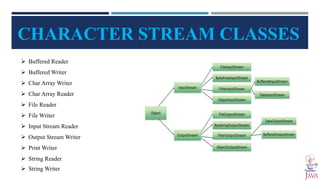
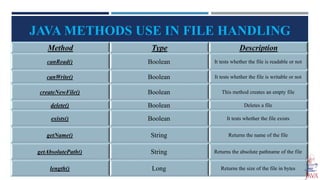
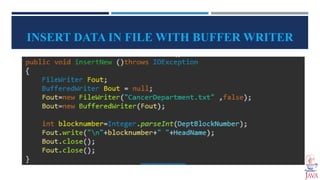
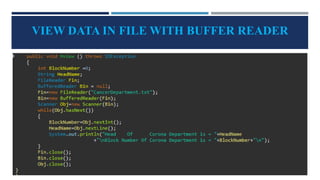
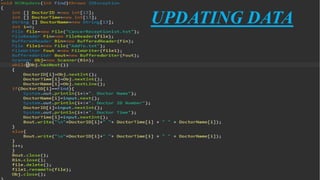
The document provides an introduction to file handling in Java, detailing how to read from and write data to files using the java.io package. It explains the types of streams (byte and character), various classes and methods for file operations, such as creating, deleting, and reading files, as well as using FileReader and FileWriter classes. Additionally, it discusses the importance of file handling in programming projects for long-term data storage.