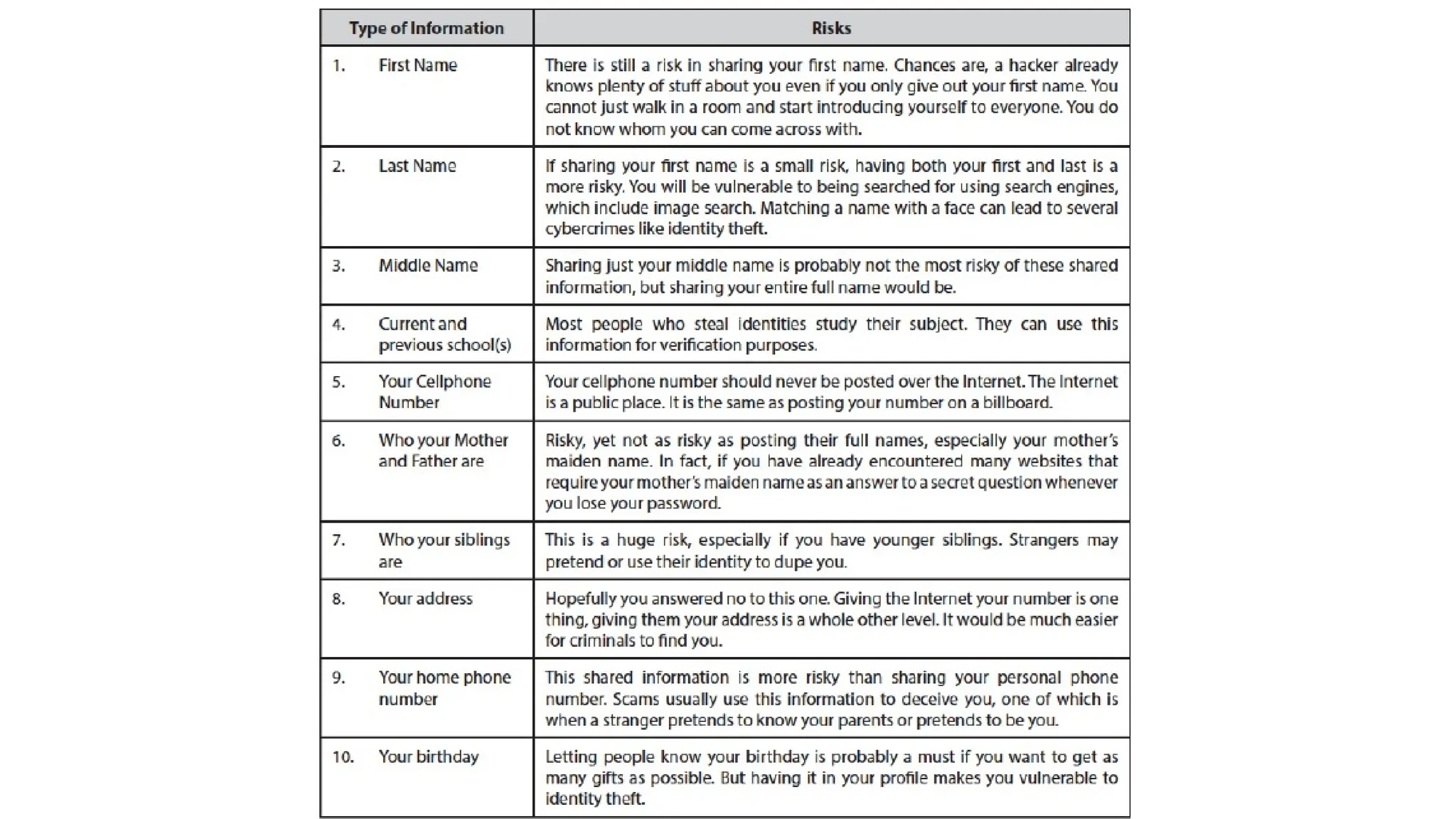
The document discusses online safety, security, ethics, and netiquette, emphasizing the importance of proper communication and internet safety practices. It provides a list of tips to navigate online spaces safely, protect against malware, avoid spam and phishing, and maintain one's online reputation. Additionally, it addresses copyright infringement and offers strategies to prevent it.