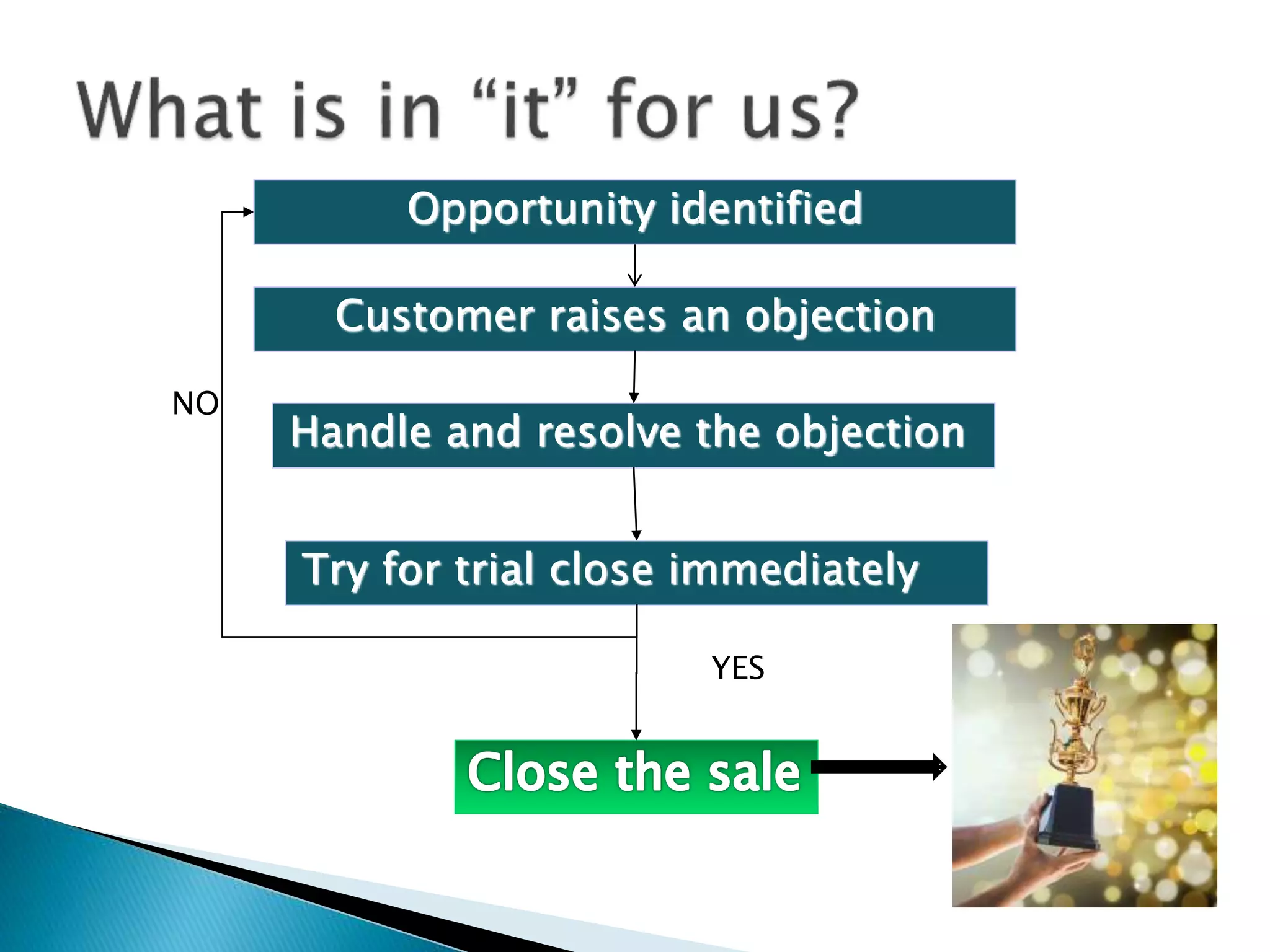
This document discusses how to handle customer objections in a sales process. It defines what an objection is and explains that objections give salespeople an opportunity to provide more information to customers. It then outlines some common objections like need, product, price and time. The document also presents the LRA method for handling objections by listening, restating, answering and acknowledging the objection. Finally, it provides some techniques for overcoming objections like providing proof, demonstrations and using testimonials.