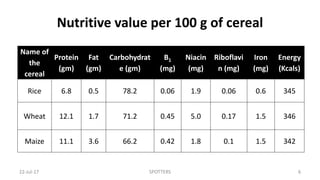
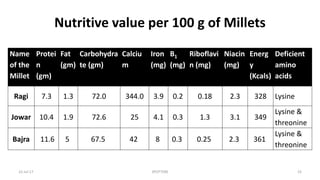
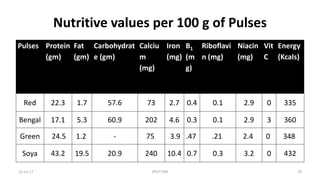
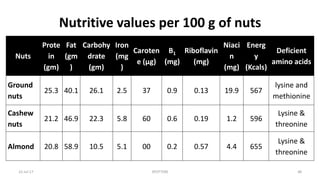
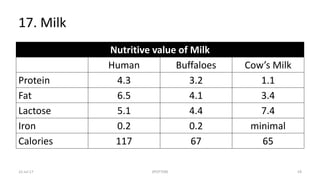
This document contains spotters (short case studies) on various foods including cereals, pulses, nuts, and dairy. It provides details on the nutritional composition, properties, and recommended consumption of each food. For example, the wheat spotter discusses that it is higher in protein than rice but lower quality, and whole wheat is preferable to refined wheat. The milk spotter notes its protein and energy content per 100ml. The document aims to inform medical students and health professionals about essential nutrition information through concise spotters on individual food items.