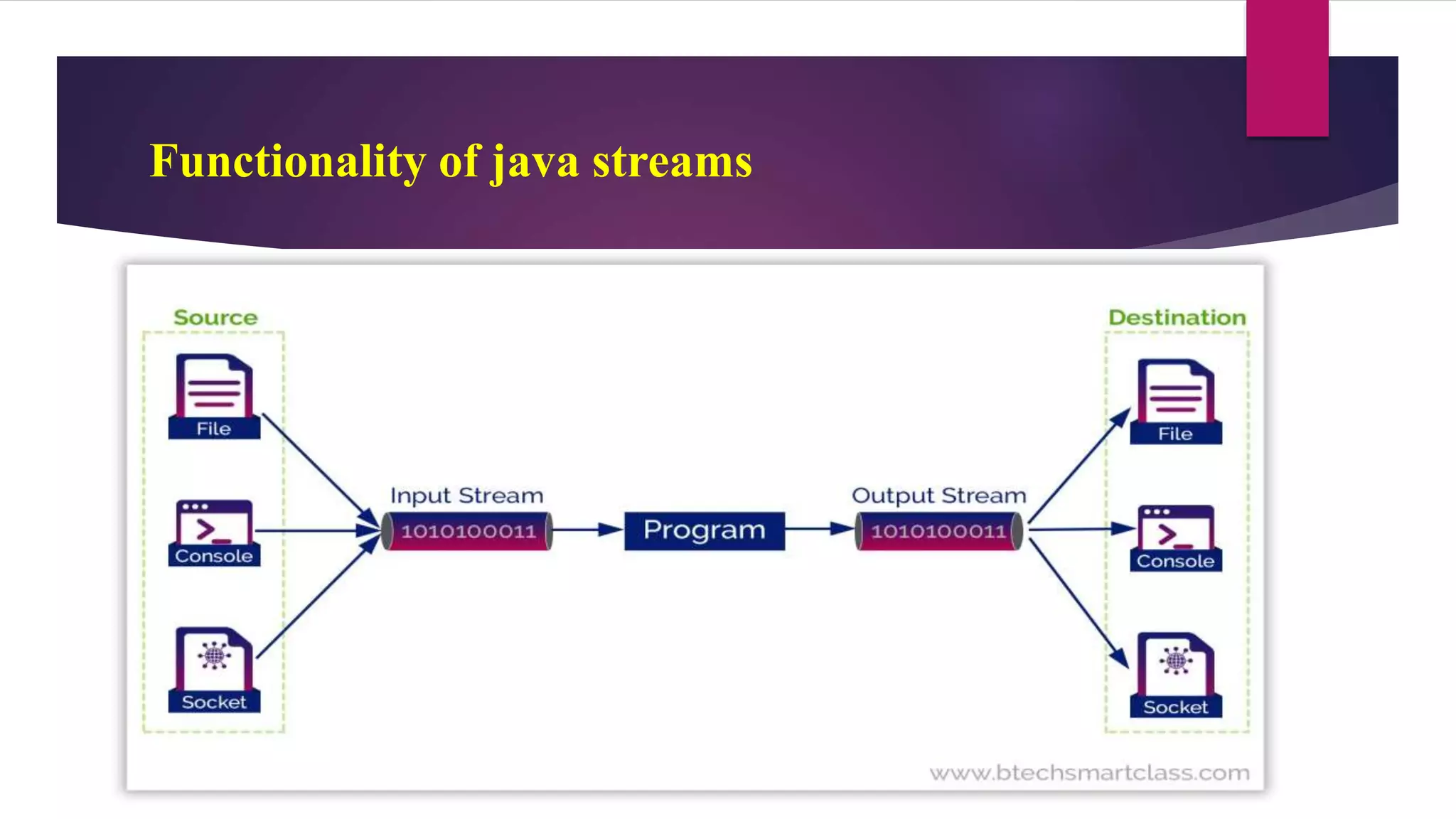
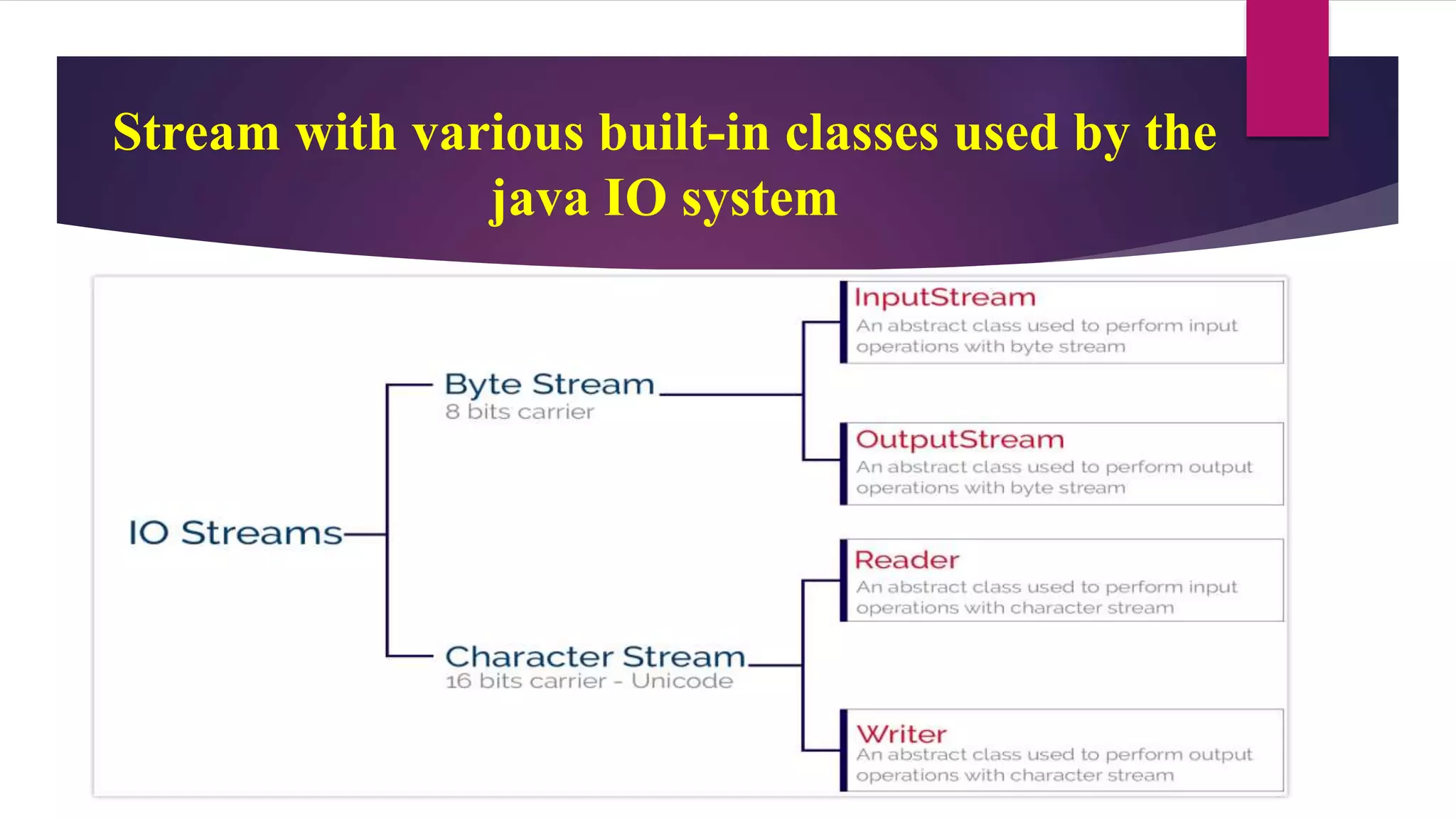
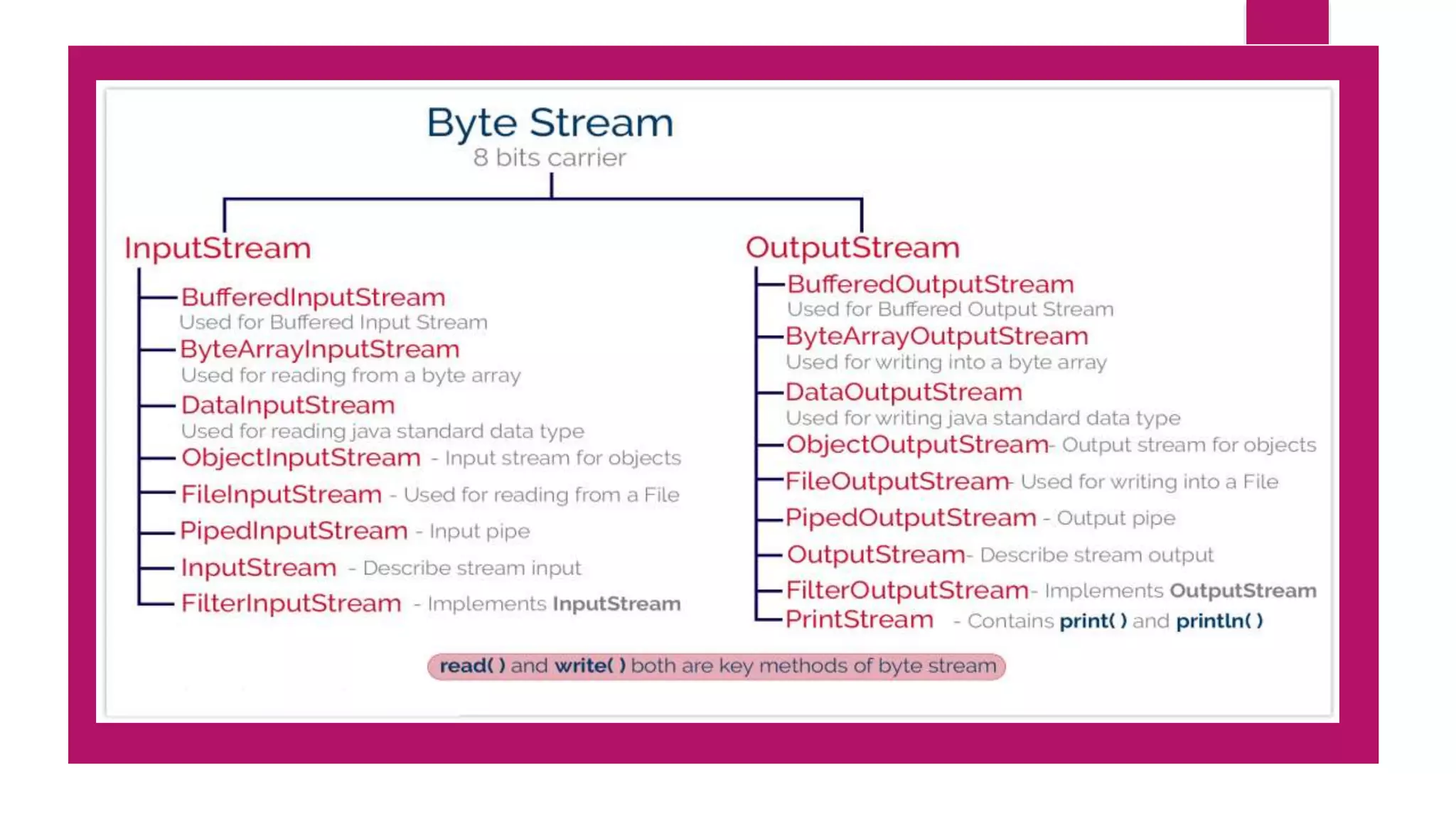
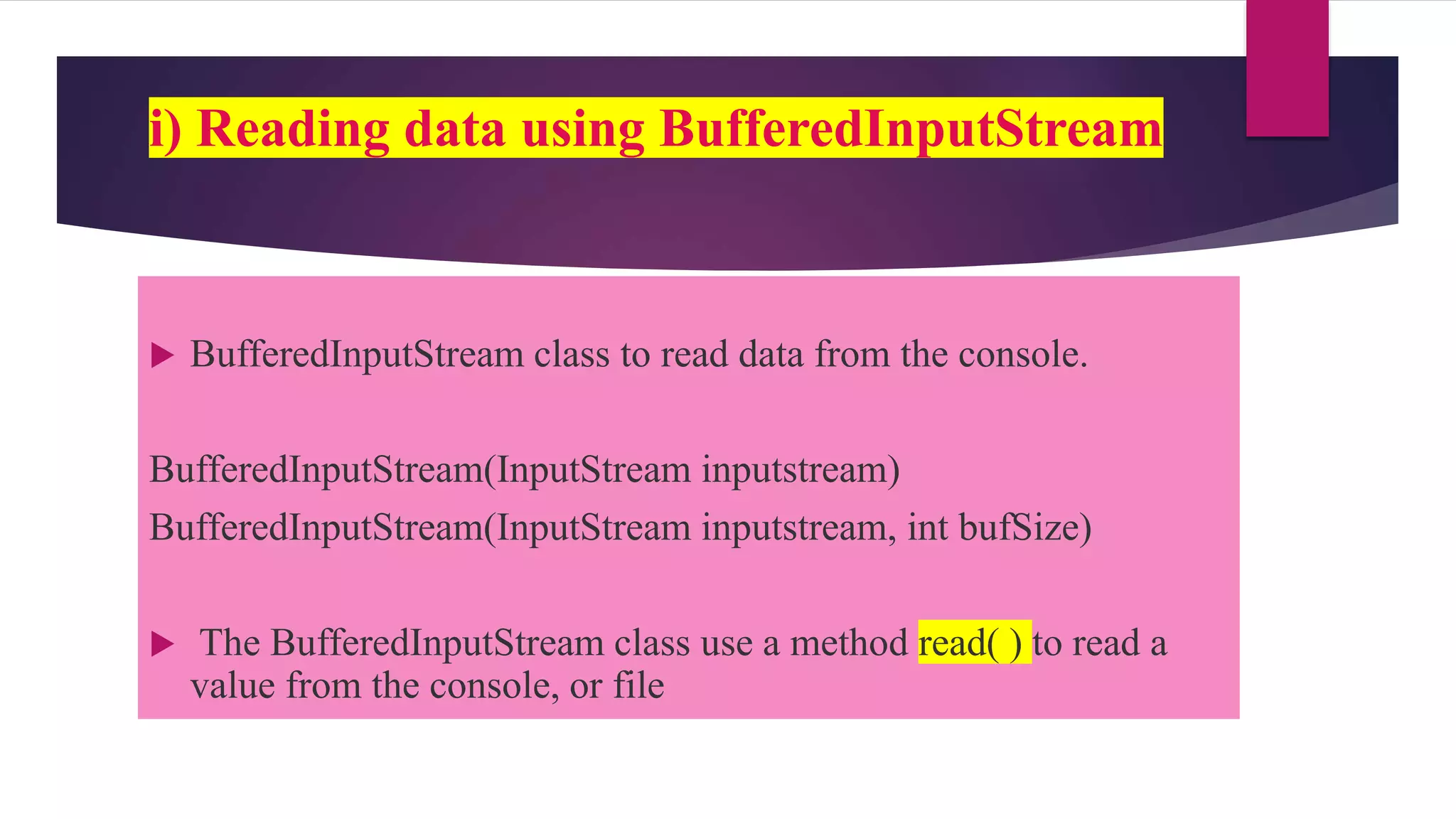
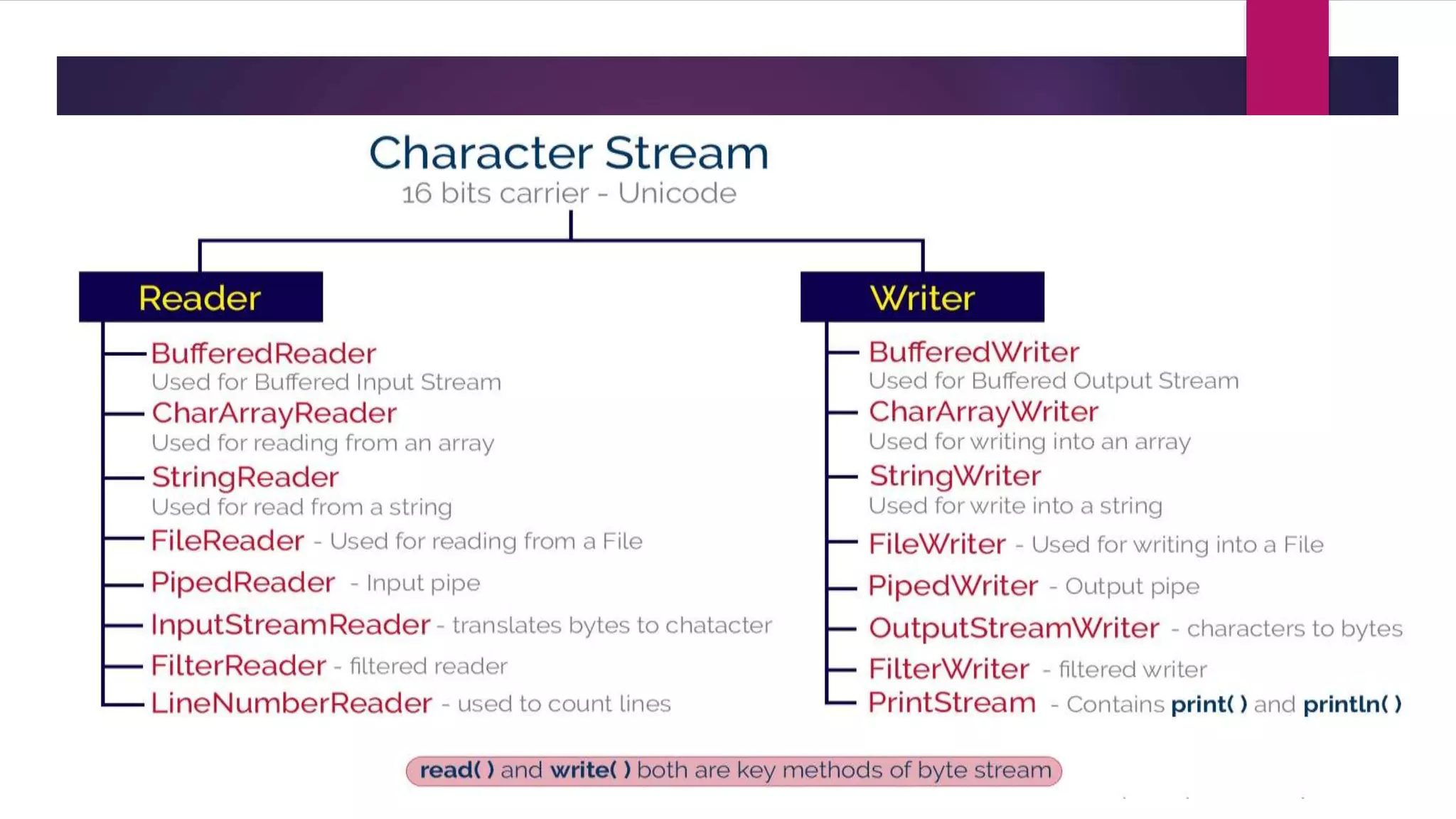
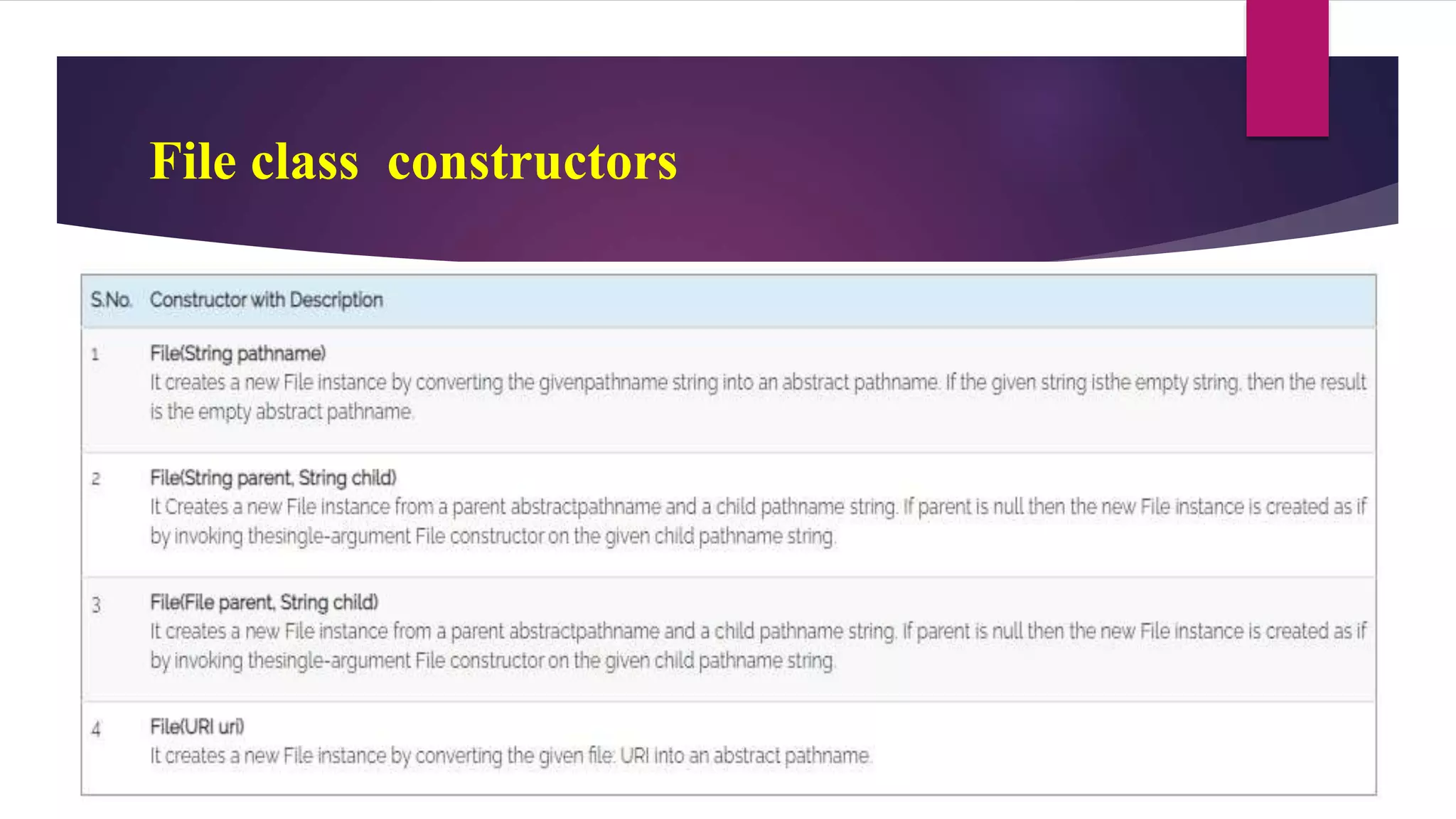
File input and output operations in Java are performed using streams. There are two types of streams - byte streams and character streams. Byte streams handle input/output at the byte level while character streams handle input/output at the character level using Unicode encoding. The File class in Java represents files and directories on the filesystem and provides methods to perform operations like creating, reading, updating and deleting files.















