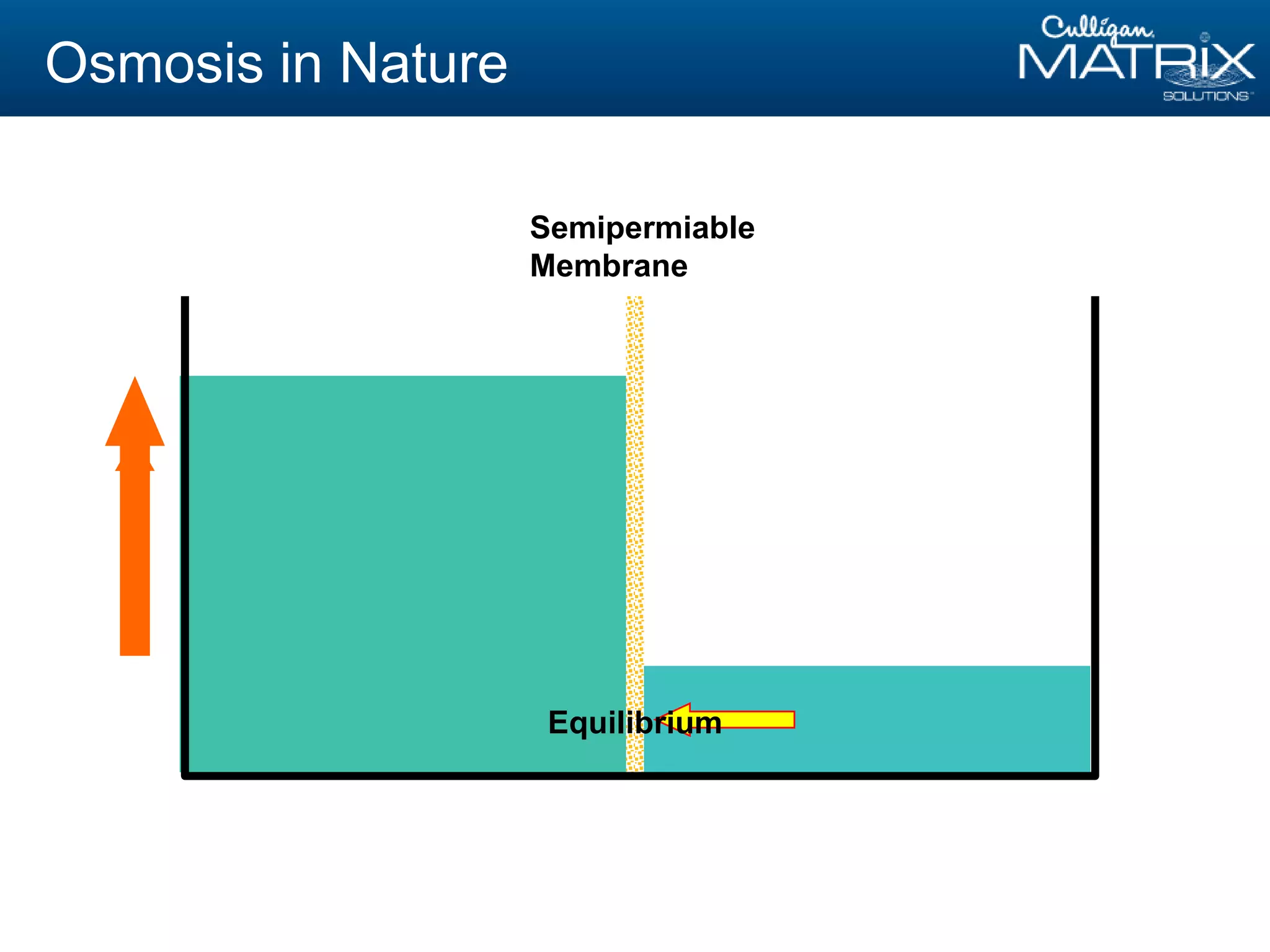
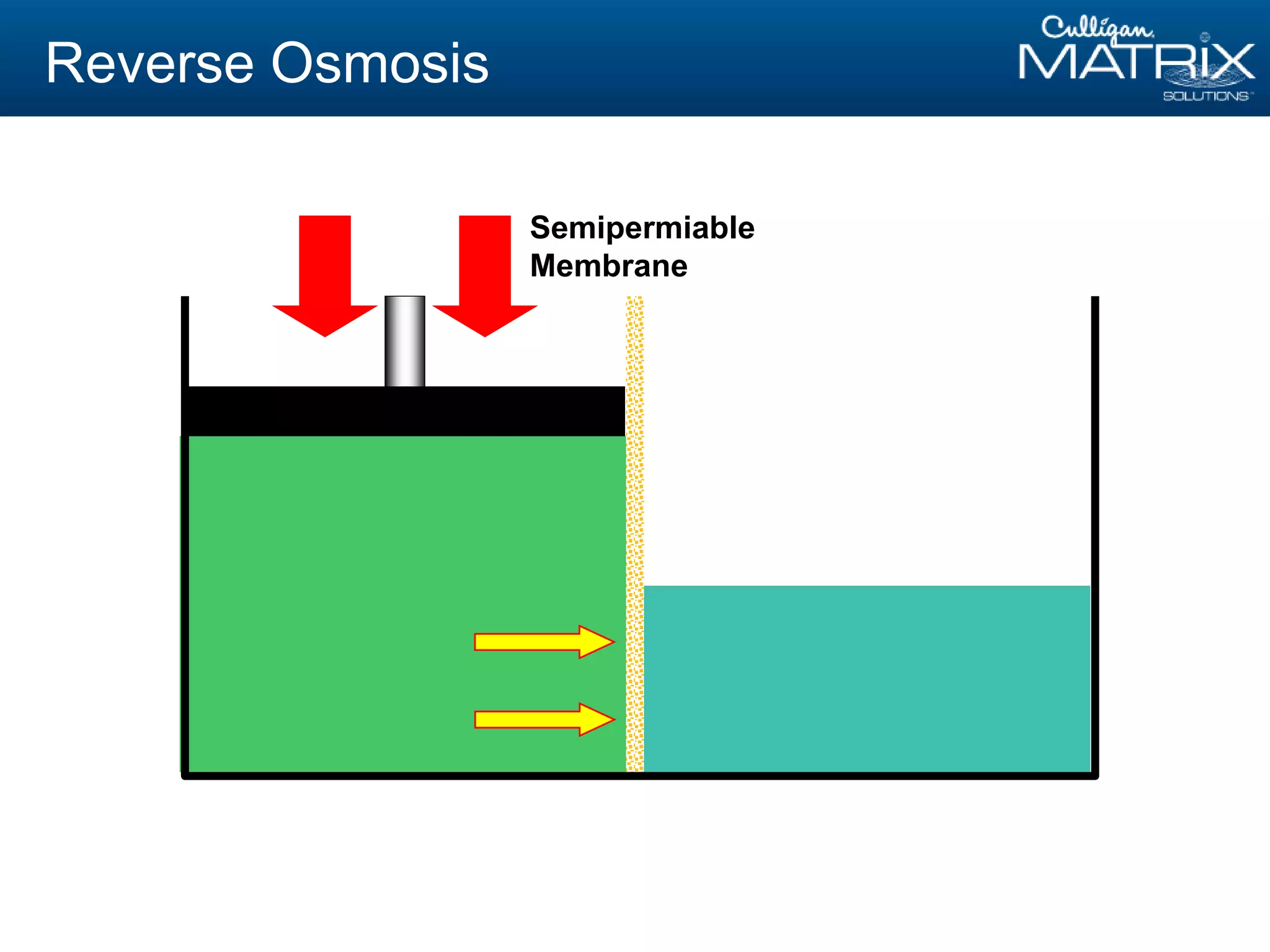
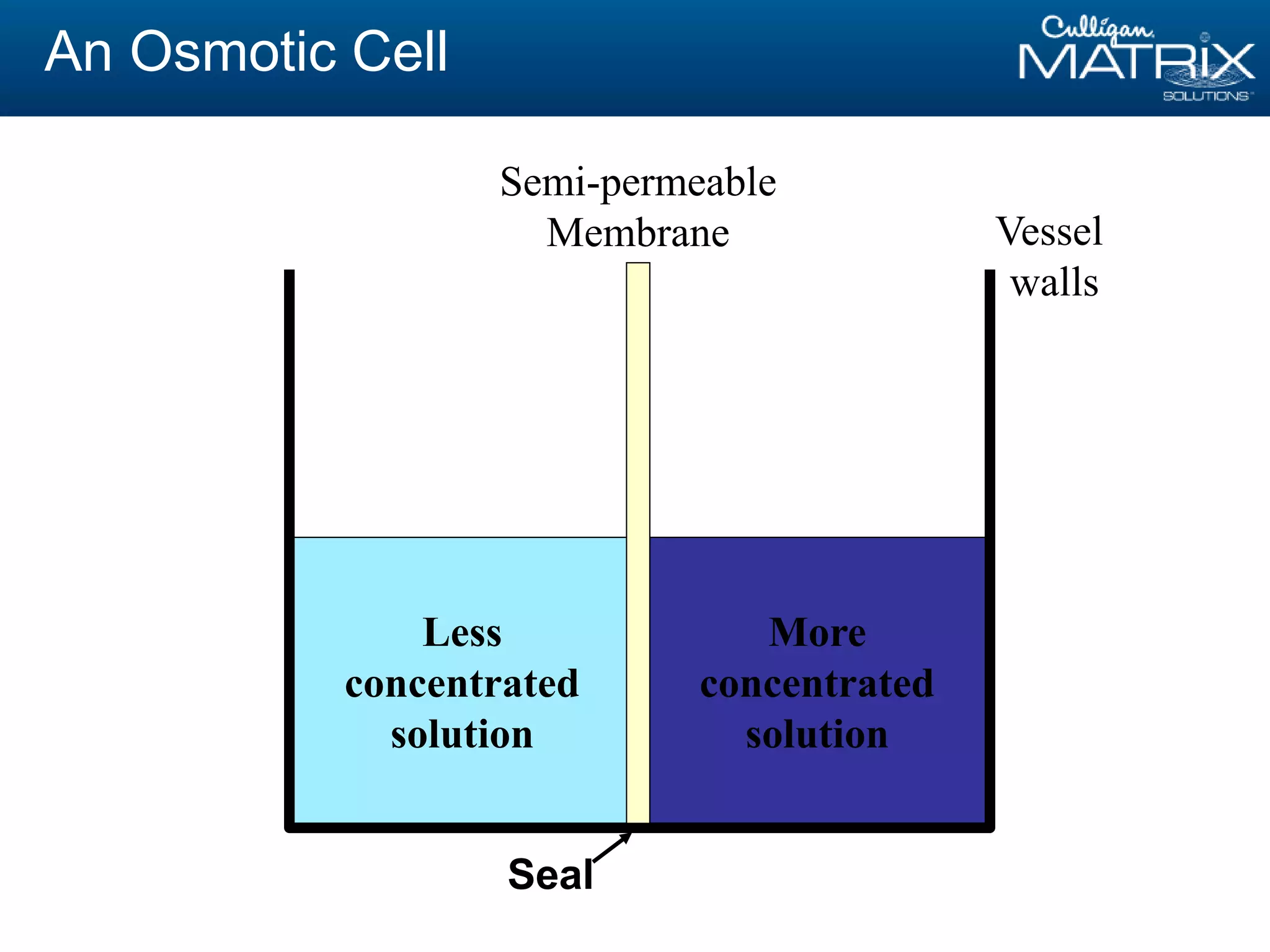
