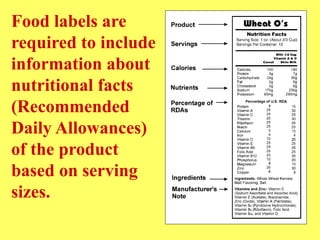
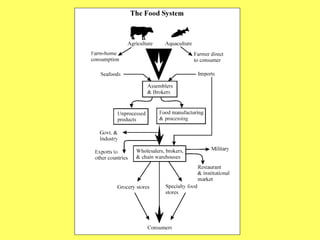
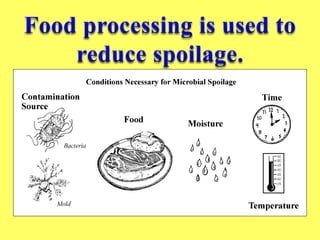
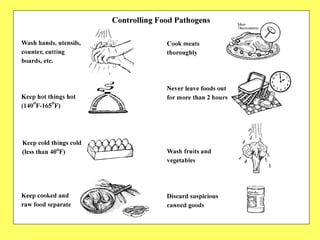
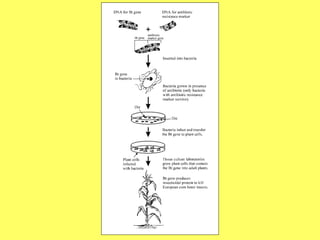
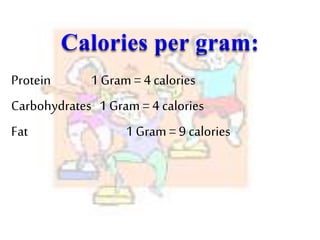
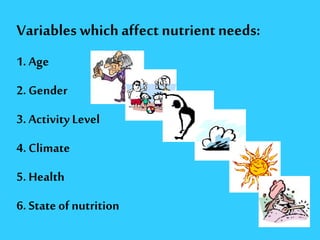
This document discusses food science and nutrition. It defines food science as applying various sciences to produce, process, package and distribute nutritious, safe foods. It describes the roles of food scientists, various food industries and government regulation. It discusses food labeling requirements and the complex system involved in getting food from farms to stores to consumers. It also covers nutrition science and the importance of a balanced diet according to the food pyramid guidelines.