![Example 1 - Reading from console
import java.io.*;
public class ExReading
{
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException
{
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(System.in);
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(isr);
String name = "";
System.out.print("Please enter your name: ");
name = in.readLine();
System.out.println("Hello, " + name + "!");](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fileinputandoutput-230211161705-026ba9b3/75/File-Input-and-output-pptx-24-2048.jpg)
![Example 2 - Reading from a file
import java.io.*;
class ExReading
{
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException
{
Reader in = new FileReader(“c/abc.txt”);
try
{
char c = (char)input.read();
System.out.println("Data read from a file - '" + c + "'");
}
catch(Exception e) {
System.out.println(e);
}
finally {
input.close();](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fileinputandoutput-230211161705-026ba9b3/75/File-Input-and-output-pptx-25-2048.jpg)
![Writing data using FileWriter
import java.io.*;
public class ExWriting
{
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException
{ Writer out = new FileWriter("C:Desktopcse.txt");
msg = "cse";
try
{
out.write(msg);
System.out.println("Writing done!!!");
}
catch(Exception e)
{ System.out.println(e); }
finally
{ out.close(); }
}} }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fileinputandoutput-230211161705-026ba9b3/75/File-Input-and-output-pptx-26-2048.jpg)





![File
import java.io.File;
class FileDemo {
static void p(String s) {
System.out.println(s);
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
File f1 = new File("/java/COPYRIGHT");
p("File Name: " + f1.getName());
p("Path: " + f1.getPath());
p("Abs Path: " + f1.getAbsolutePath());
p("Parent: " + f1.getParent());
p(f1.exists() ? "exists" : "does not exist");
p(f1.canWrite() ? "is writeable" : "is not writeable");
p(f1.canRead() ? "is readable" : "is not readable");
p("is " + (f1.isDirectory() ? "" : "not" + " a directory"));
p(f1.isFile() ? "is normal file" : "might be a named pipe");
p(f1.isAbsolute() ? "is absolute" : "is not absolute");
p("File last modified: " + f1.lastModified());
p("File size: " + f1.length() + " Bytes");
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fileinputandoutput-230211161705-026ba9b3/75/File-Input-and-output-pptx-33-2048.jpg)

![Creating File using File class
import java.io.*;
class ExFile
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
try {
File file = new File(“c/abc.txt");
if (file.createNewFile())
{
System.out.println("New File is created!");
} else
{
System.out.println("File already exists.");
}
} catch (IOException e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fileinputandoutput-230211161705-026ba9b3/75/File-Input-and-output-pptx-35-2048.jpg)
![List out all files in a directory or path
import java.io.*;
class ExFileList
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
File f=new File(“c:/abc/cse");
String filenames[]=f.list();
for(String filename:filenames)
{
System.out.println(filename);
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fileinputandoutput-230211161705-026ba9b3/75/File-Input-and-output-pptx-36-2048.jpg)