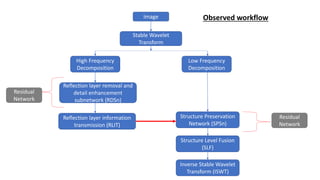
The document discusses an object detection method using a structure-preserving wavelet pyramid reflection removal network aimed at enhancing object recognition by eliminating reflections. It explains how the wavelet transform decomposes reflection maps into various frequencies, with specific networks handling low and high frequency images to separate reflections from background structures. The methodology includes advanced techniques such as structure level fusion and reflection layer information transmission, and poses questions regarding performance metrics and comparisons with other methods.