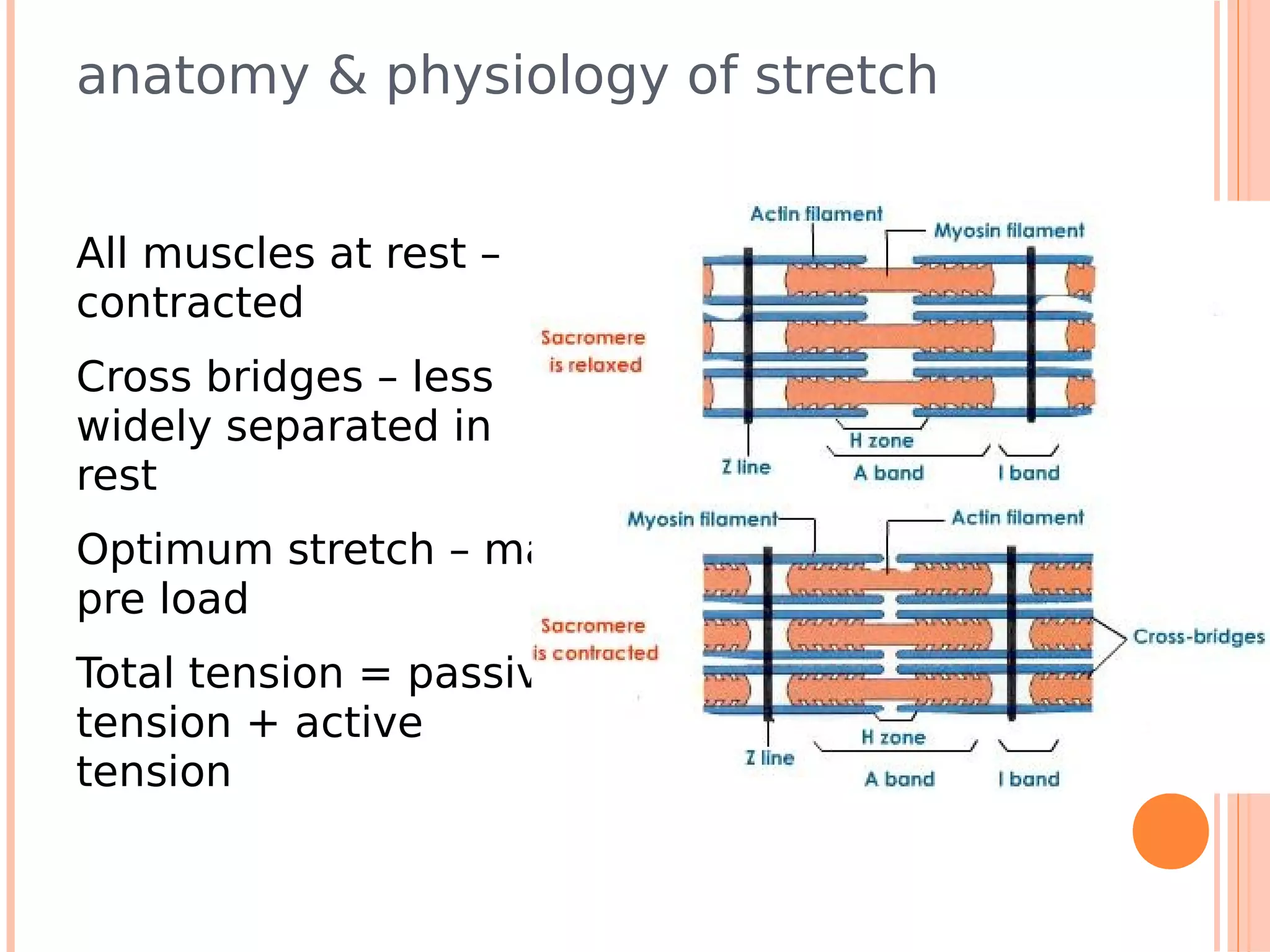
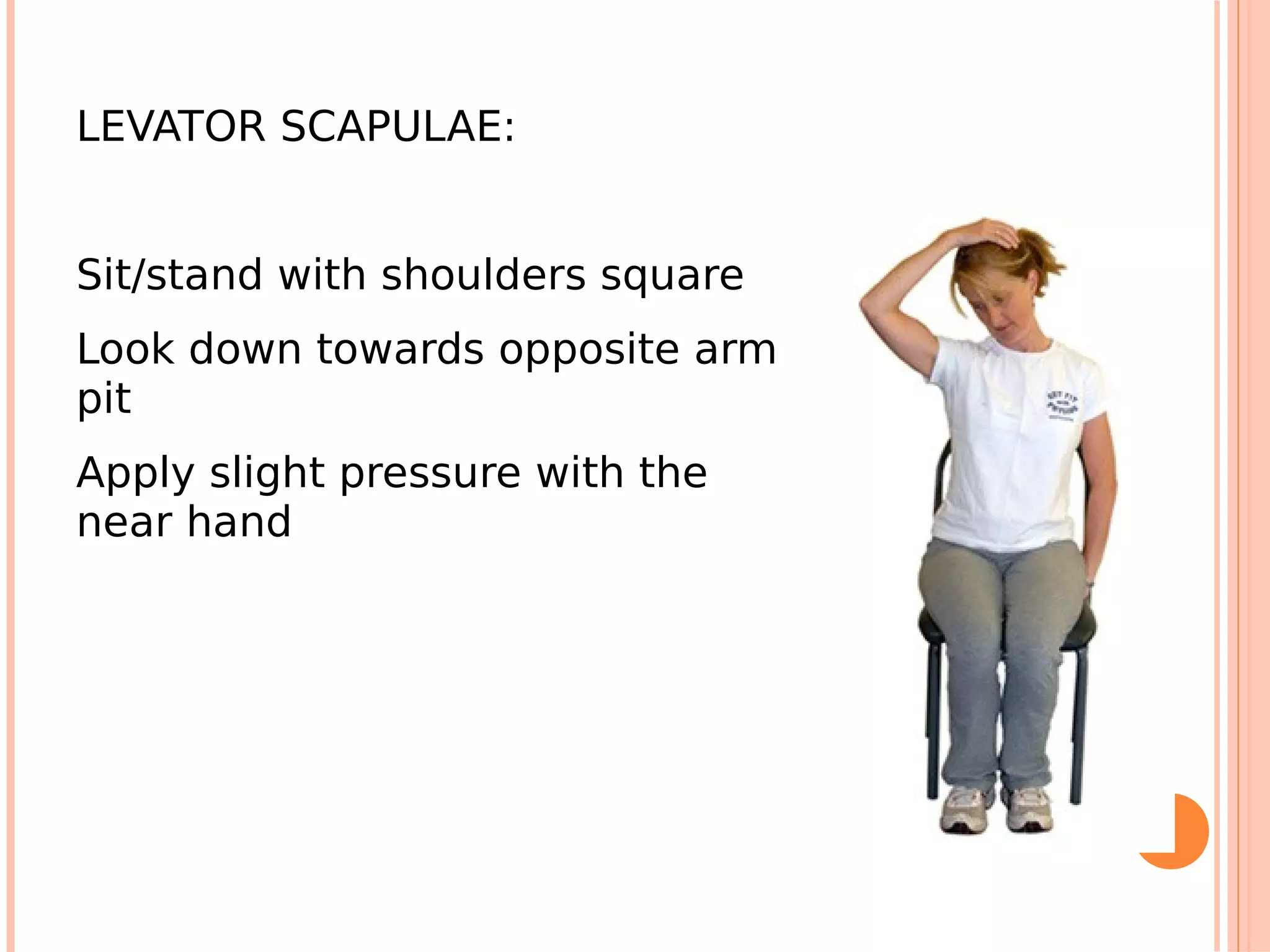
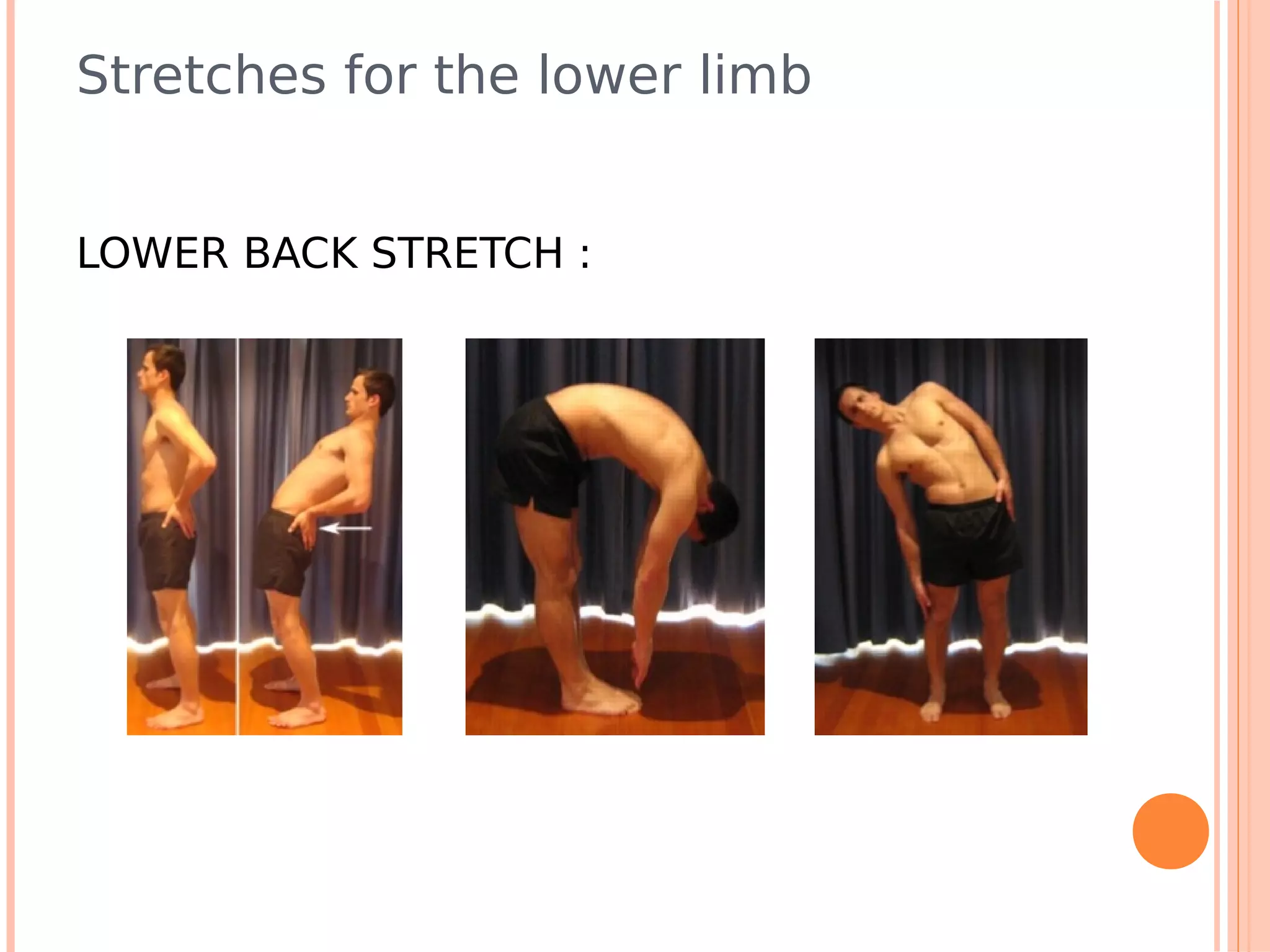
