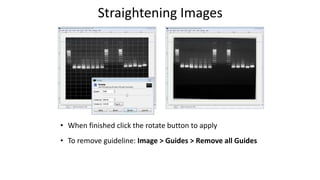
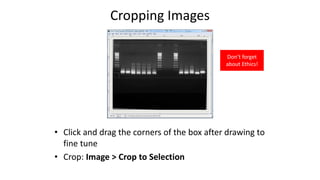
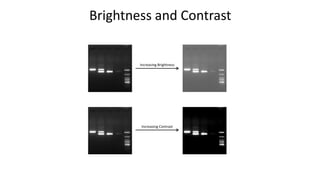
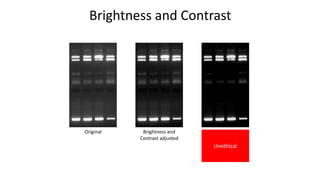
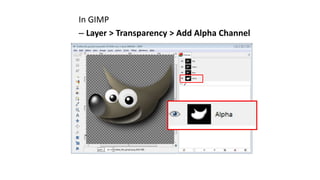
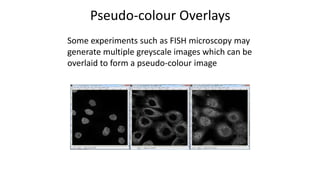
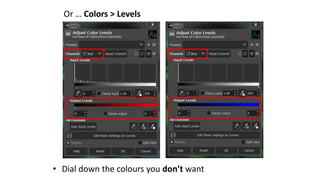
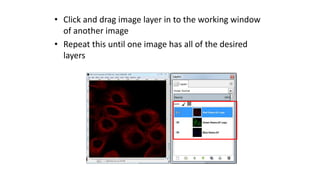
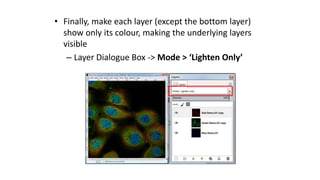
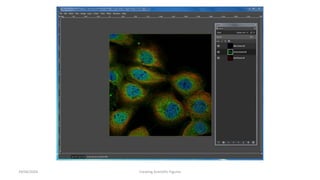
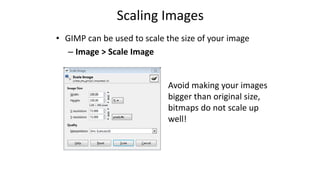
This document is a tutorial on using GIMP, an open-source bitmap graphics editor, covering basic functions such as opening and saving images, straightening, cropping, adjusting brightness and contrast, and using alpha channels. It emphasizes ethical considerations in image editing and provides step-by-step instructions for tasks like pseudo-color overlays and exporting images in various formats. The tutorial also addresses proper scaling of images to avoid quality loss.