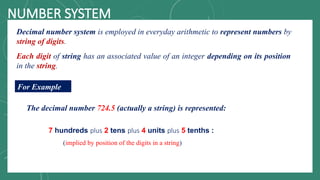
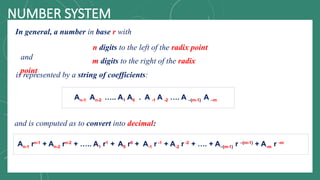
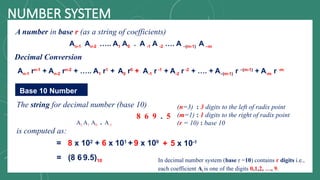
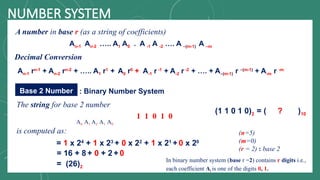
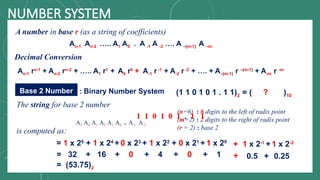
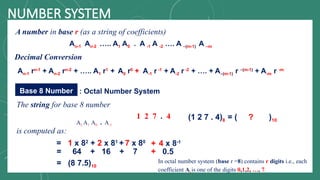
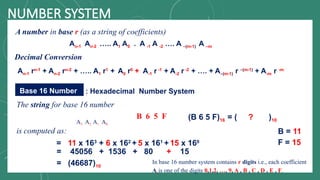
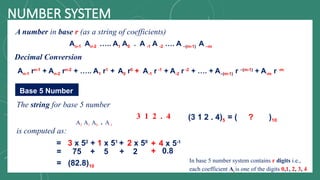
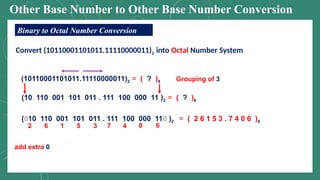
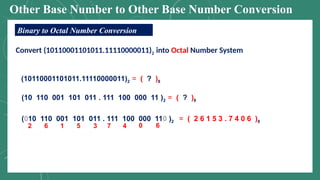
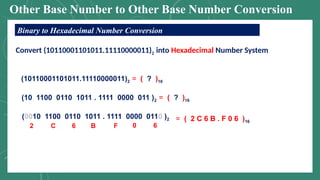
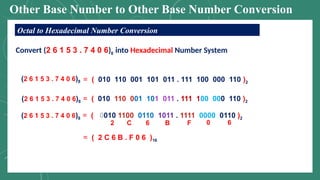
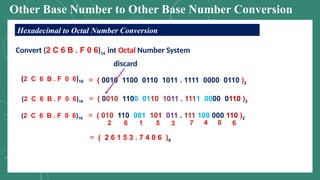
The document discusses various number systems including decimal, binary, octal, and hexadecimal, explaining how numbers are represented and converted between these systems. It details the processes for converting numbers from decimal to other bases as well as conversions between different bases. Additionally, it includes examples of the conversions for clarity.