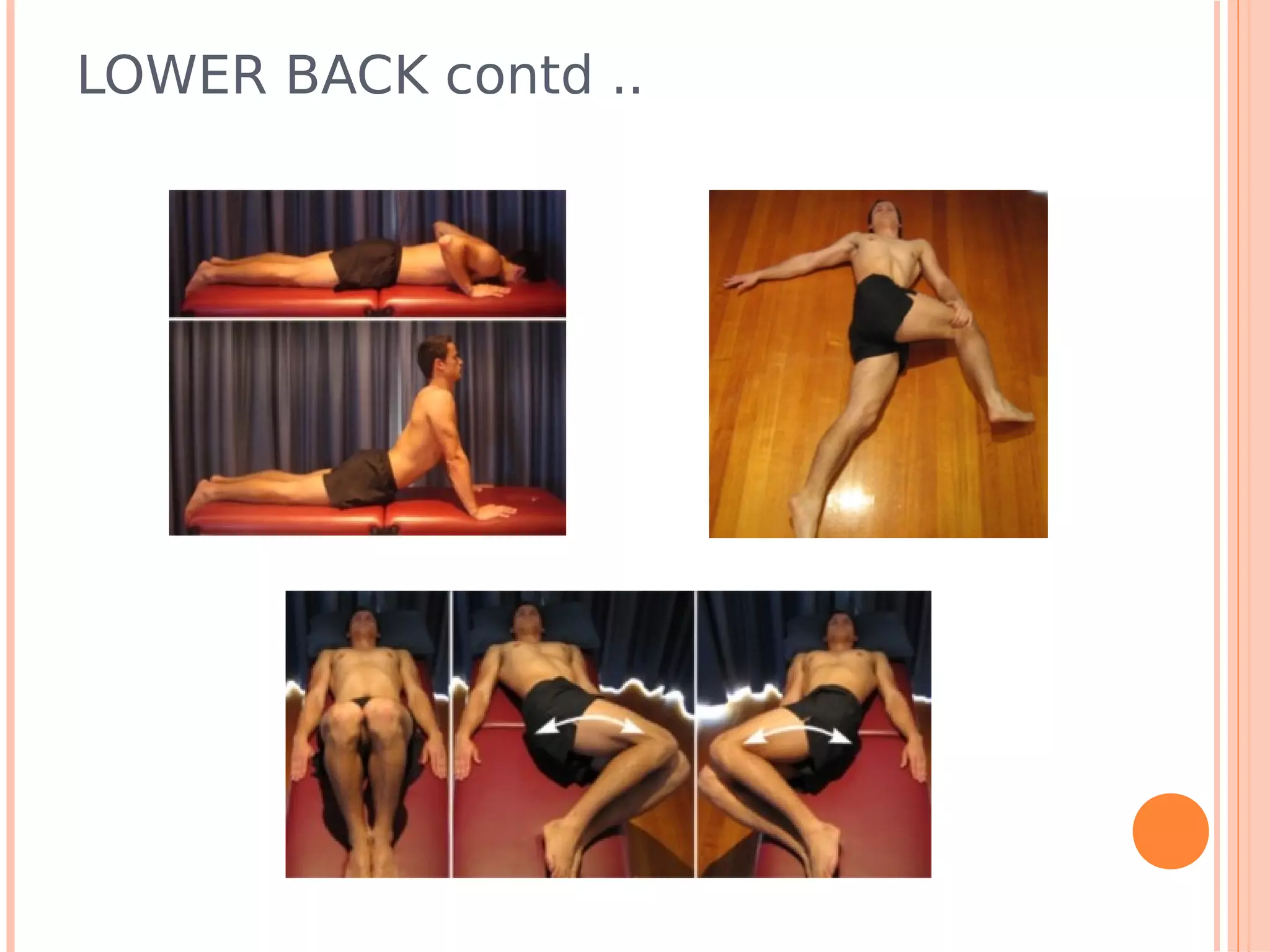
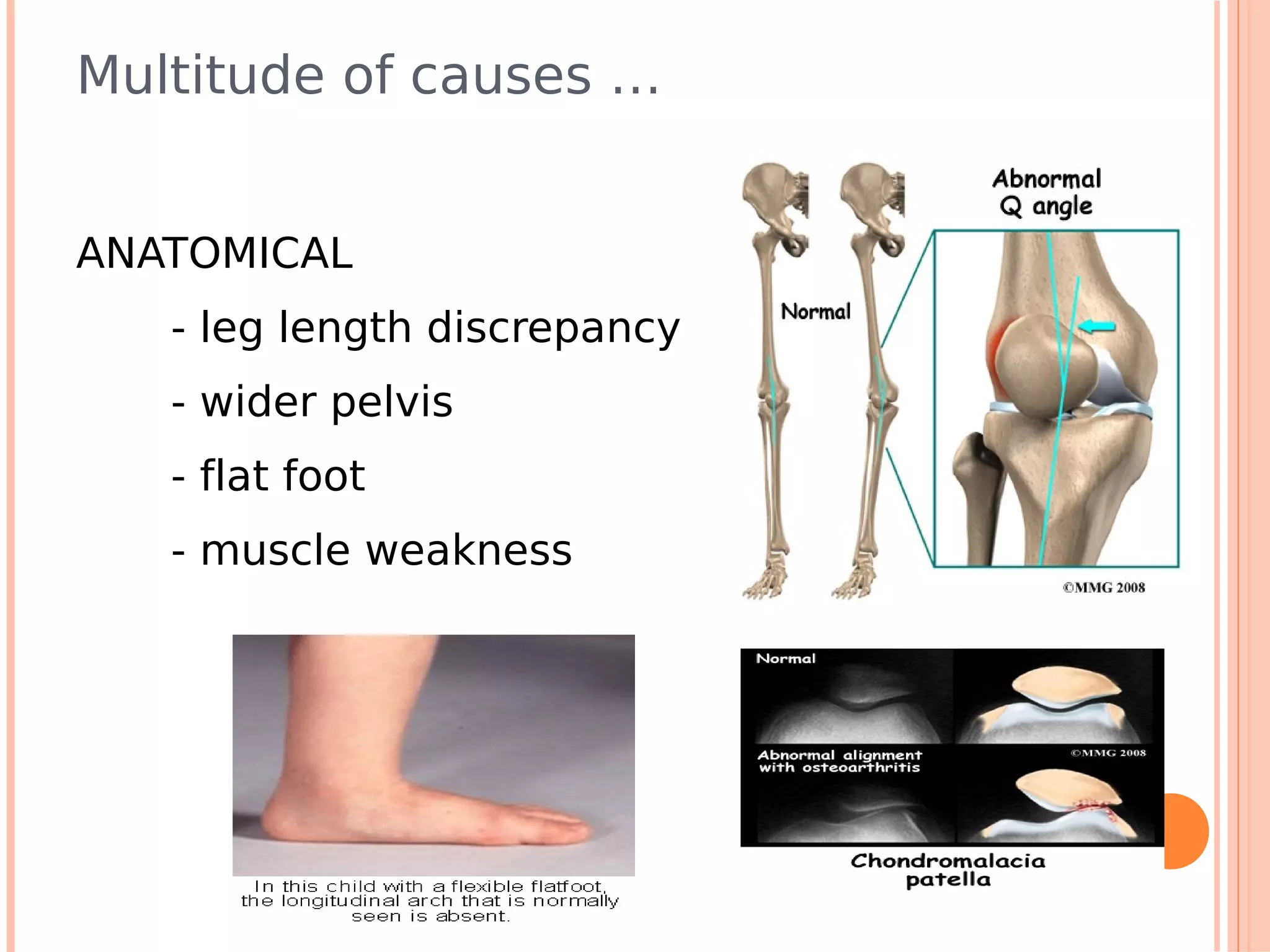
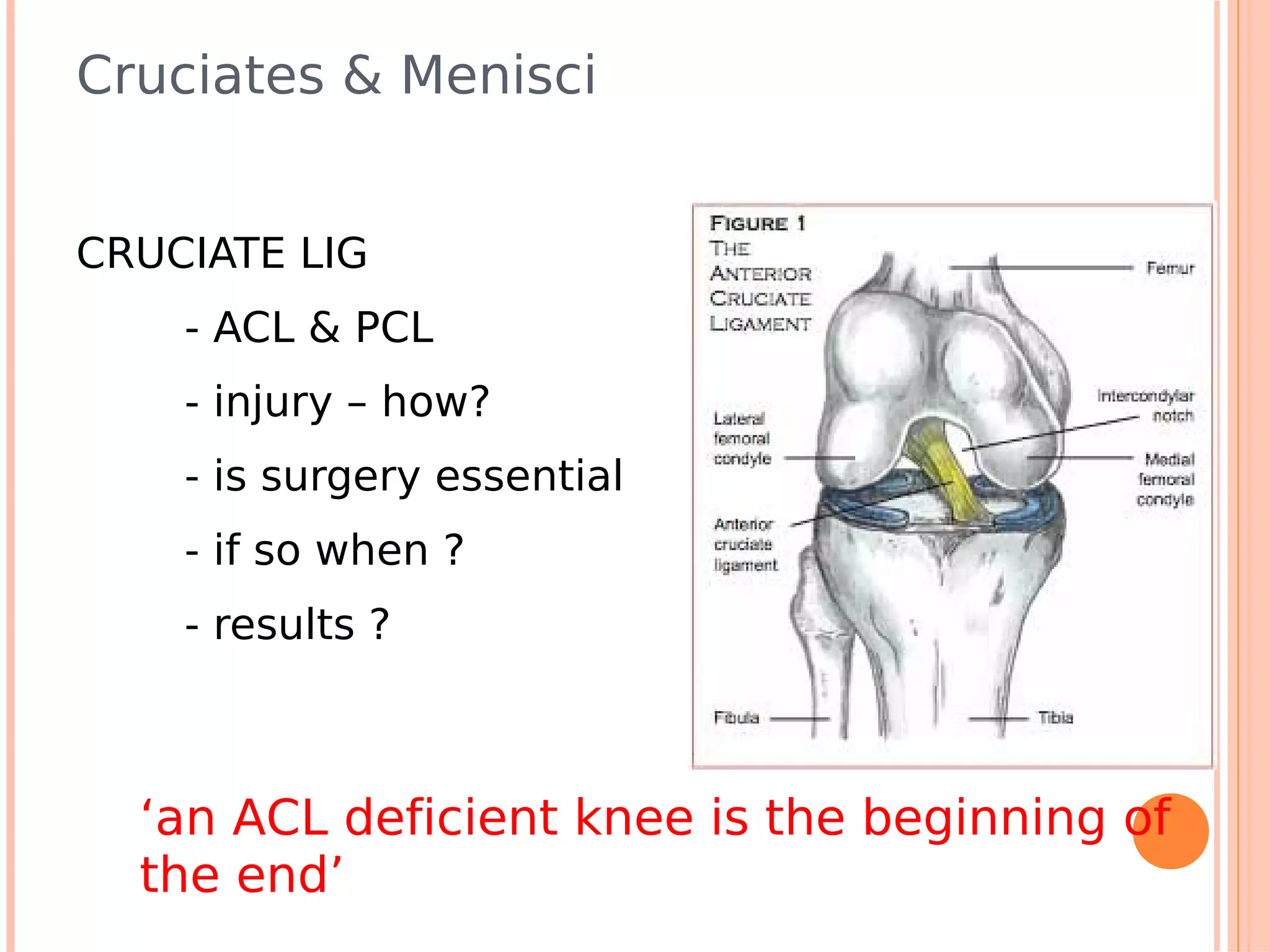
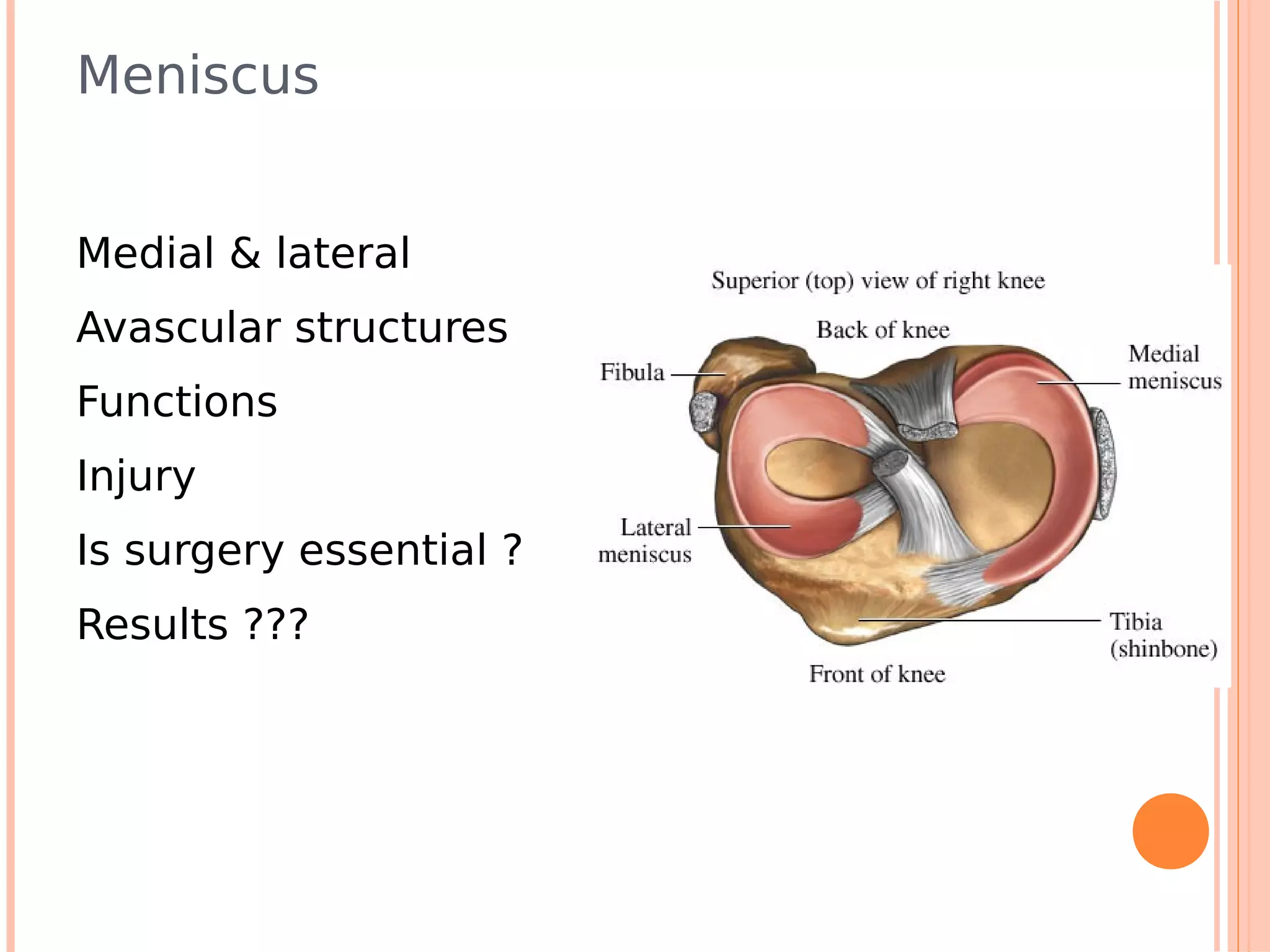
