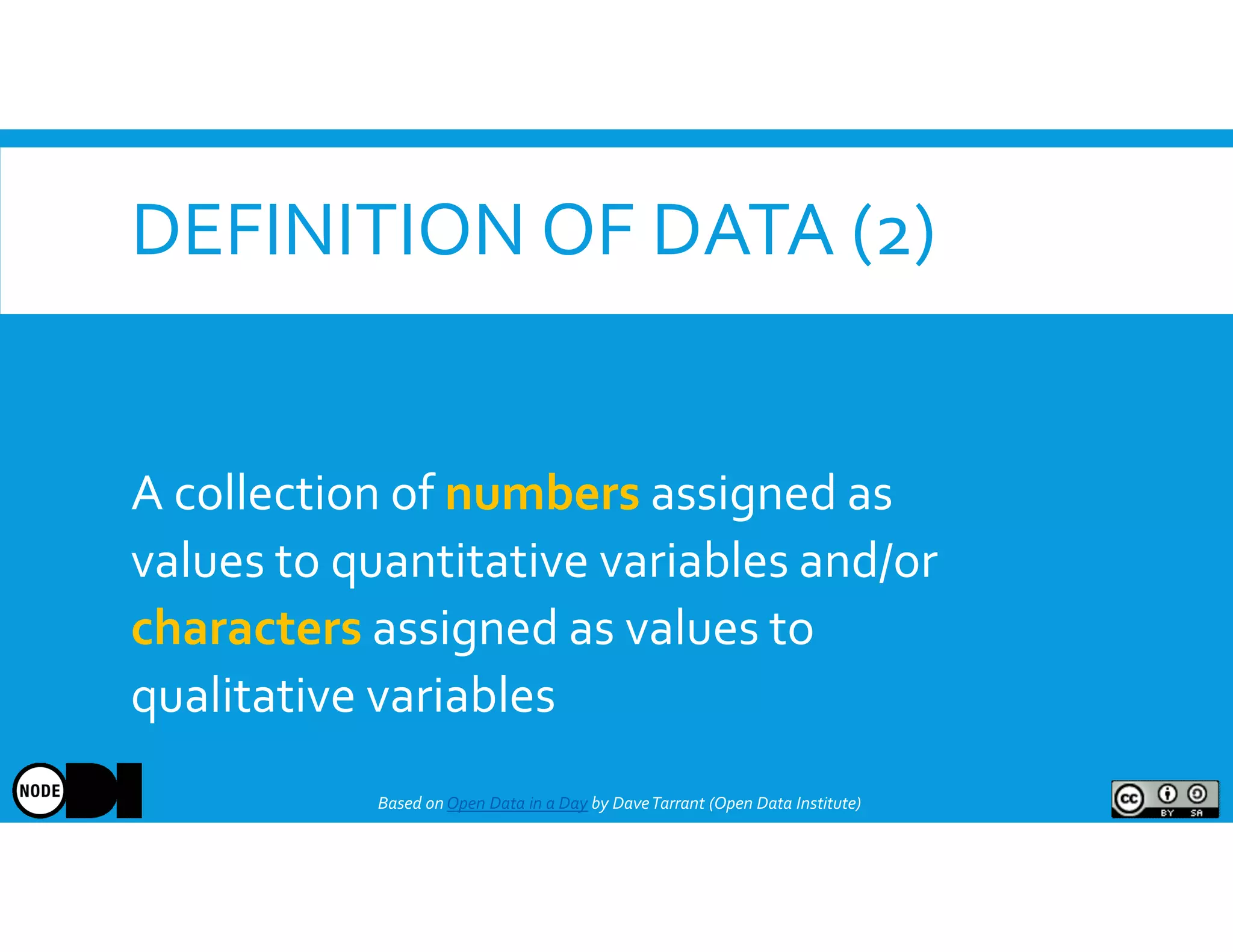
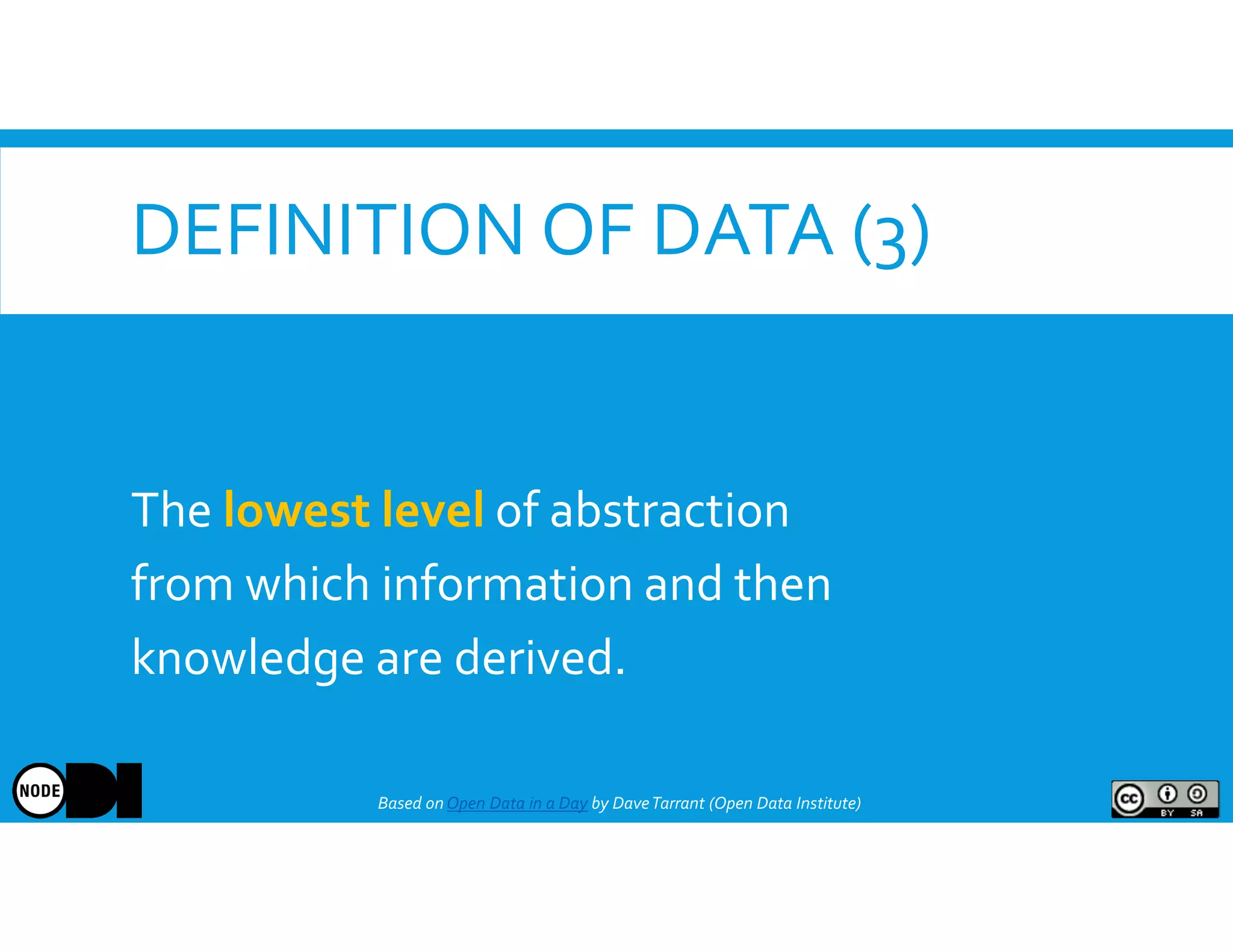
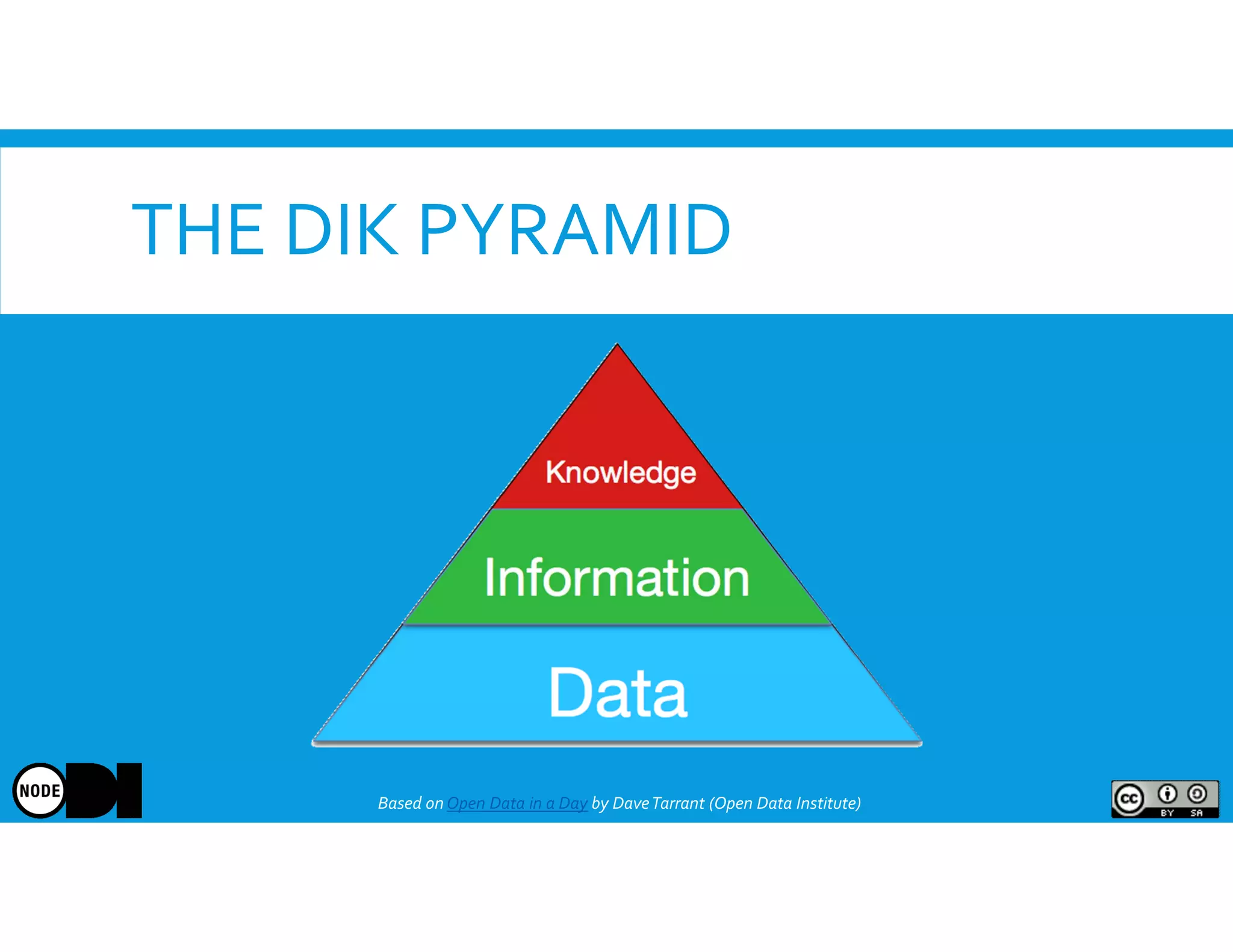
