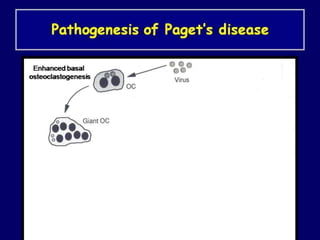
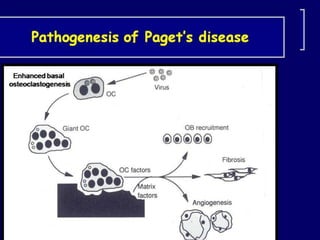
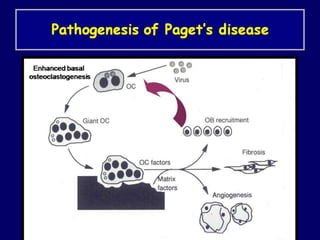
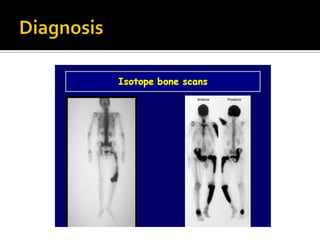
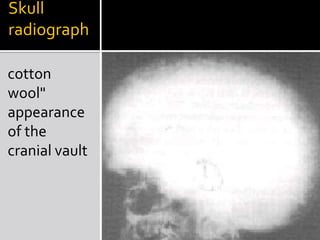
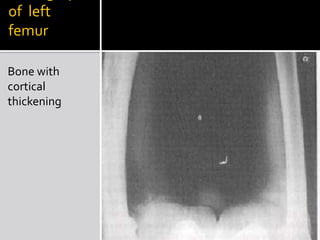
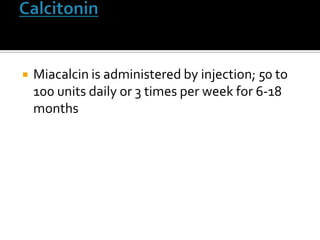
Paget's disease of bone is a chronic disorder that results in enlarged and deformed bones. It causes excessive breakdown and formation of bone tissue. Common symptoms include bone pain, headaches, hearing loss, and bone deformities. It is diagnosed through x-rays showing abnormal bone growth patterns. Treatment involves bisphosphonate drugs, calcitonin injections, surgery for joint problems or deformities, and maintaining calcium/vitamin D levels through diet and exercise. Exercise can help with mobility and reduce pain.