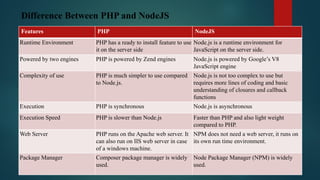
The document provides an overview of Node.js, a runtime environment for executing JavaScript code outside the browser, highlighting its advantages, such as performance, scalability, and a strong community. It also compares Node.js to PHP, emphasizing differences in execution speed, usage complexity, and functionality through various modules (path, os, and file system). Furthermore, it discusses applications that benefit from Node.js, including real-time web applications and multiplayer games.



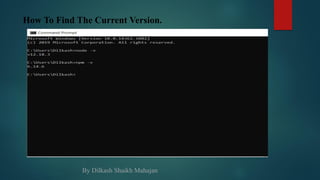




![ fs.appendFile(path, data[options], callback)
Asynchronously append data to a file, creating the file if it does not yet exist.
fs.mkdir(path[options], callback)
Asynchronously creates a directory.
fs.readFile(path[options], encoding, callback)
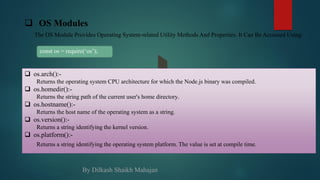
Returns the host name of the operating system as a string.
fs.rename(oldPath, newPath, callback)
Asynchronously rename file at oldPath to the pathname provided as newPath. In the case
that newPath already exists, it will be overwritten.
fs.writeFile(file, data[, options], callback)
When file is a filename, asynchronously writes data to the file, replacing the file if it already
exists. data can be a string or a buffer.
FILE SYSTEM Modules
The fs module enables interacting with the file system in a way modeled on standard POSIX functions. We are see
asynchronous way.
const fs = require(‘fs’);
By Dilkash Shaikh Mahajan](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nodejs-201127173406/85/Node-JS-Dilkash-Shaikh-Mahajan-11-320.jpg)
