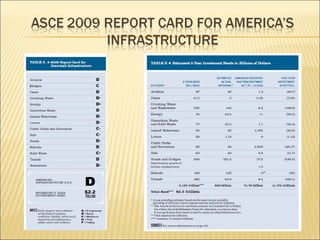
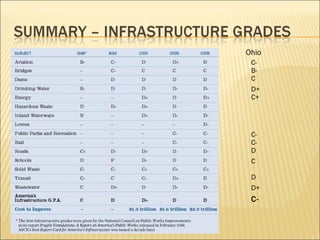
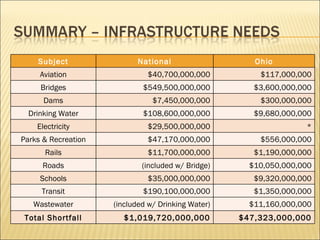
The document outlines the state of public works and infrastructure in Ohio, grading various systems including aviation, roads, bridges, and transit. Overall, the state faces significant funding shortfalls and maintenance needs across multiple sectors, with many systems receiving grades of C or lower. It emphasizes the need for increased leadership, investment, and sustainable planning to address future challenges.