Embed presentation
Download to read offline




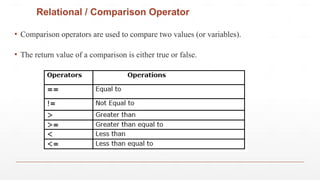


In Java, operators are special symbols or keywords used to perform operations on variables and values. They form the foundation of many expressions and control the logic and behavior of programs. Java provides several types of operators, each serving different purposes. Arithmetic operators such as +, -, *, /, and % are used for basic mathematical operations. Relational (comparison) operators like ==, !=, >, <, >=, and <= are used to compare two values and return a boolean result. Logical operators such as && (AND), || (OR), and ! (NOT) are used to combine or reverse boolean expressions. Assignment operators, like =, +=, -=, *=, and /=, are used to assign values to variables. Java also includes increment and decrement operators (++ and --), bitwise operators for manipulating bits, and ternary operator (? :) for conditional expressions. These operators make Java a flexible and expressive language, enabling developers to write efficient and concise code for a wide range of tasks, from simple calculations to complex decision-making logic.







