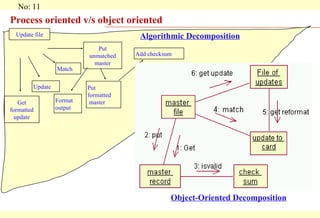
Object oriented thinking focuses on modeling real world objects and their interactions. Objects contain attributes and behaviors, and interact by sending and receiving messages. Classes define common properties and behaviors for objects through templates. Class hierarchies allow for generalization and specialization of classes. Object oriented design leads to reusable, maintainable, and scalable systems through concepts like encapsulation, inheritance, polymorphism, and abstraction.






![How do objects interact ? Message: [sender, return value] Message: [receiver, operation, parameter] Adv.: low coupling and highly reusable and easy maintainable Sender object Receiver object](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oot-090308095443-phpapp02/85/Oot-7-320.jpg)