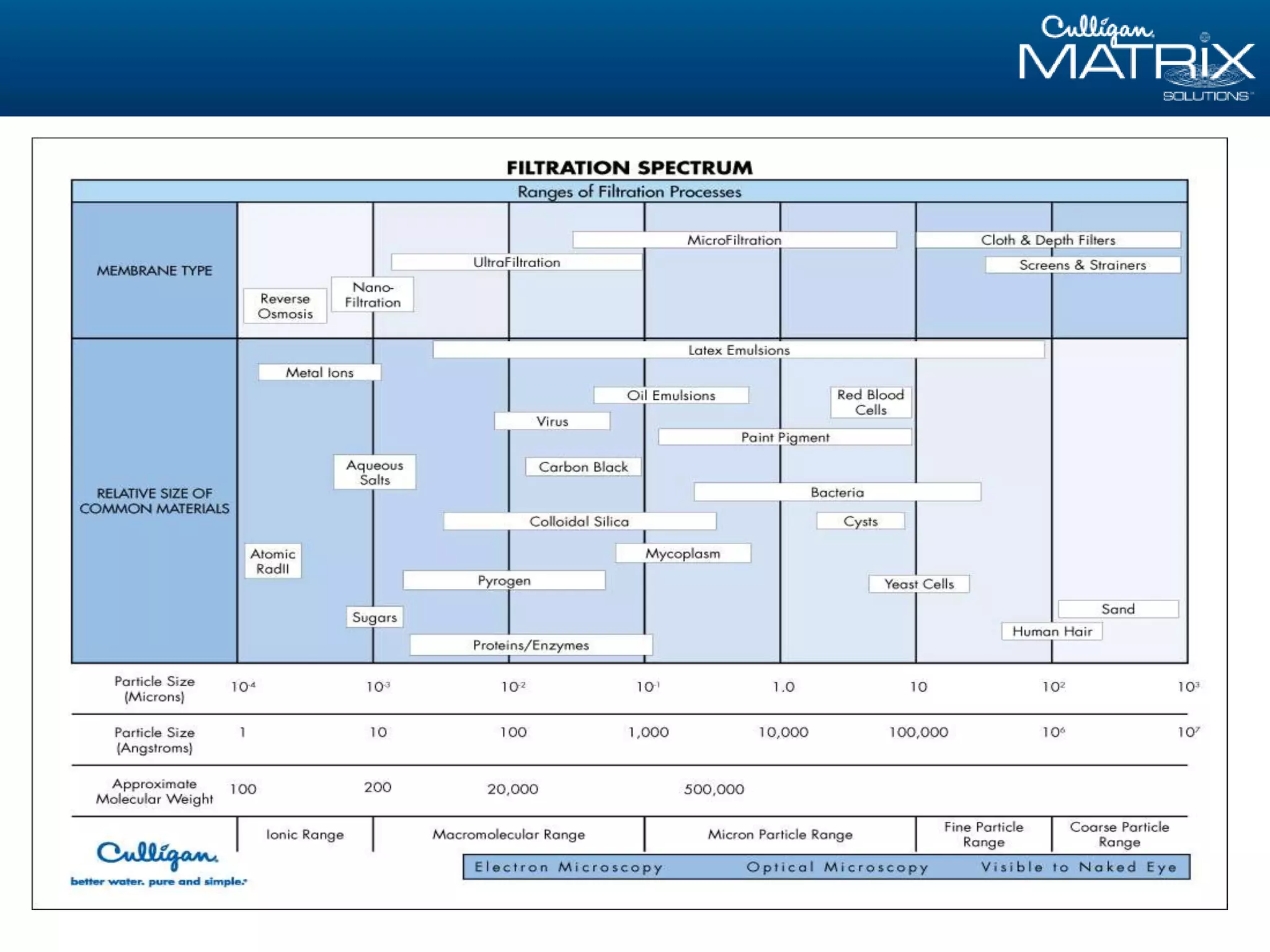
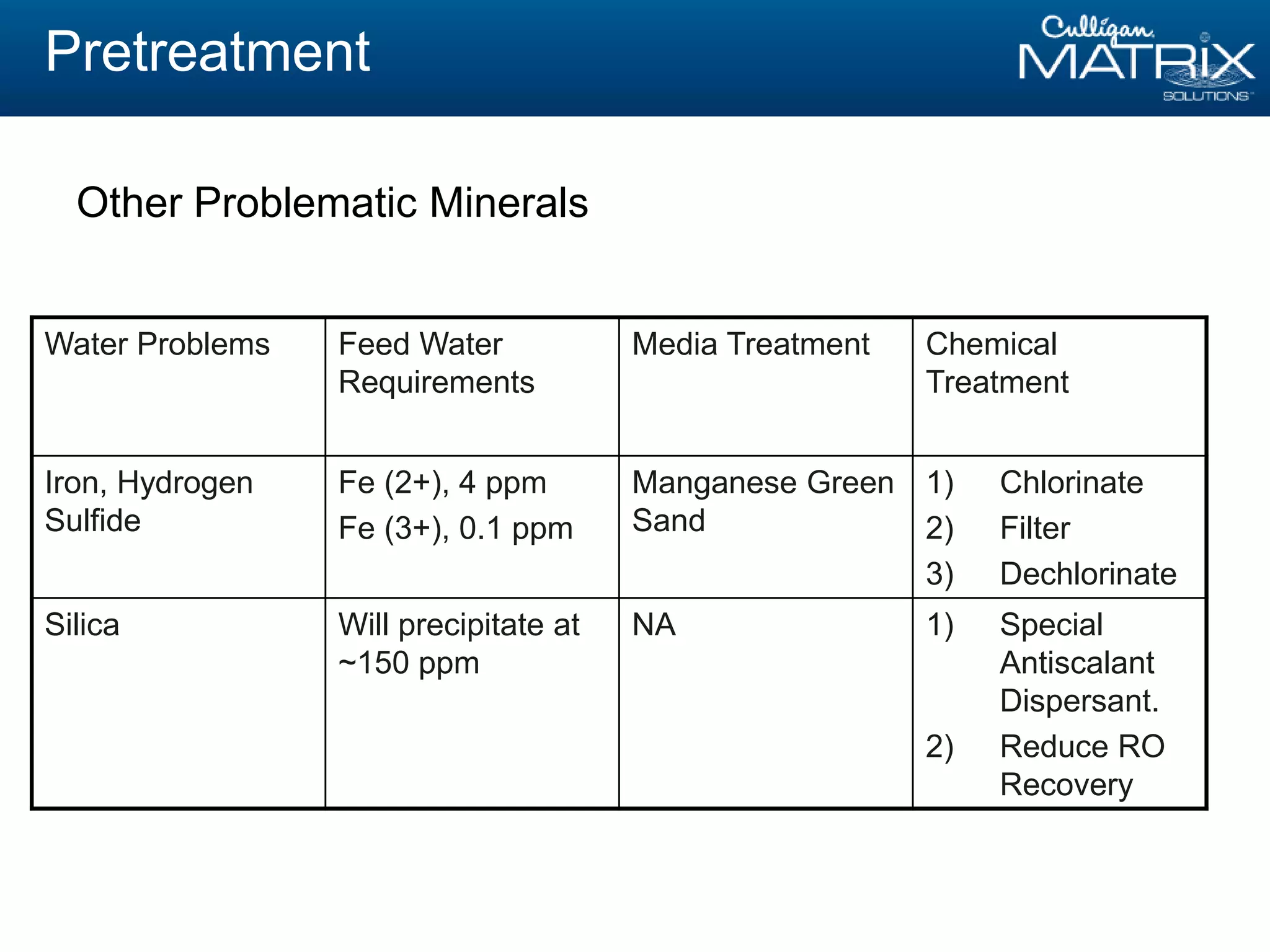
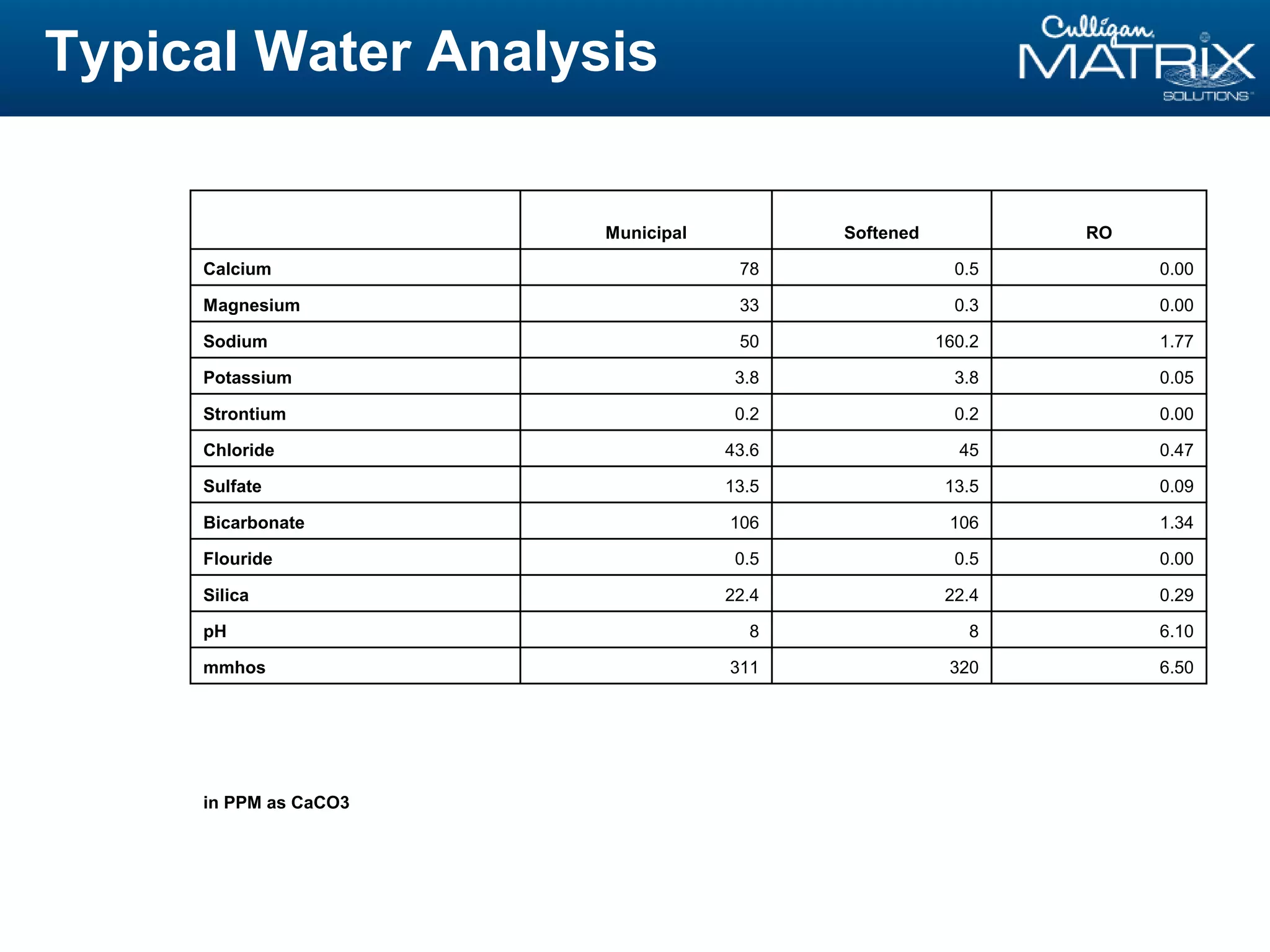
