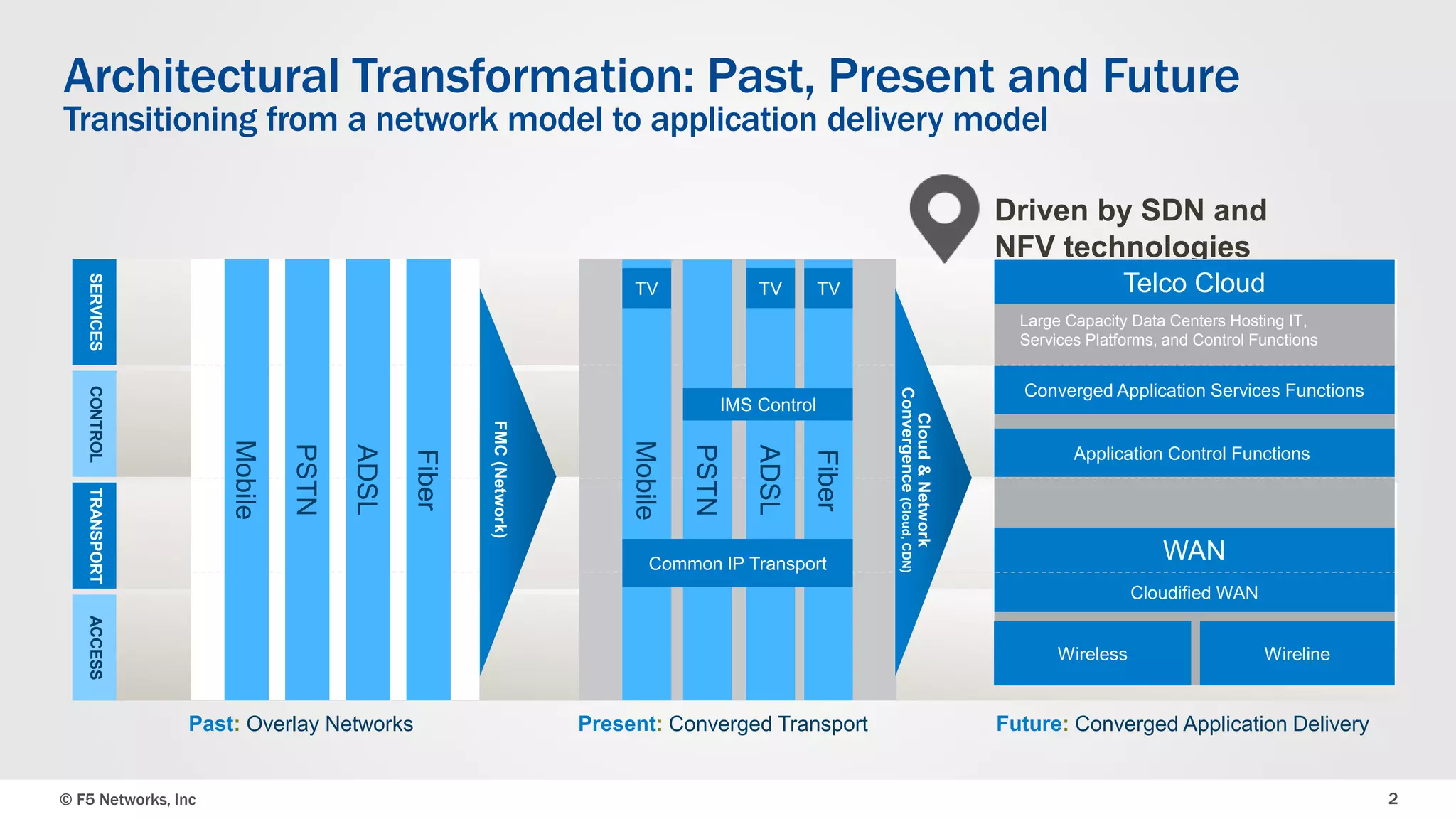
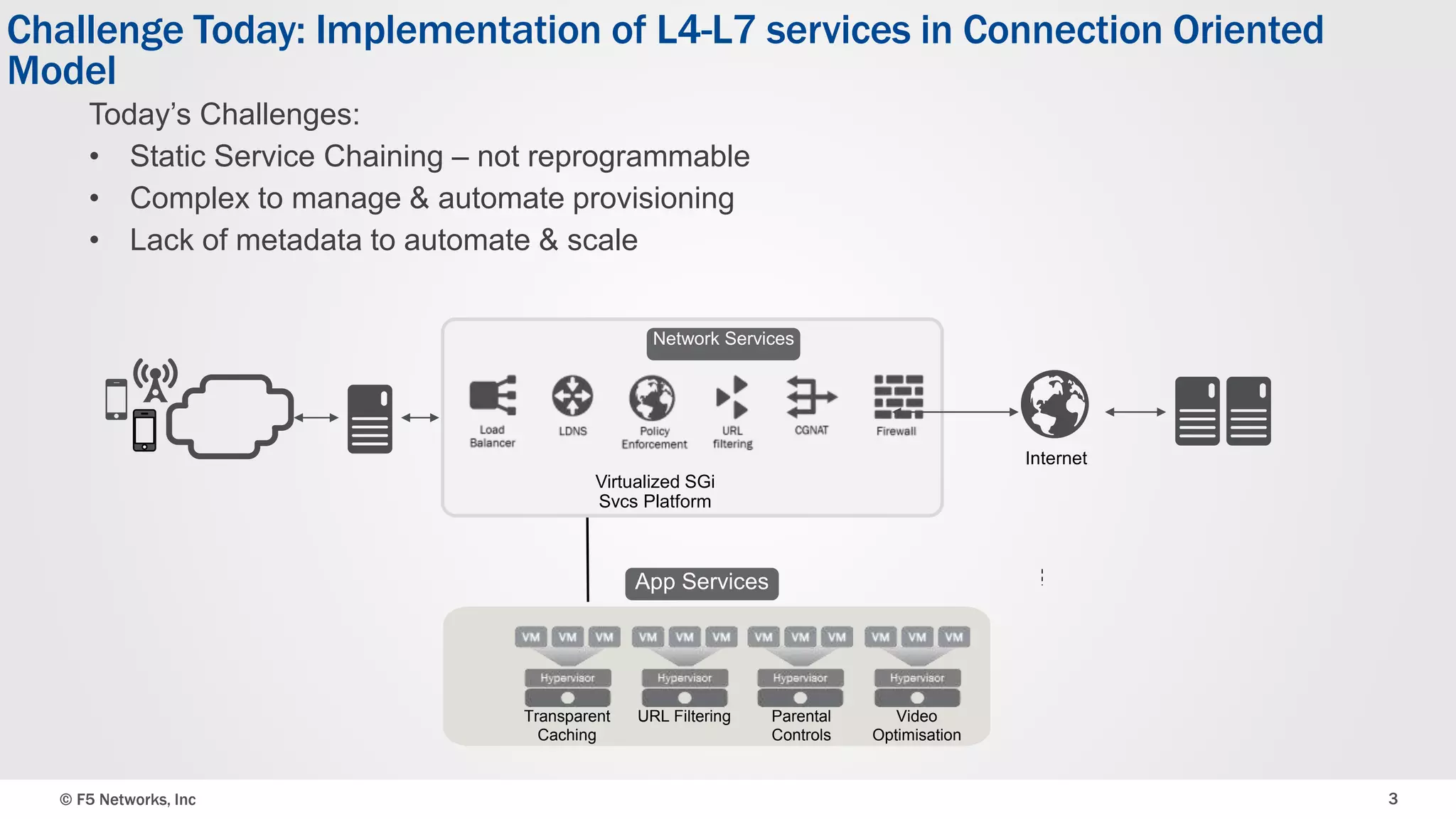
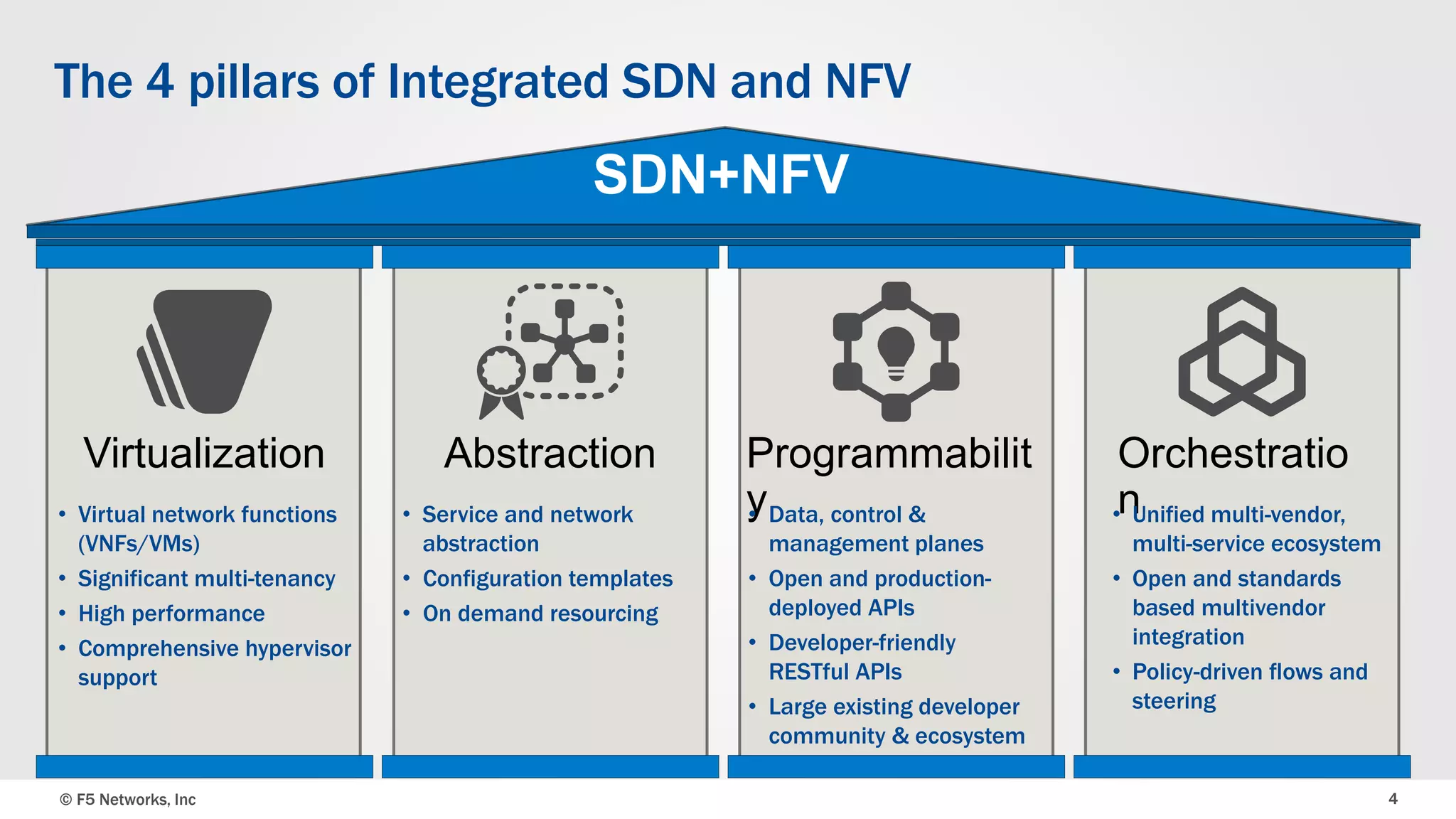
