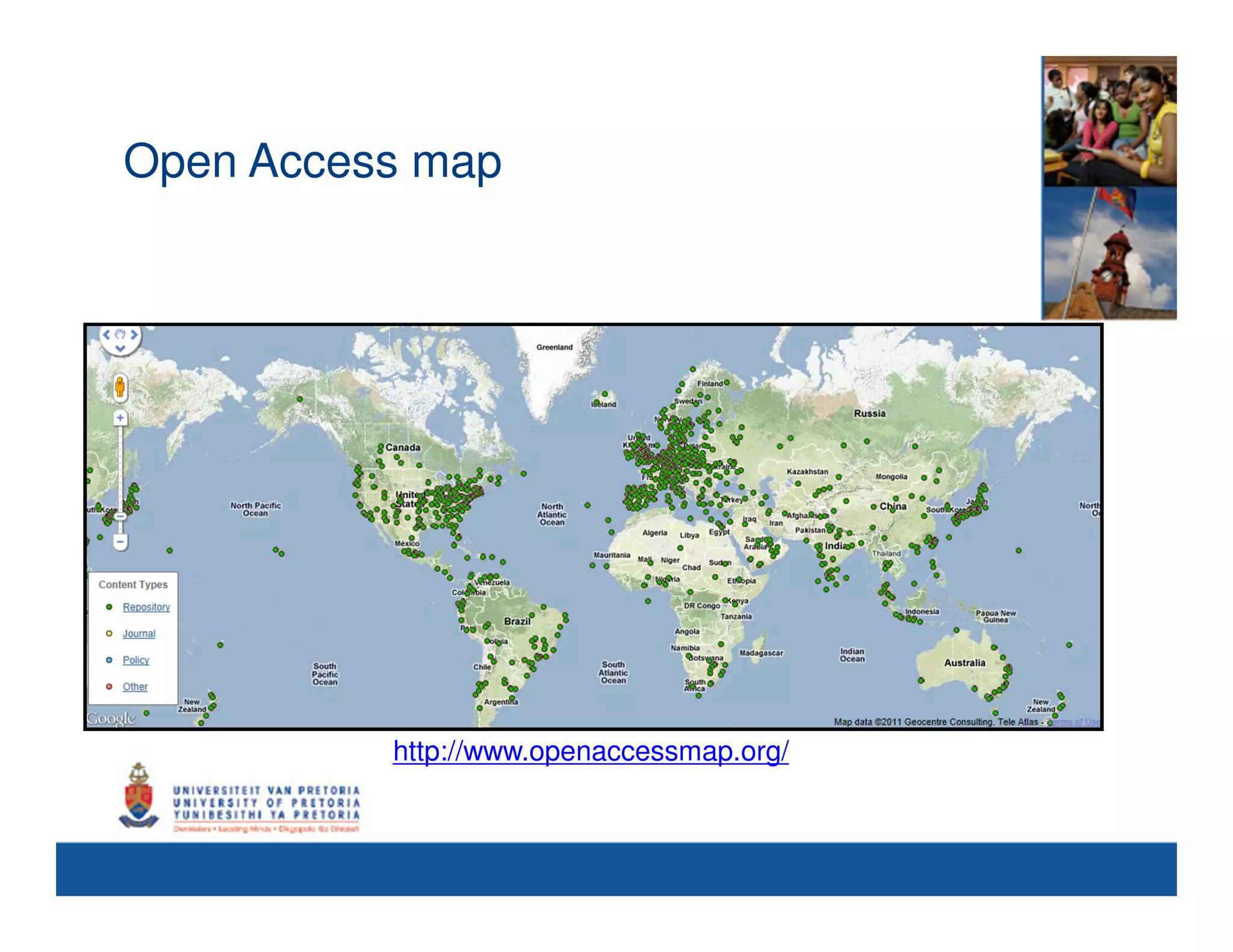
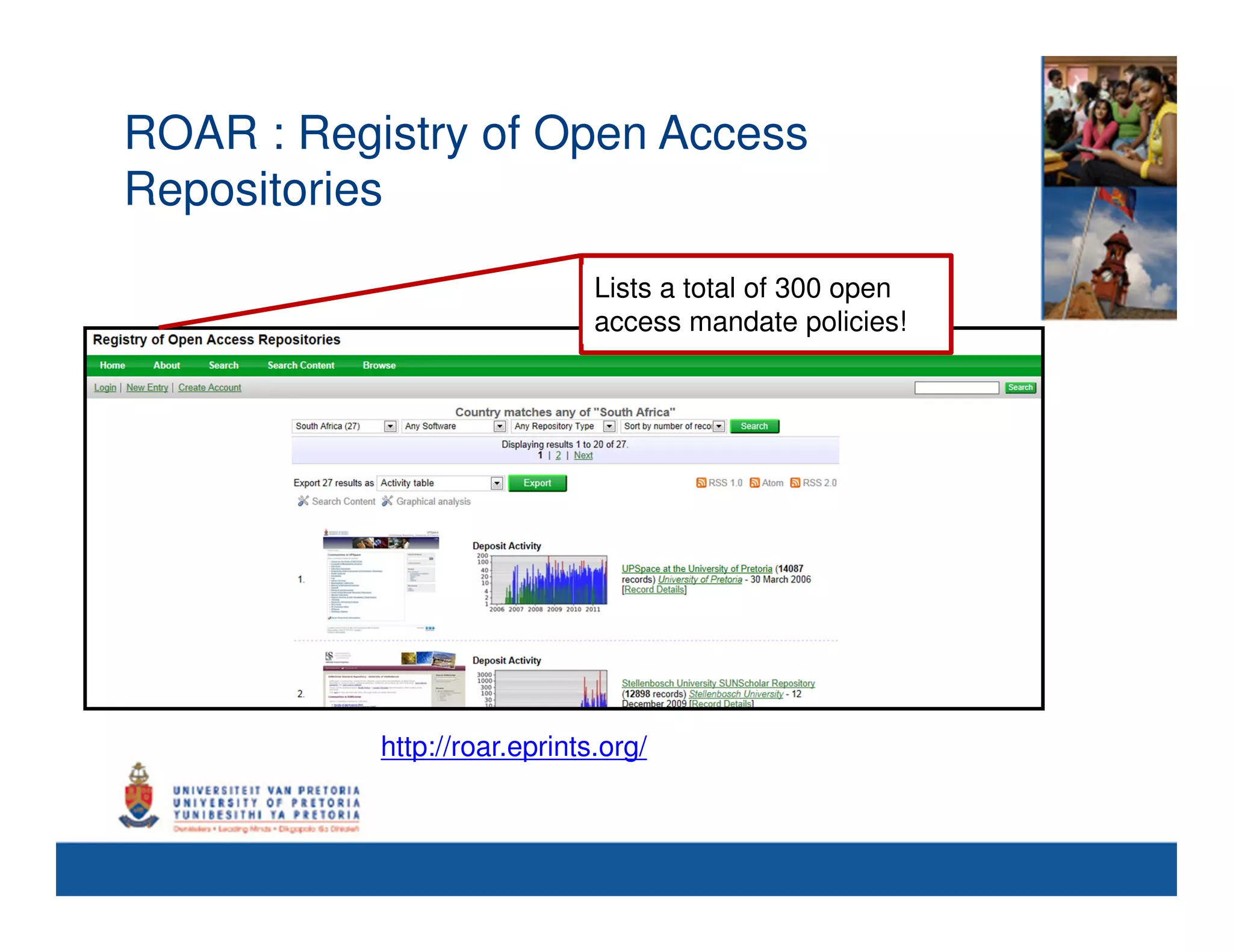
This document summarizes a presentation on opening access to research from an African perspective. It discusses how Africa produces a small percentage of the world's literature due to the high costs of accessing information online. Open access initiatives like institutional repositories and open access journals could help address this by making research articles freely available. The presentation outlines the open access landscape in Africa, including existing repositories and journals, as well as copyright issues and how universities and researchers can help promote open access. International collaboration through organizations like ASSAf and EIFL is also important for increasing the visibility and impact of African research.