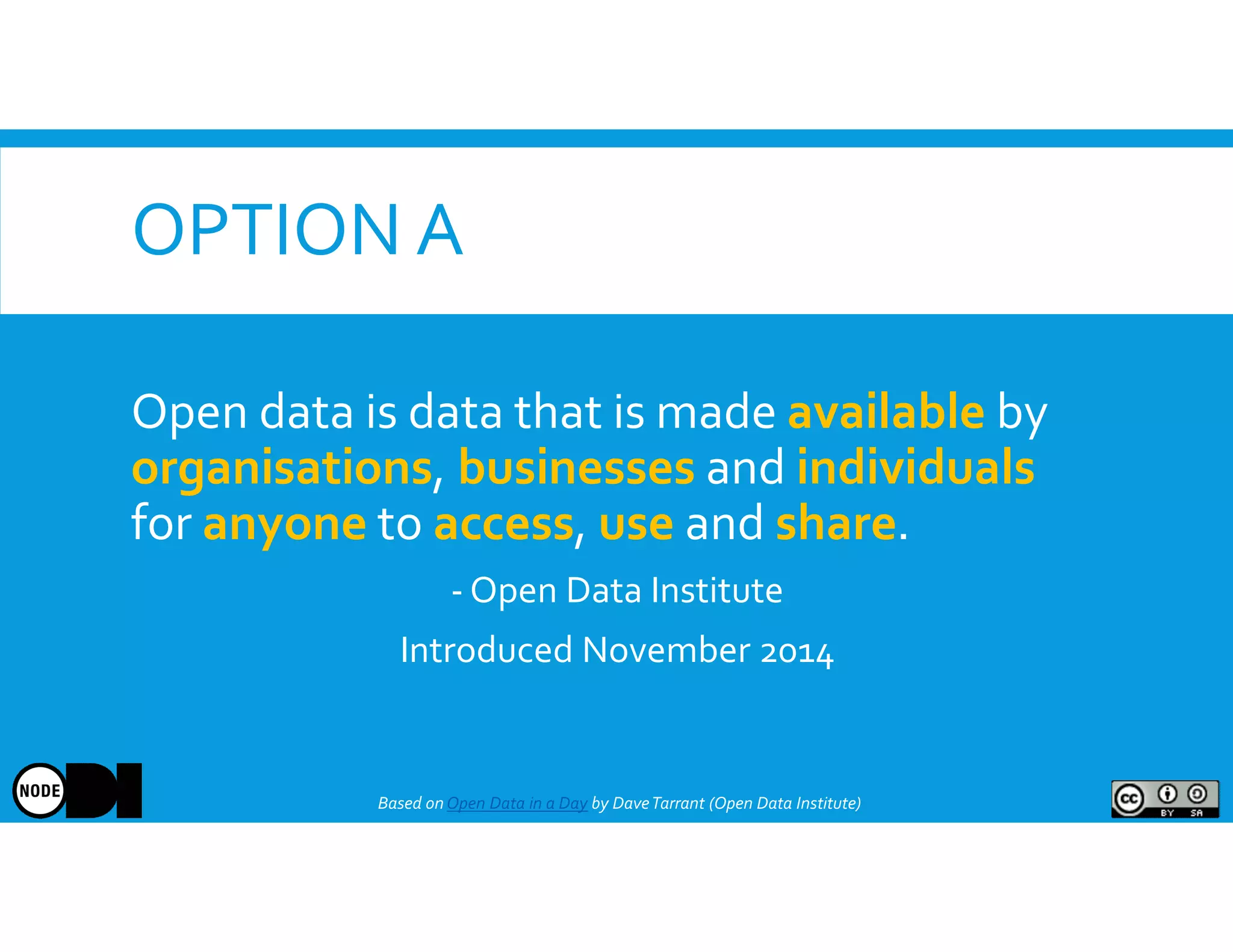
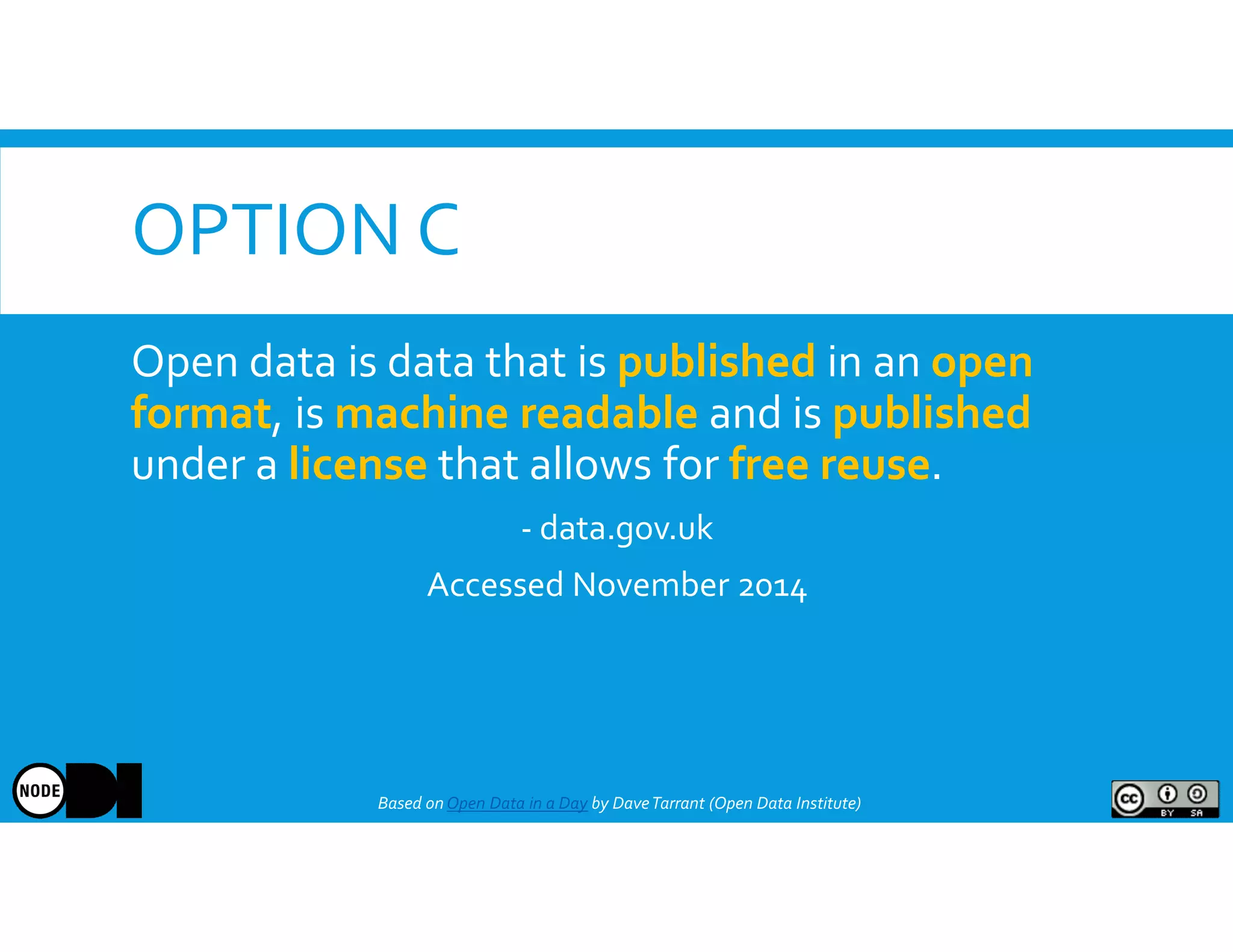
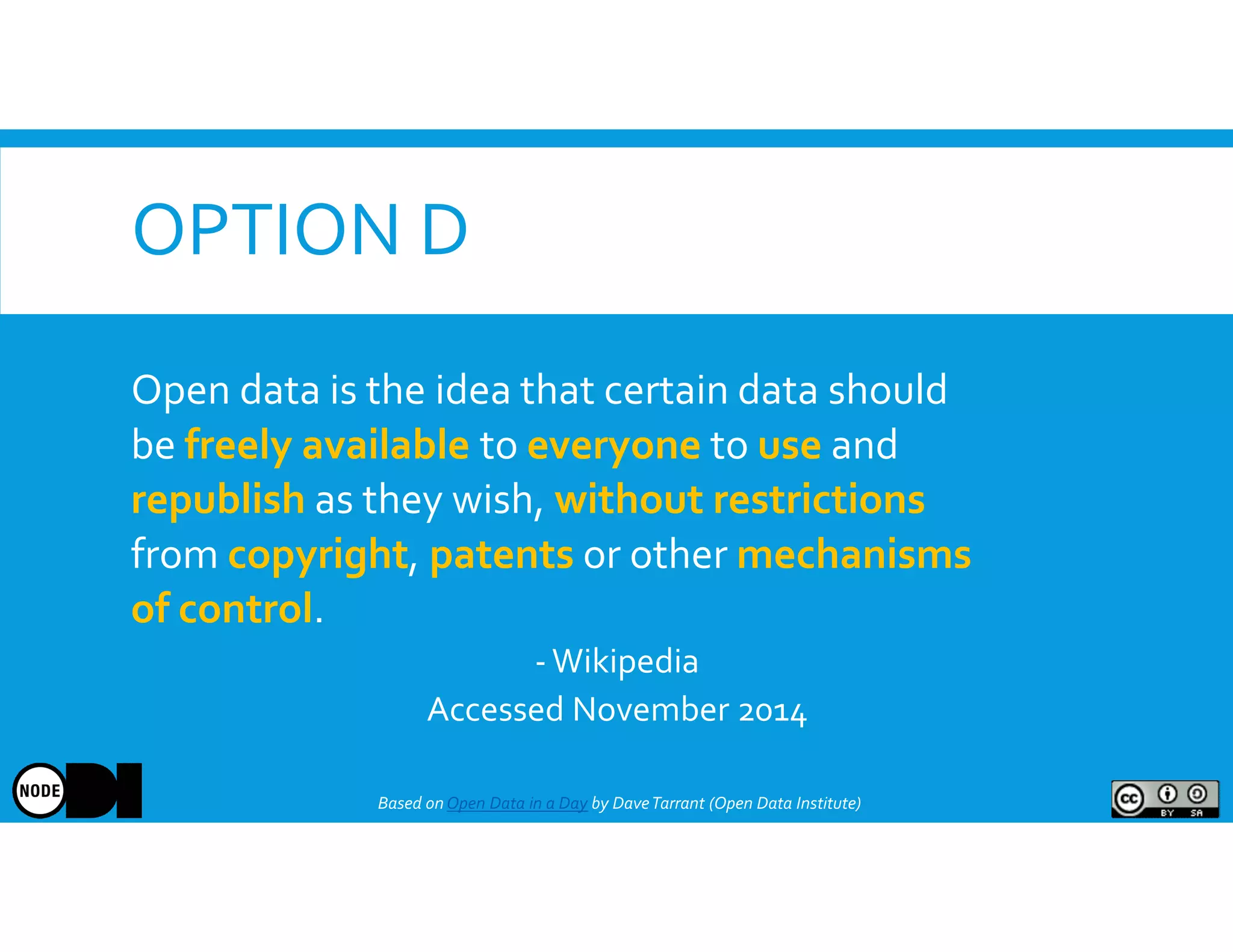
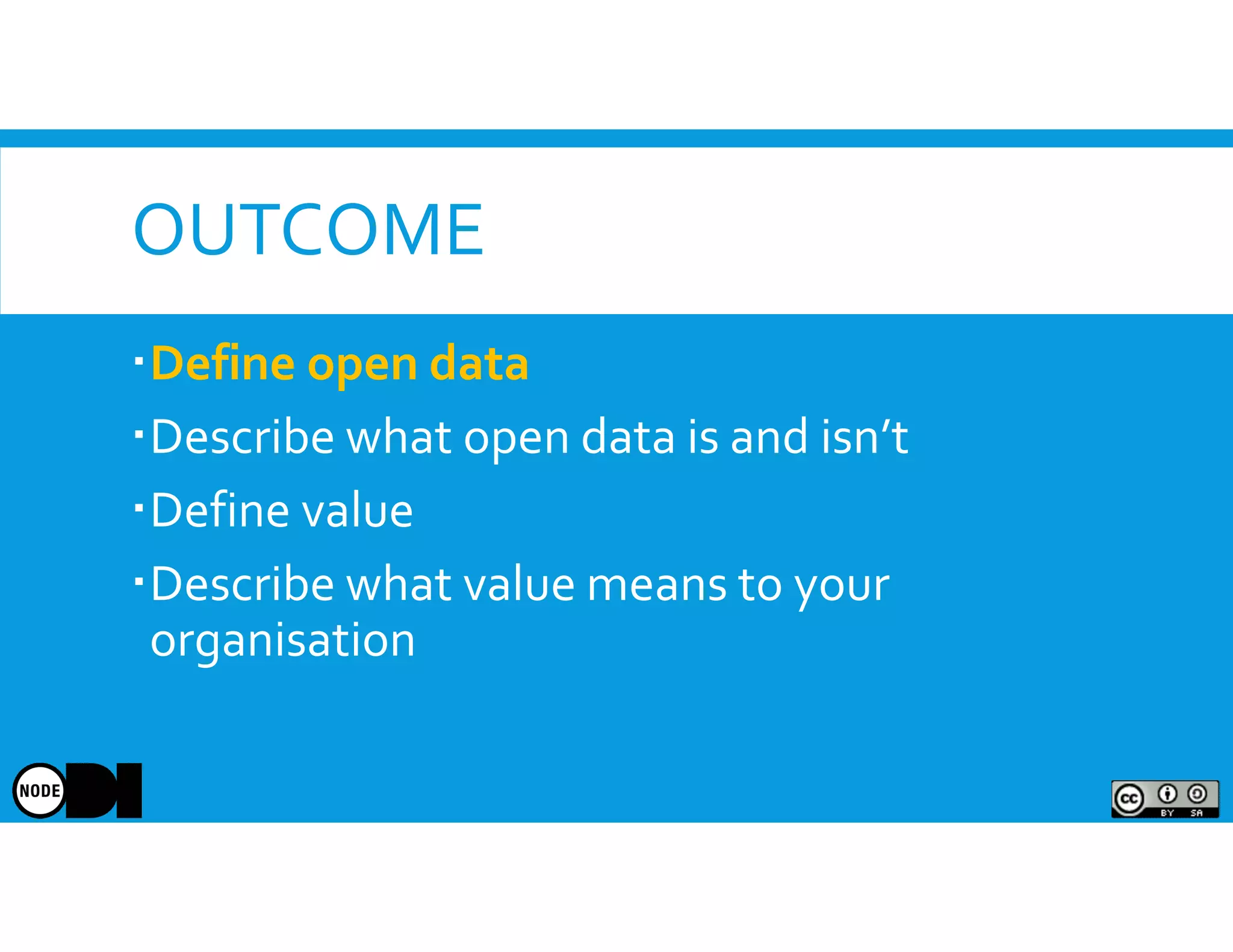
