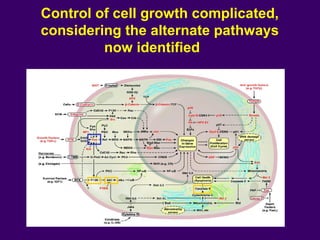
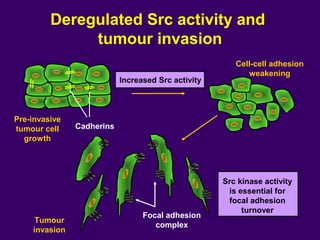
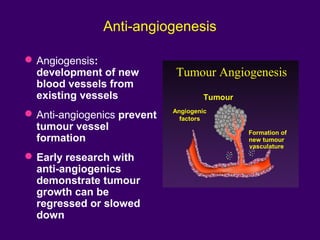
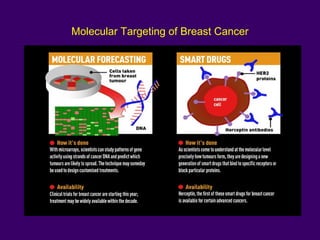
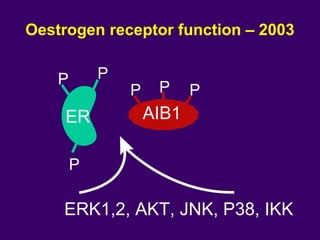
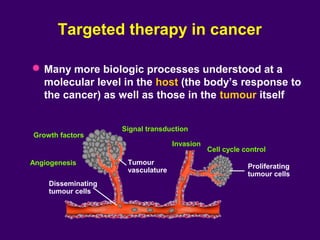
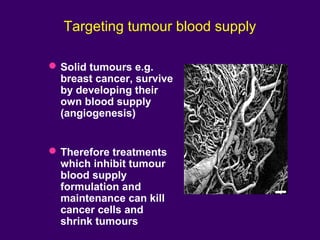
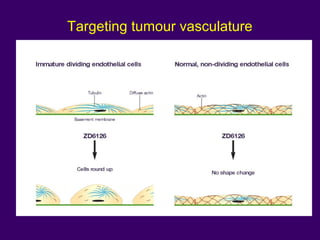
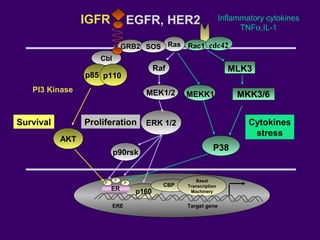
The document discusses several approaches for controlling cell growth and tumor progression, including targeting key molecular pathways, blocking angiogenesis through anti-angiogenic therapies, and using gene therapy to supply healthy genes. It also outlines how increased understanding of biological processes in tumors and the body's response has enabled molecular targeting of specific proteins and pathways involved in tumor growth, invasion, and metastasis. Promising targets mentioned include EGFR, angiogenesis factors, and the tumor vasculature.