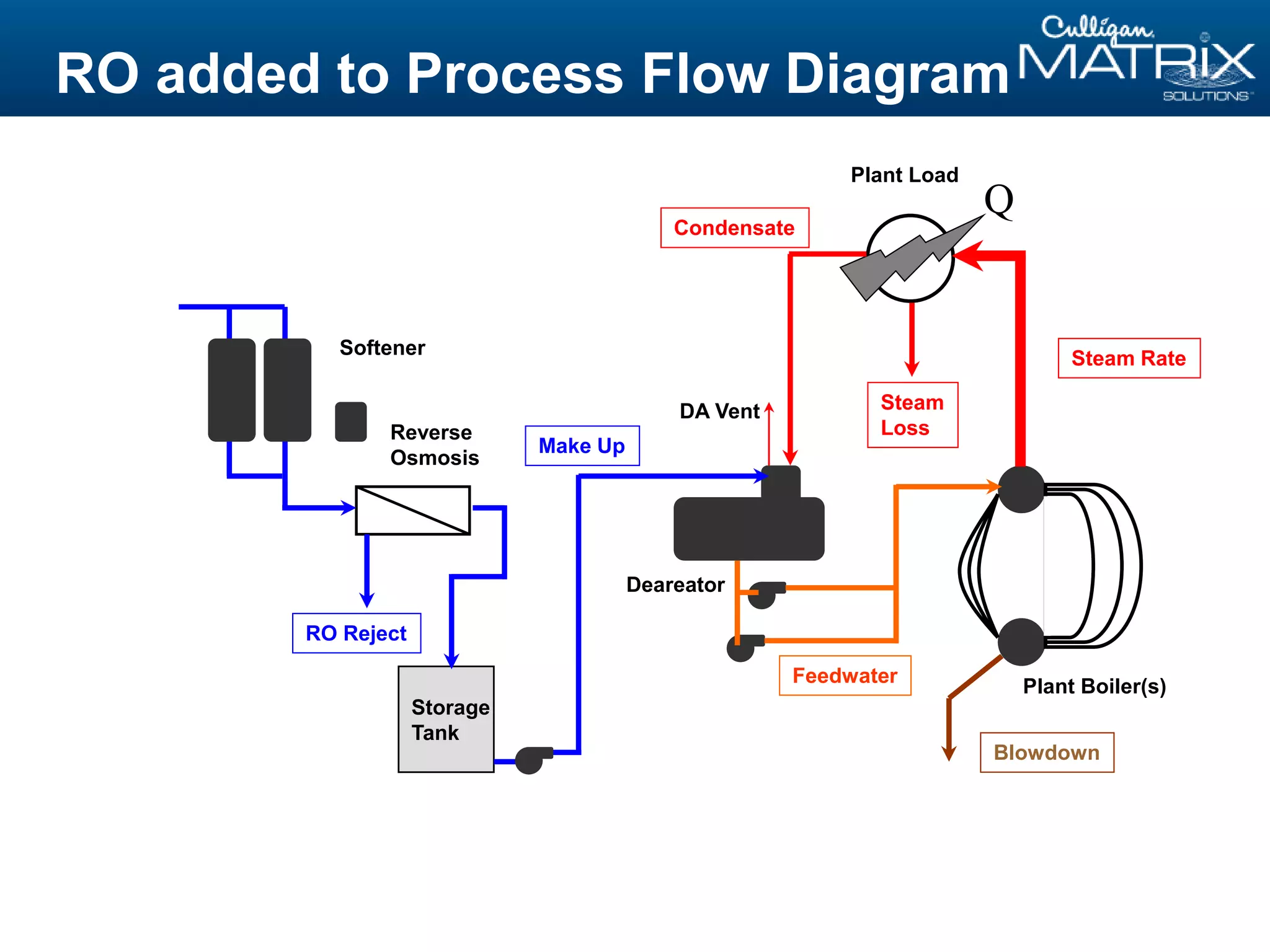
This document provides an overview of reverse osmosis (RO) basics presented by Nitin Chauhan of Culligan. It outlines the fundamentals of RO including membrane selection and system design criteria. It discusses how RO can provide energy savings, water savings, and chemical savings. A case study from the Department of Energy shows potential cost savings from using RO for boiler feedwater. The document also provides background on Culligan International, Hall's Water Group, and Culligan of Greater Cleveland.