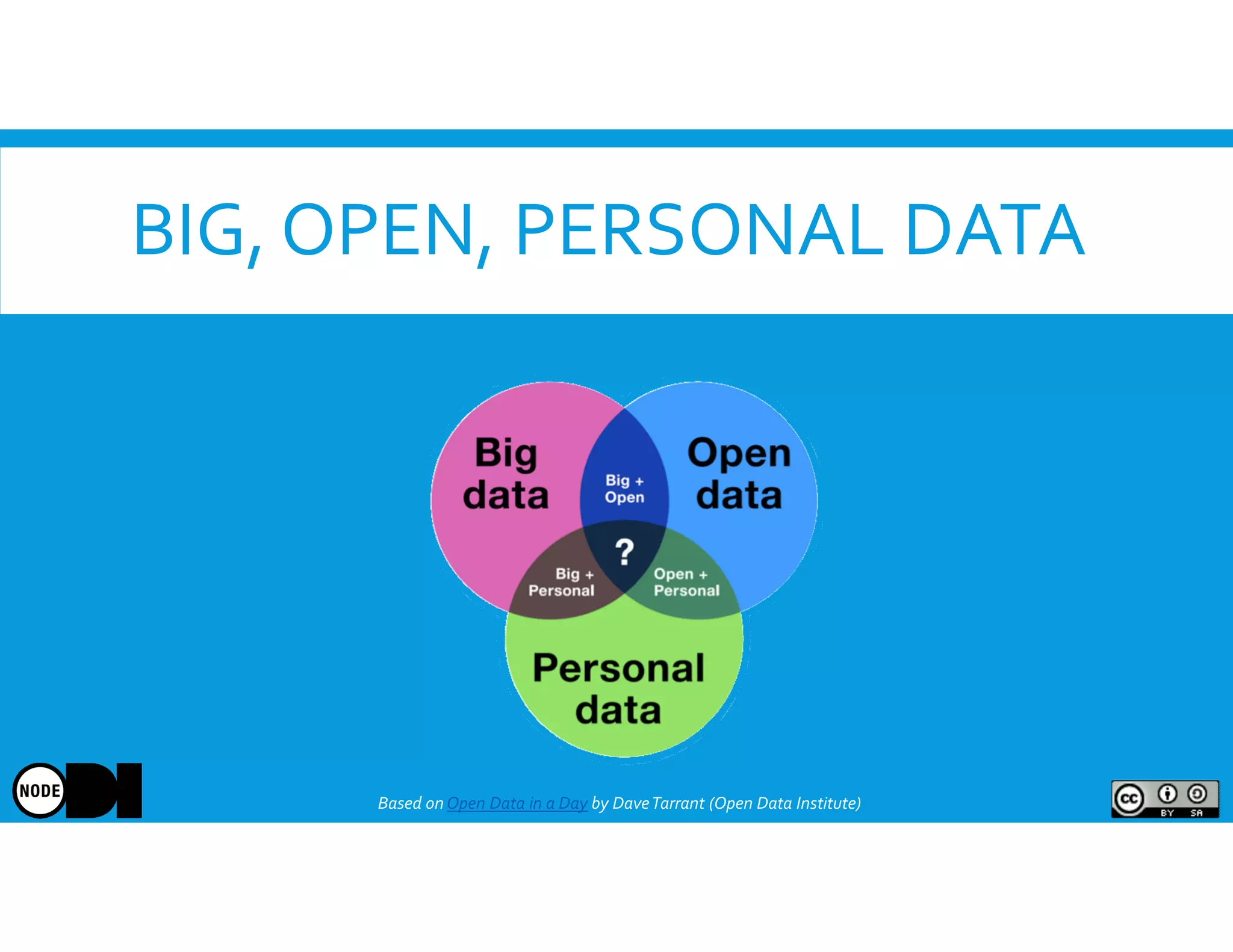
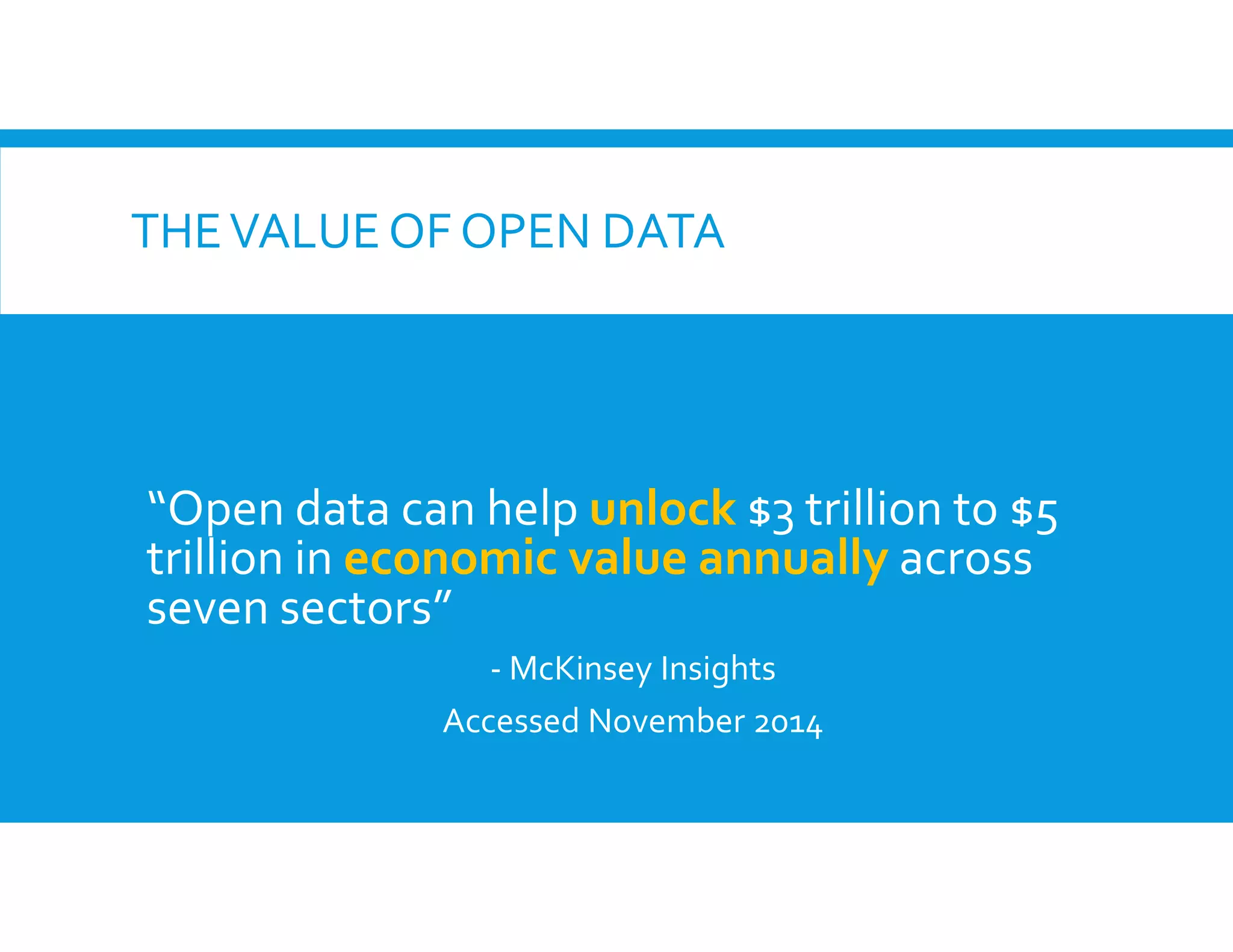
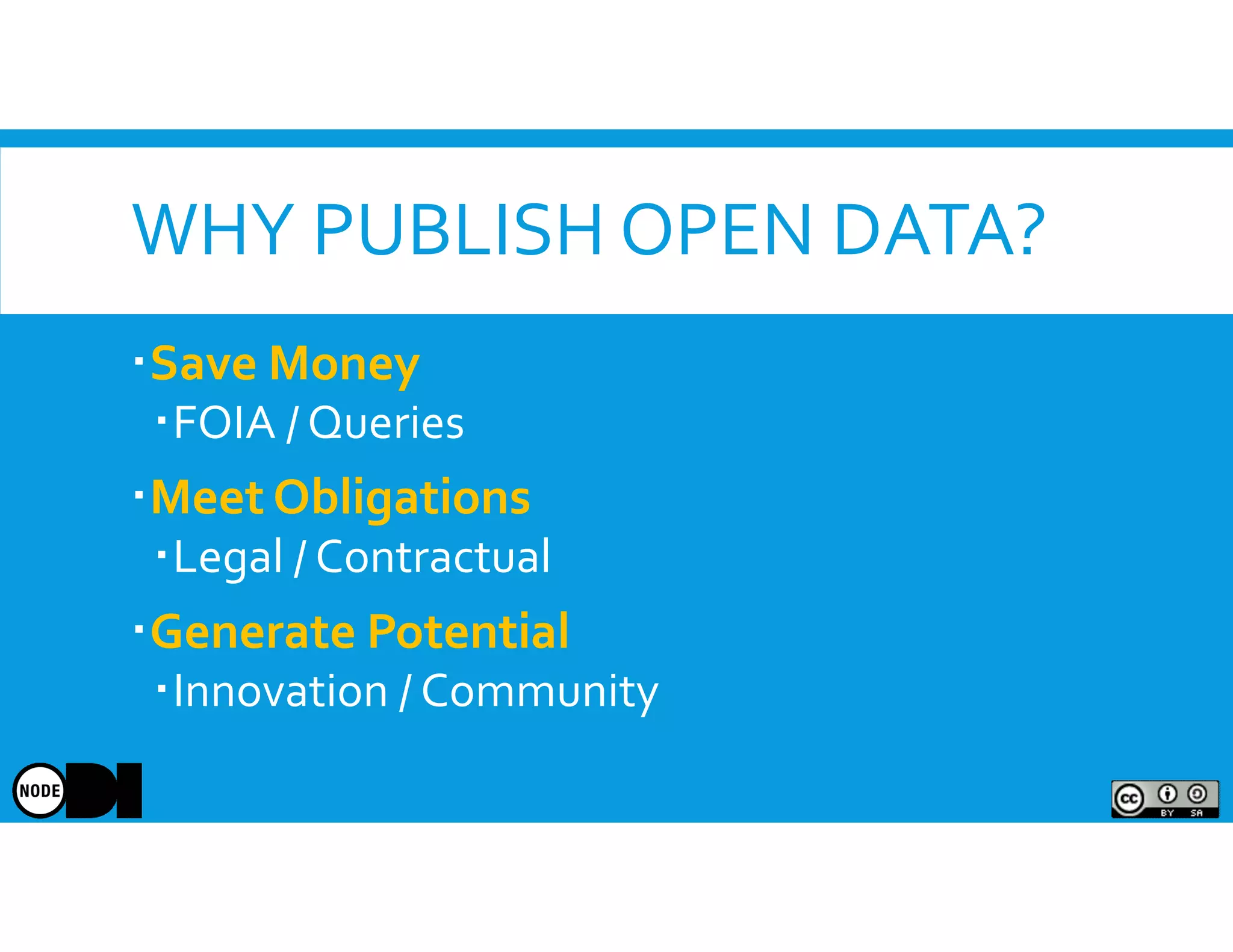
