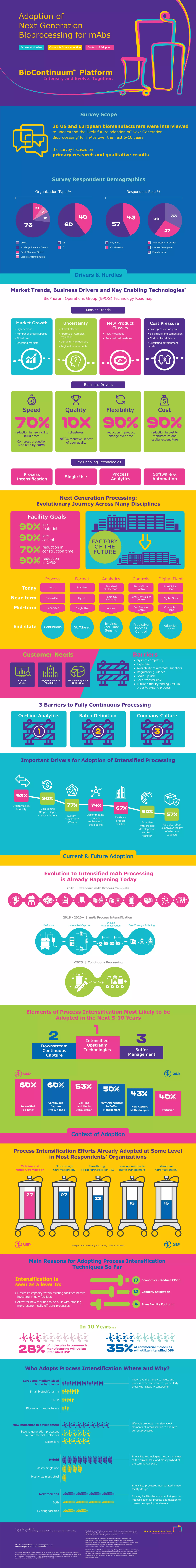
The document discusses the evolution and adoption of next-generation bioprocessing for monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) through the Biocontinuum platform, highlighting drivers and barriers to process intensification. Key benefits include reduced costs, facility footprint, and enhanced processing capabilities, while challenges include system complexity and regulatory guidance. Future trends point to significant adoption of intensified processing technologies within the next 5-10 years as the biopharmaceutical landscape evolves.