This document discusses nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) in 3 paragraphs or less:
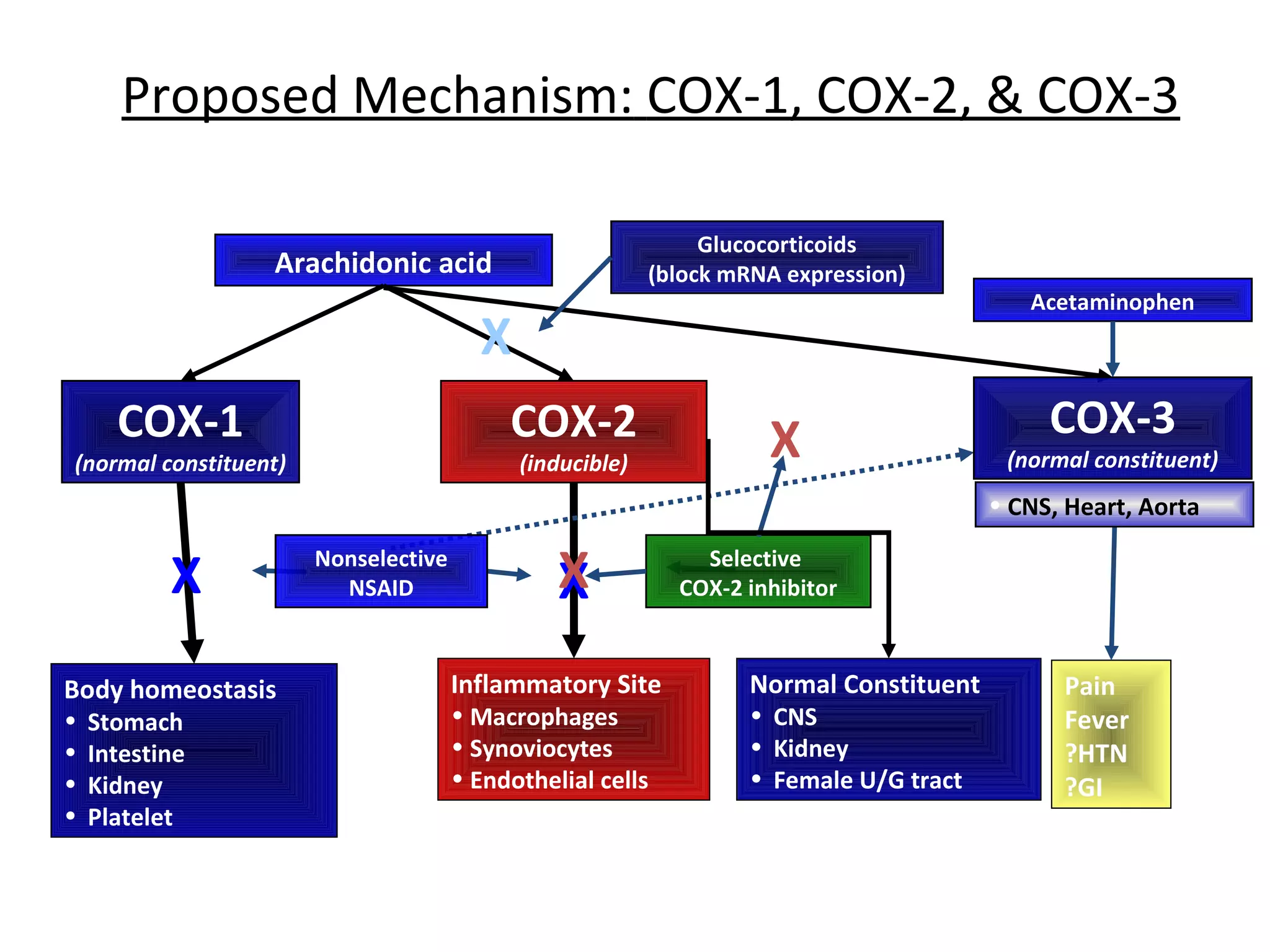
NSAIDs are a chemically diverse group of drugs that are grouped together because they have common analgesic and antipyretic effects and anti-inflammatory effects at higher doses. They act primarily on peripheral pain mechanisms and in the central nervous system. All NSAIDs inhibit prostaglandin synthesis by blocking the cyclooxygenase enzymes.
NSAIDs were developed from white willow bark and include aspirin, ibuprofen, naproxen, and others. They are classified based on their chemical structure and selectivity for the COX-1 and COX-2 enzymes. Traditional NSAIDs