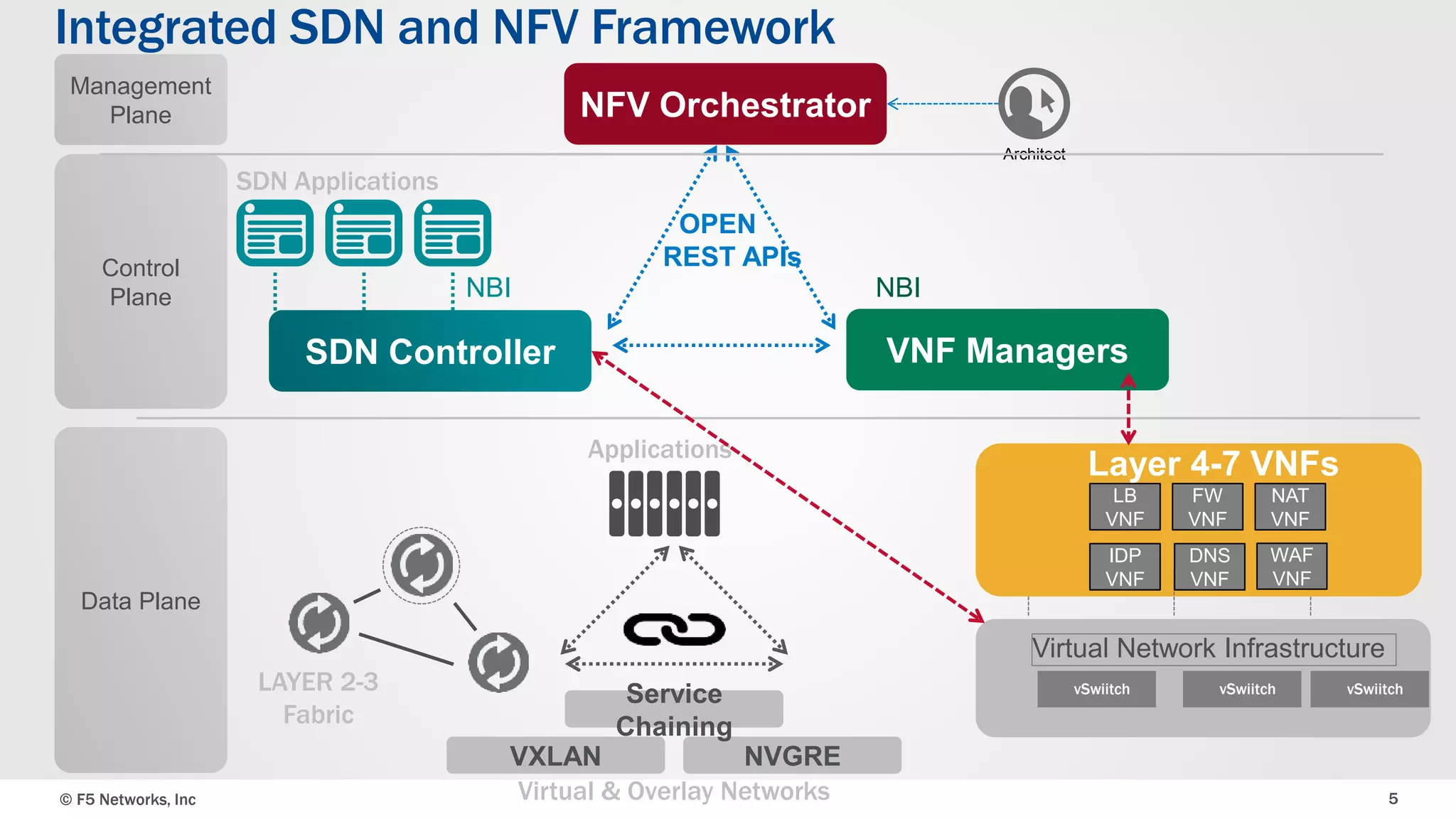
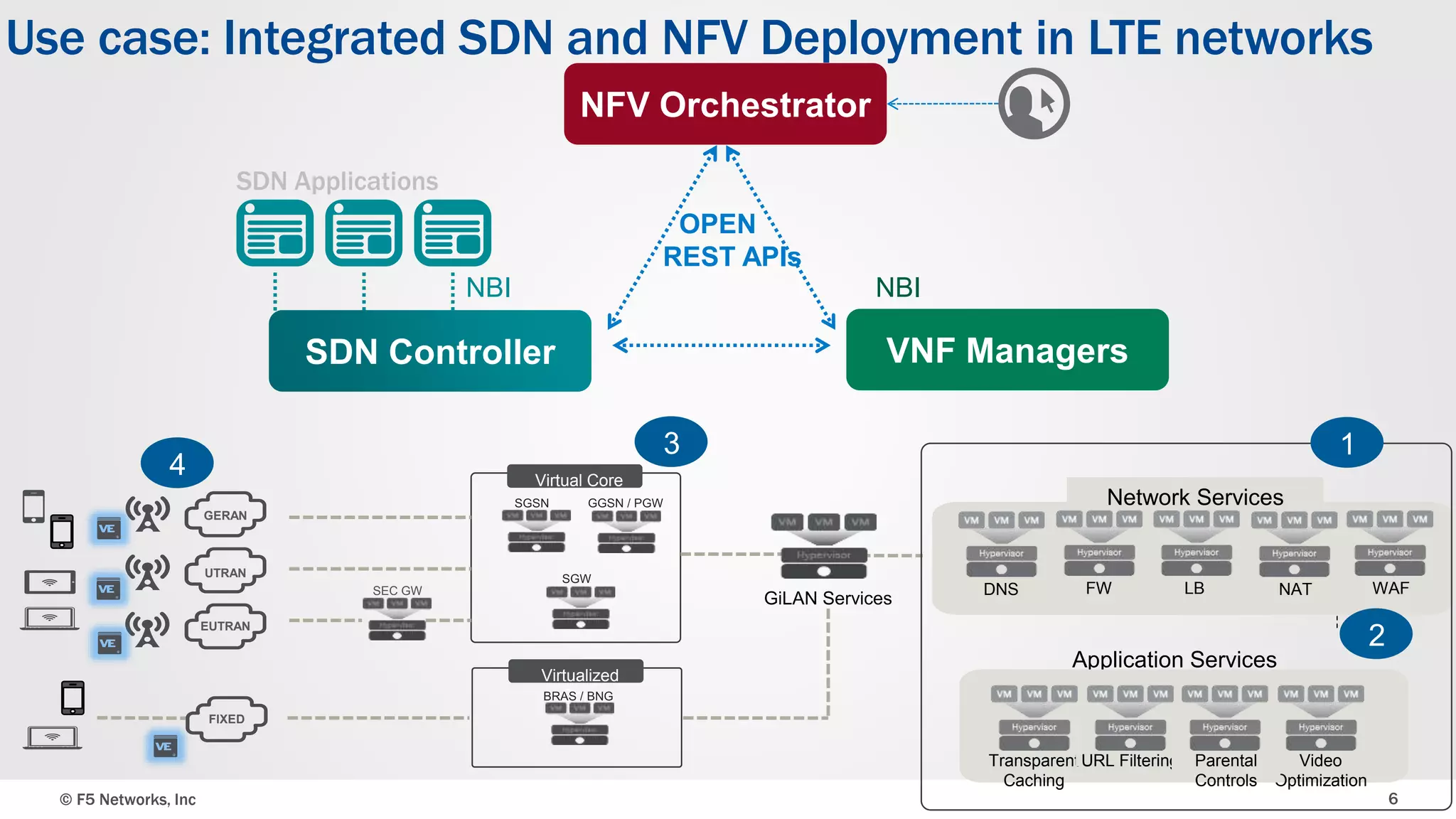
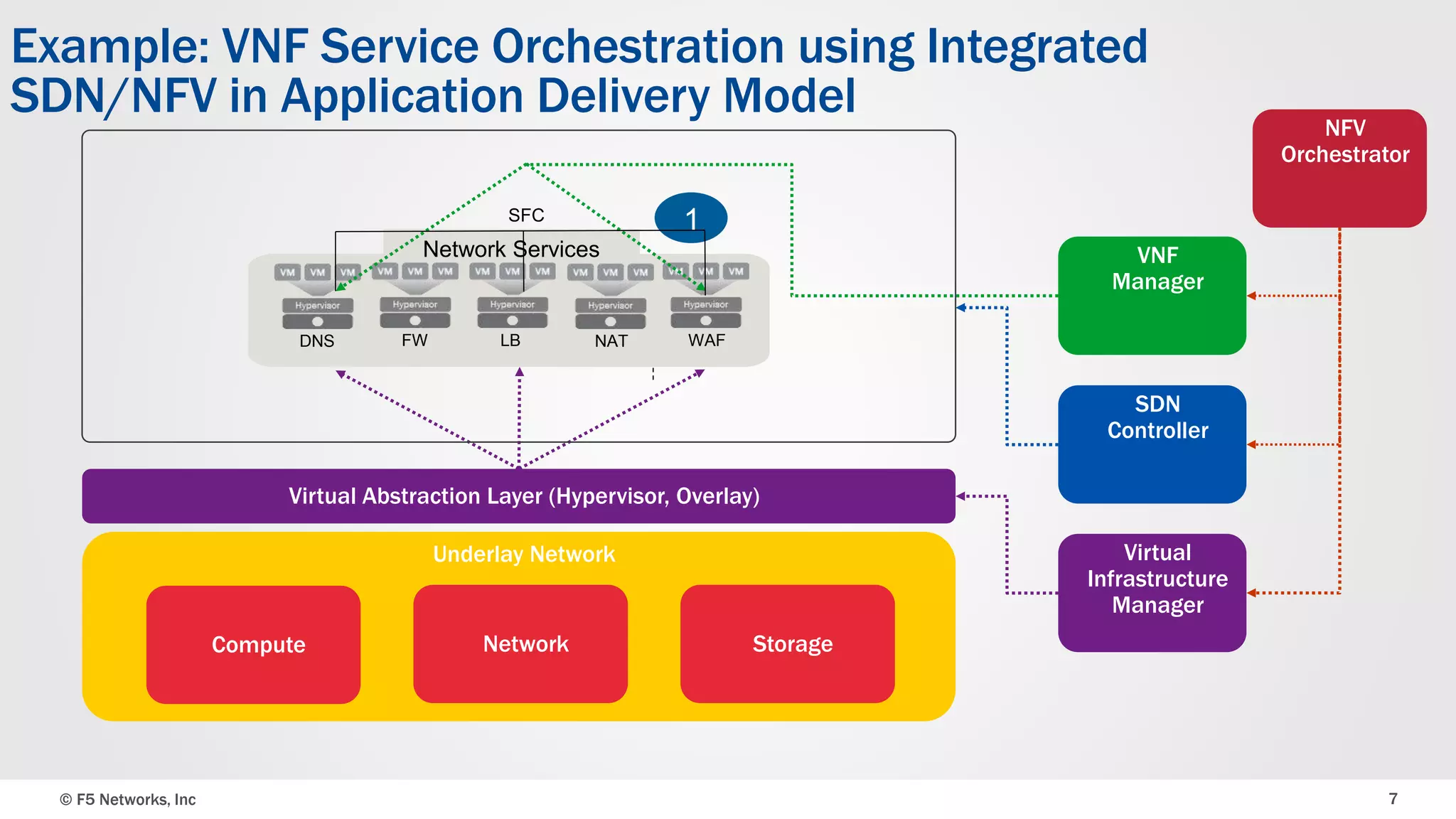
The document discusses an integrated SDN/NFV framework aimed at transforming network models to application delivery models leveraging SDN and NFV technologies. It highlights the challenges faced in implementing Layer 4-7 services, including static service chaining, complex management, and the absence of automation. The framework emphasizes virtualization, abstraction, programmability, and orchestration to facilitate a unified, multi-vendor ecosystem for enhanced application delivery.