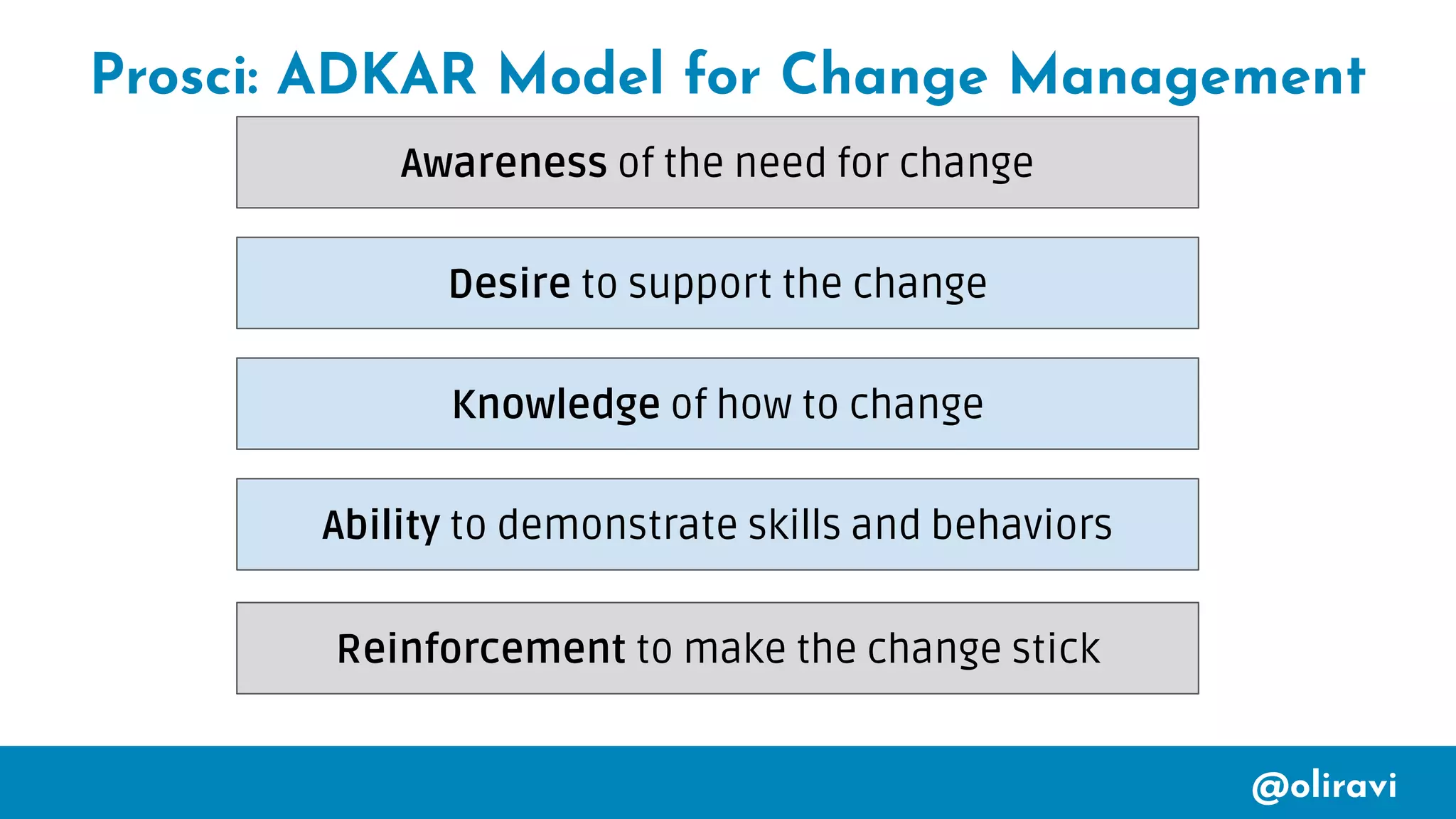
The document focuses on utilizing social engineering techniques to enhance team dynamics through assessment, action planning, and conflict resolution. It emphasizes the importance of observing team interactions and behaviors in order to initiate effective change and communication strategies. Key concepts include analyzing team strengths, quick wins for changes, and understanding individual team members' values and responses.














![@oliravi
“Ethnography is the work of describing a culture. The
central aim of ethnography is to understand another way of
life from the native point of view. [...]
Rather than studying people, ethnography means
learning from people.”
- James P. Spradley, Participant Observation](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/copyofolivialiddell-chicagophpusergroup-sociallyengineeringyourpathwaytoabetterteam-200210222253/75/Olivia-Liddell-Chicago-PHP-User-Group-Socially-Engineering-Your-Pathway-to-a-Better-Team-16-2048.jpg)