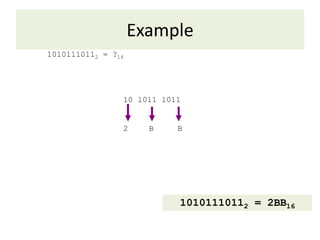
The document discusses various number systems including decimal, binary, octal, and hexadecimal. It provides details on how to convert between these different bases including examples of converting decimal to binary, binary to decimal, hexadecimal to binary, decimal to octal, octal to decimal, hexadecimal to decimal, decimal to hexadecimal, binary to octal, binary to hexadecimal, octal to hexadecimal, and hexadecimal to octal. Conversion techniques involve grouping bits, multiplying place values, and keeping track of remainders from division.