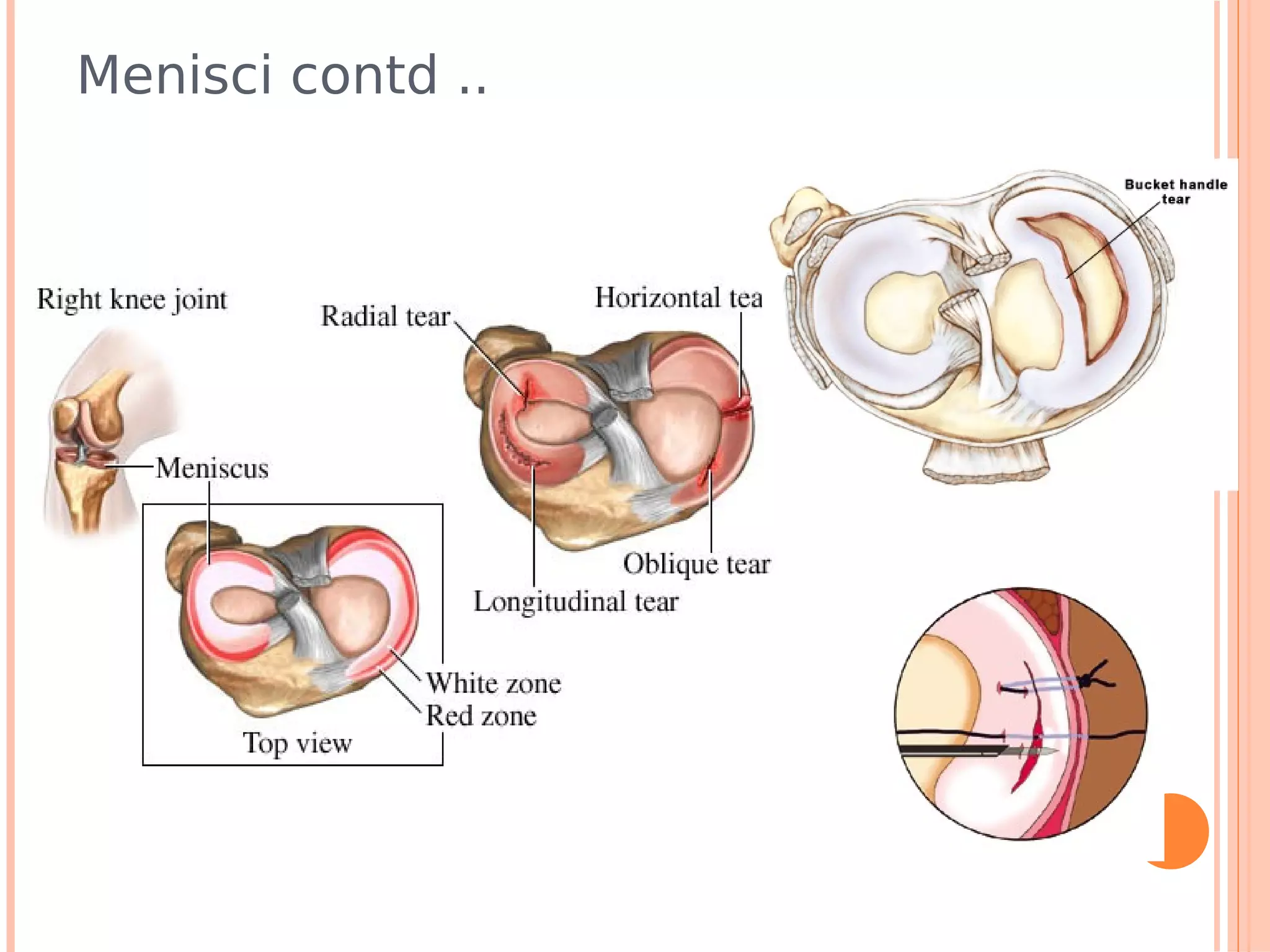
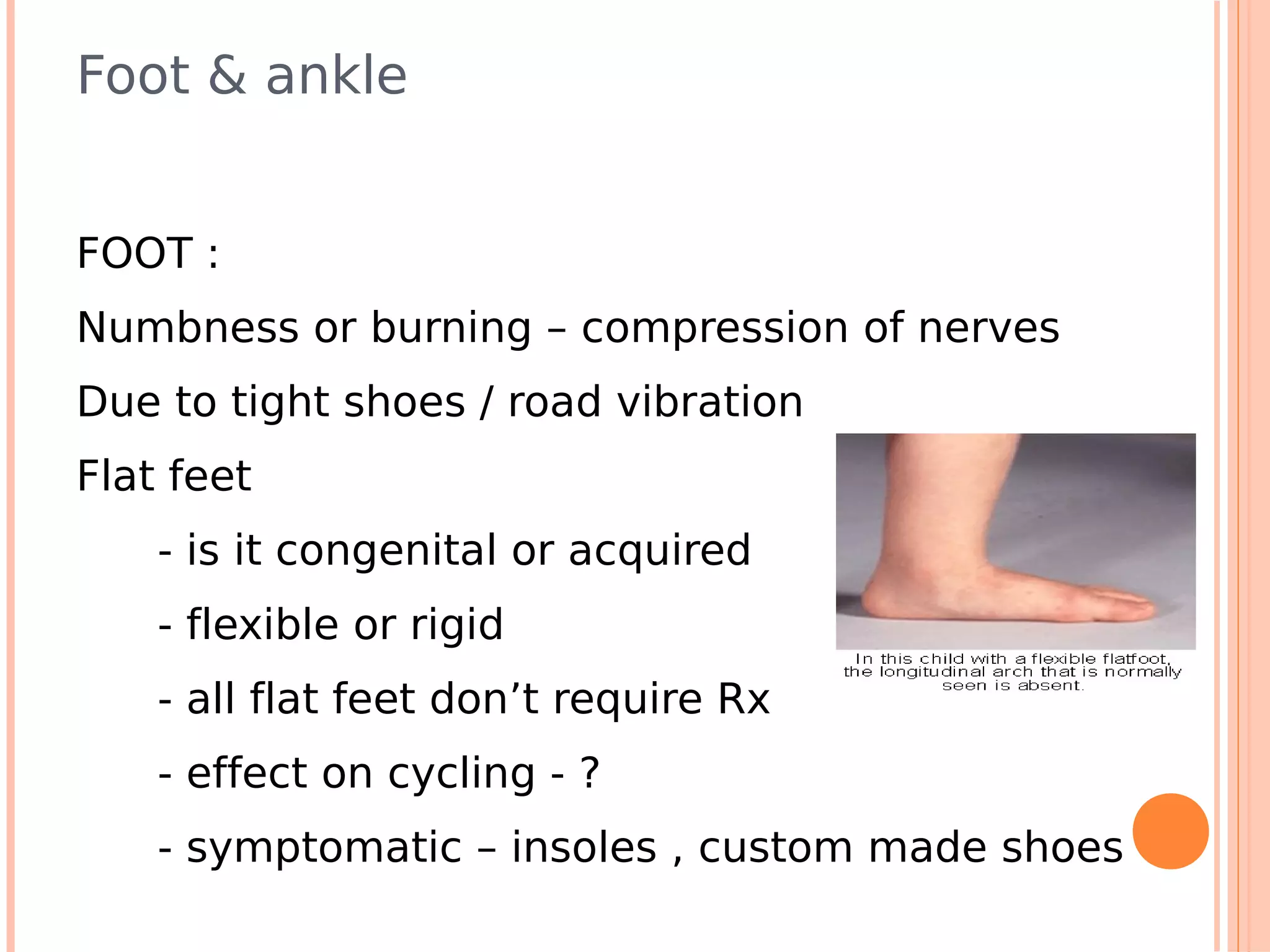
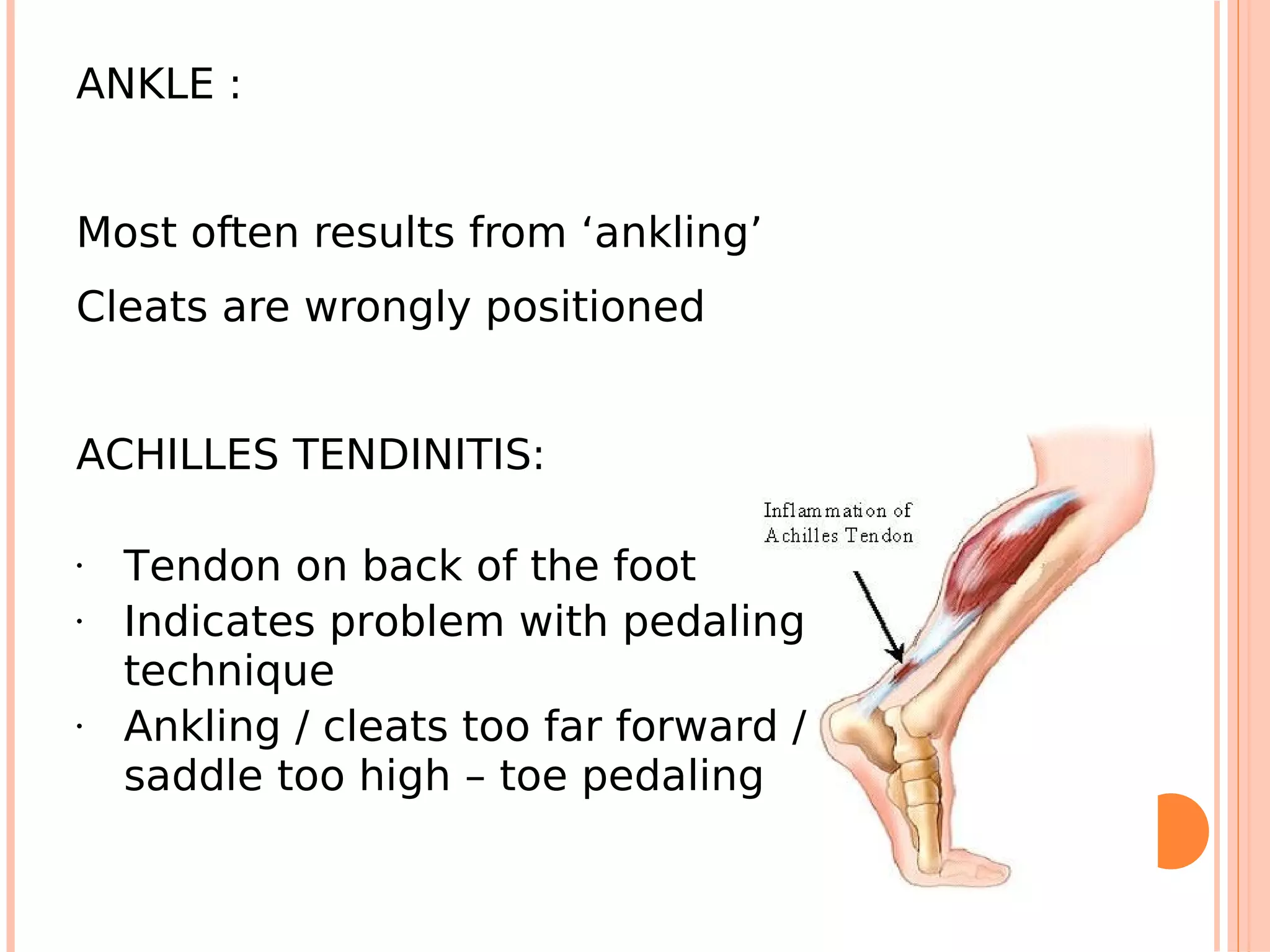
This document summarizes a workshop on sports injuries and prevention for cyclists. It discusses common cycling injuries like low back pain, knee pain, and issues with the hands, neck, and shoulders. It emphasizes the importance of proper bike fitting and stretching to prevent injuries. For injuries like knee pain, it reviews potential causes such as poor biomechanics, overuse, and medical issues. Treatment depends on the specific condition but may include exercises, braces, surgery, and physical therapy. Overall the workshop aimed to educate cyclists on injury prevention through stretching, correct bike fitting, and addressing underlying biomechanical faults or medical problems.