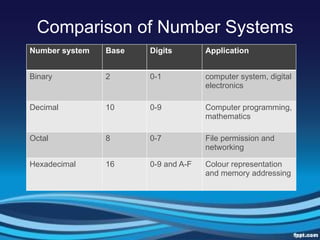
The document discusses various number systems, including binary, decimal, octal, and hexadecimal, highlighting their histories, structures, and applications. Each system serves distinct purposes in fields such as computer science, finance, and engineering. Number systems are essential for effective data representation and problem-solving in mathematics and everyday life.