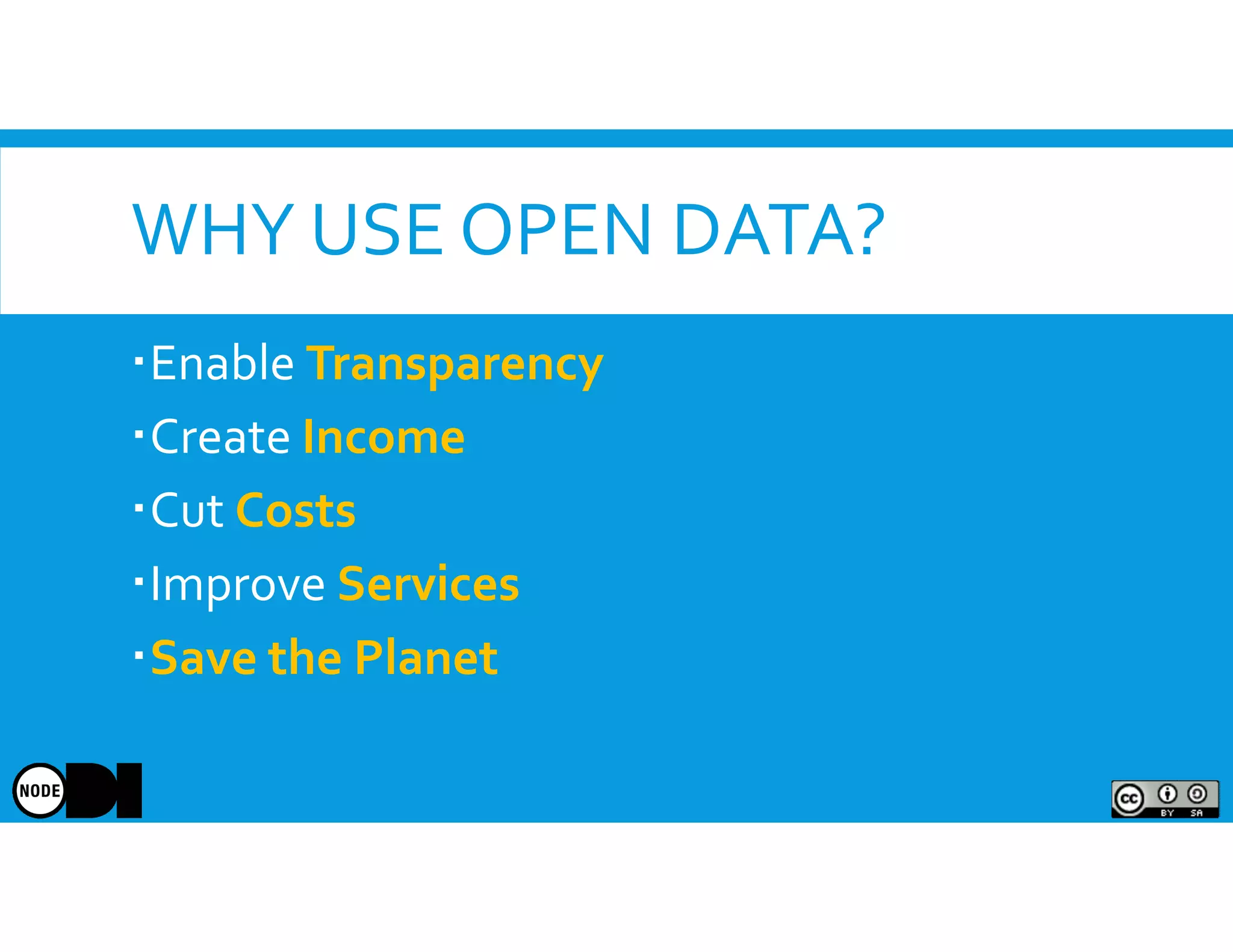
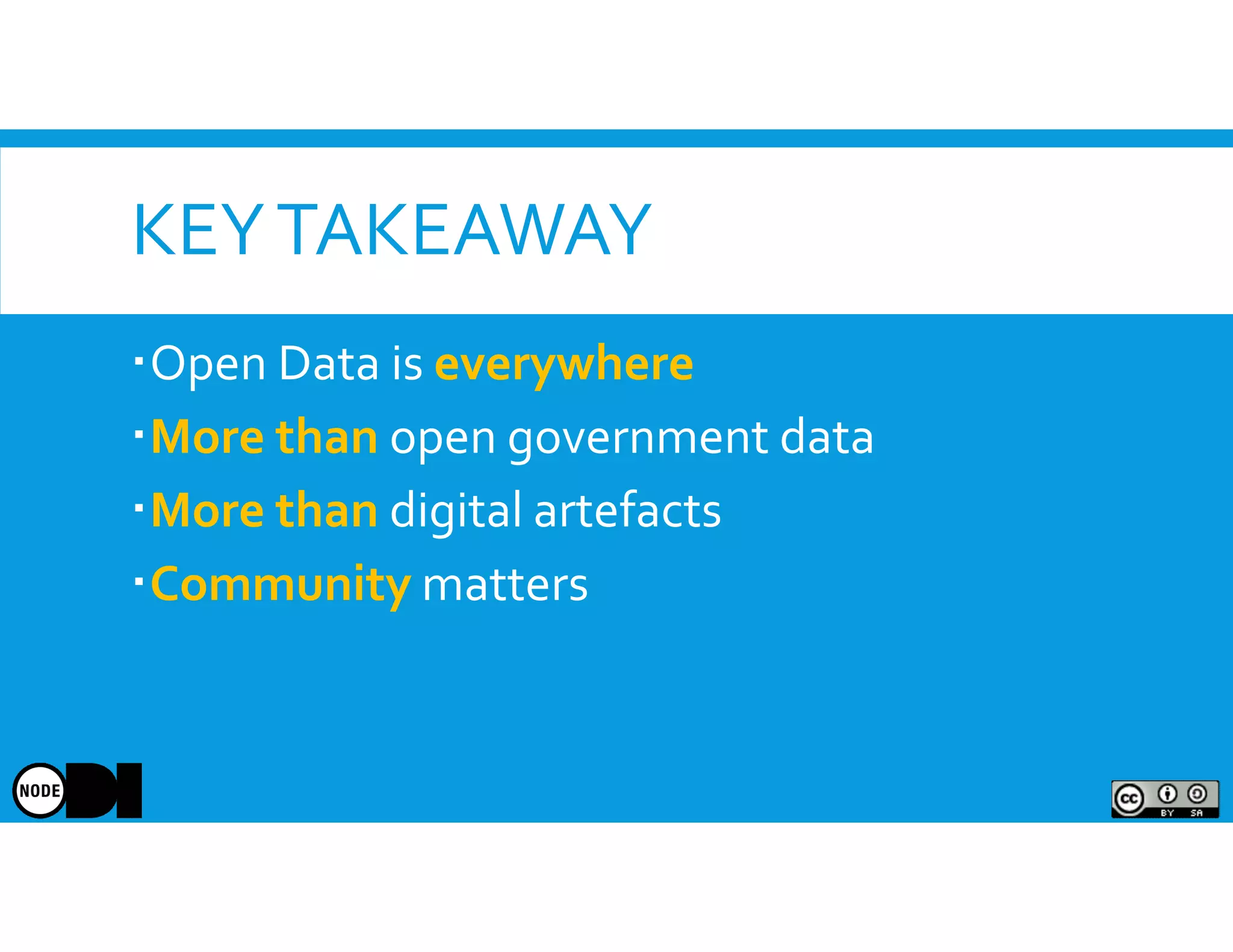
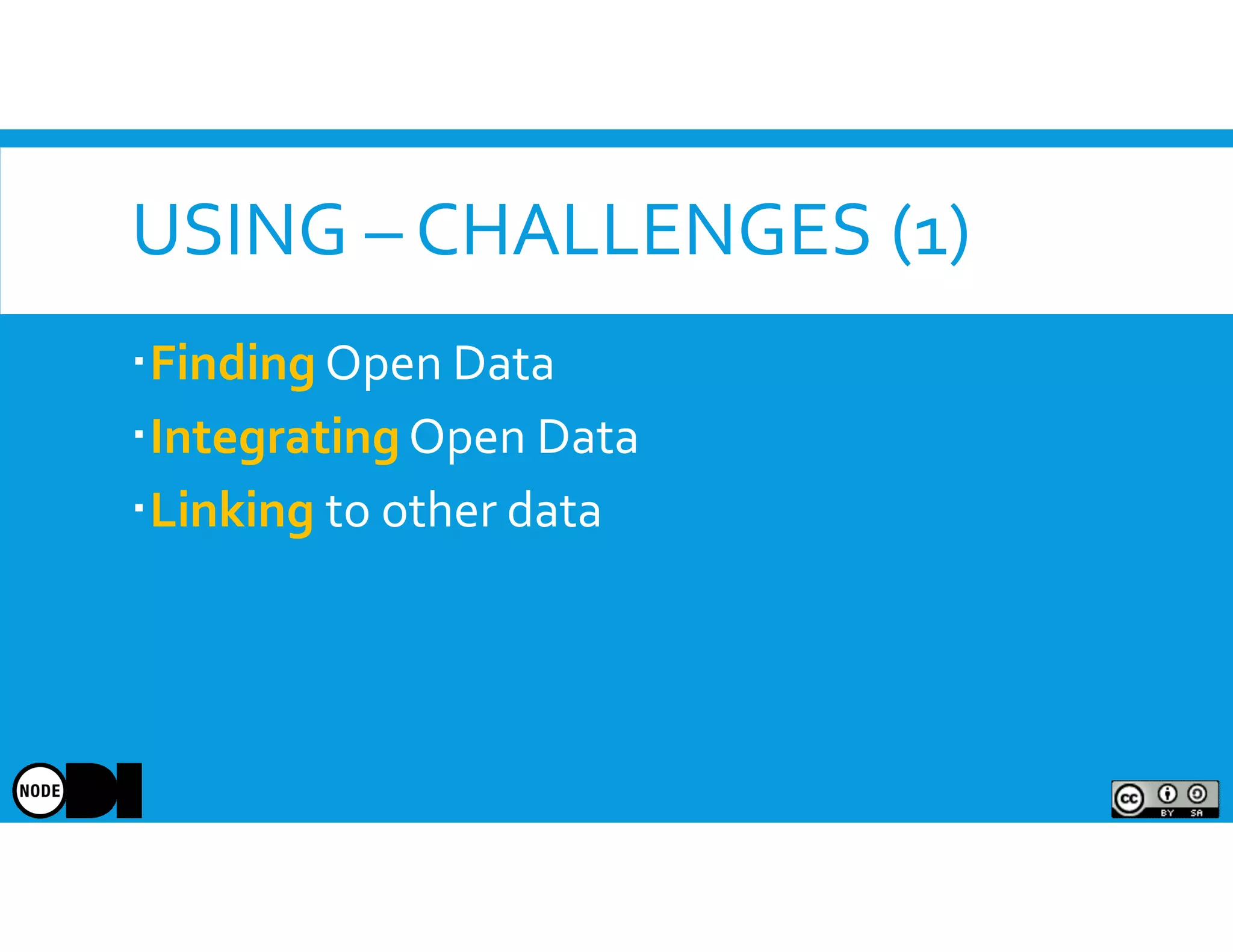
