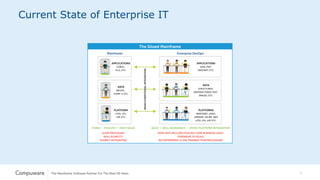
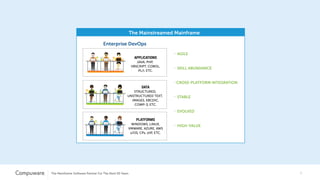
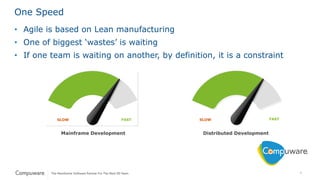
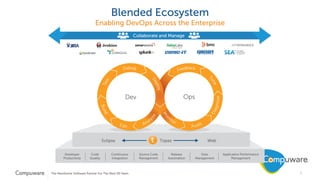
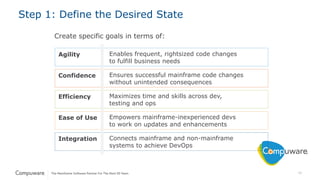
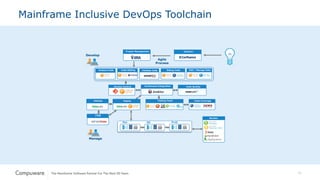
The document discusses the integration of mainframe systems into a DevOps software delivery environment, outlining current practices and tools necessary for modernizing mainframe development. It includes ten steps to adopt Agile methodologies and automations, emphasizing improvements in agility, efficiency, and collaboration across platforms. Each step provides goals and success indicators, focusing on training, operational data usage, and cross-platform integration to enhance productivity and minimize errors.