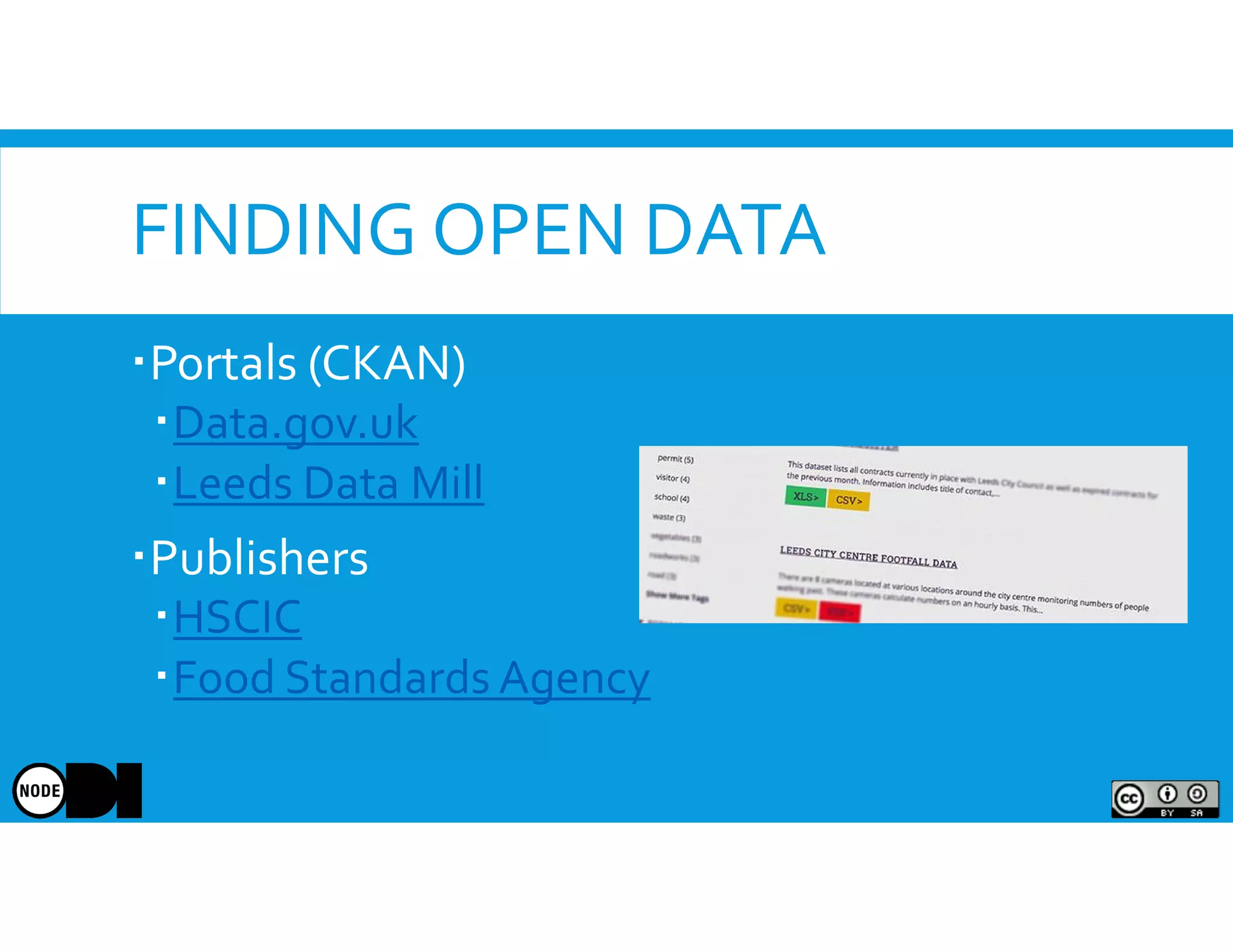
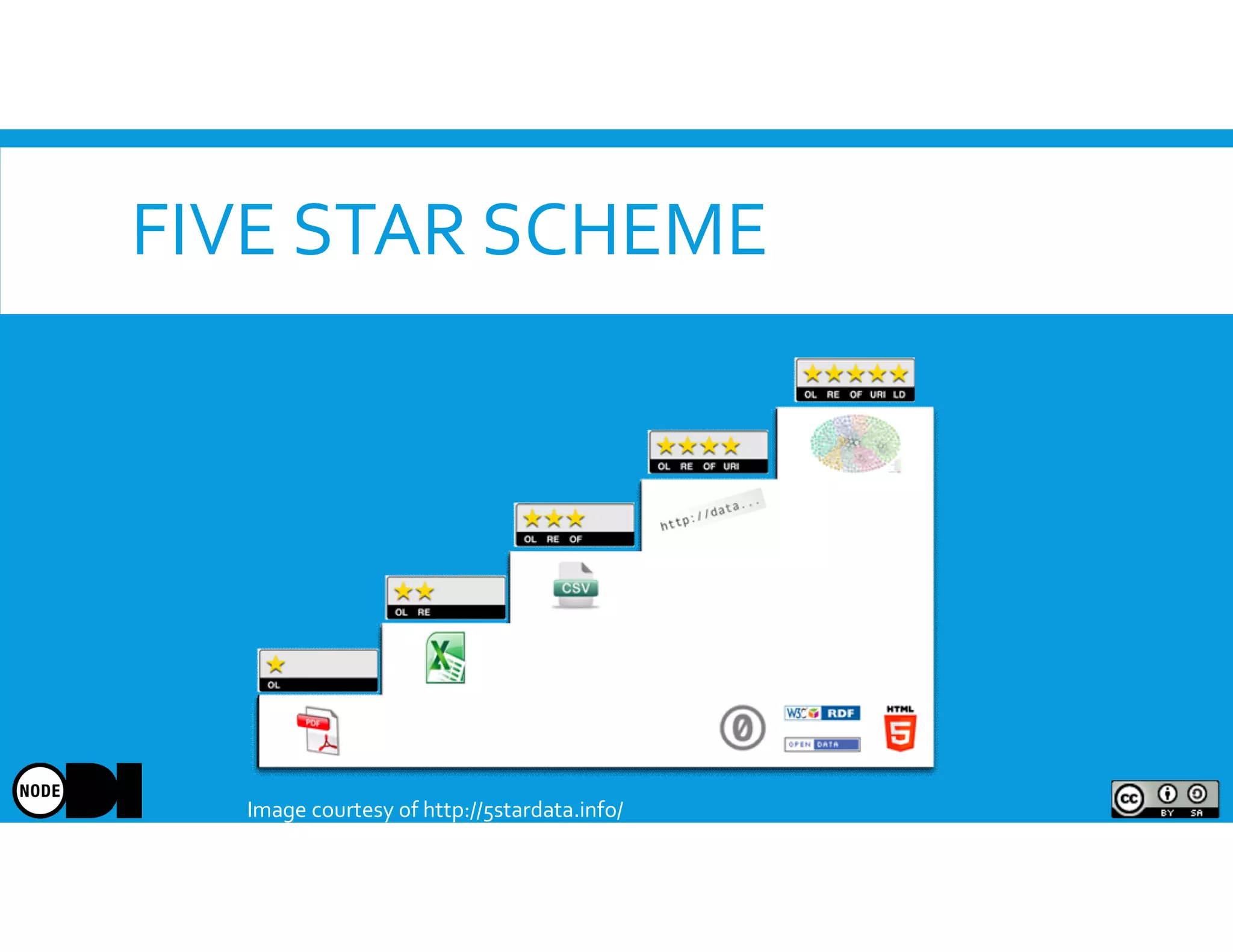
The document discusses the significance of open data, defining it as data made freely available for anyone to access, use, and share. It outlines the value of open data to organizations, including potential economic benefits and enhanced transparency, while also addressing the challenges of publishing and using it. The training aims to provide a foundational understanding of open data's definition and relevance to organizations, alongside practical exercises and case studies.