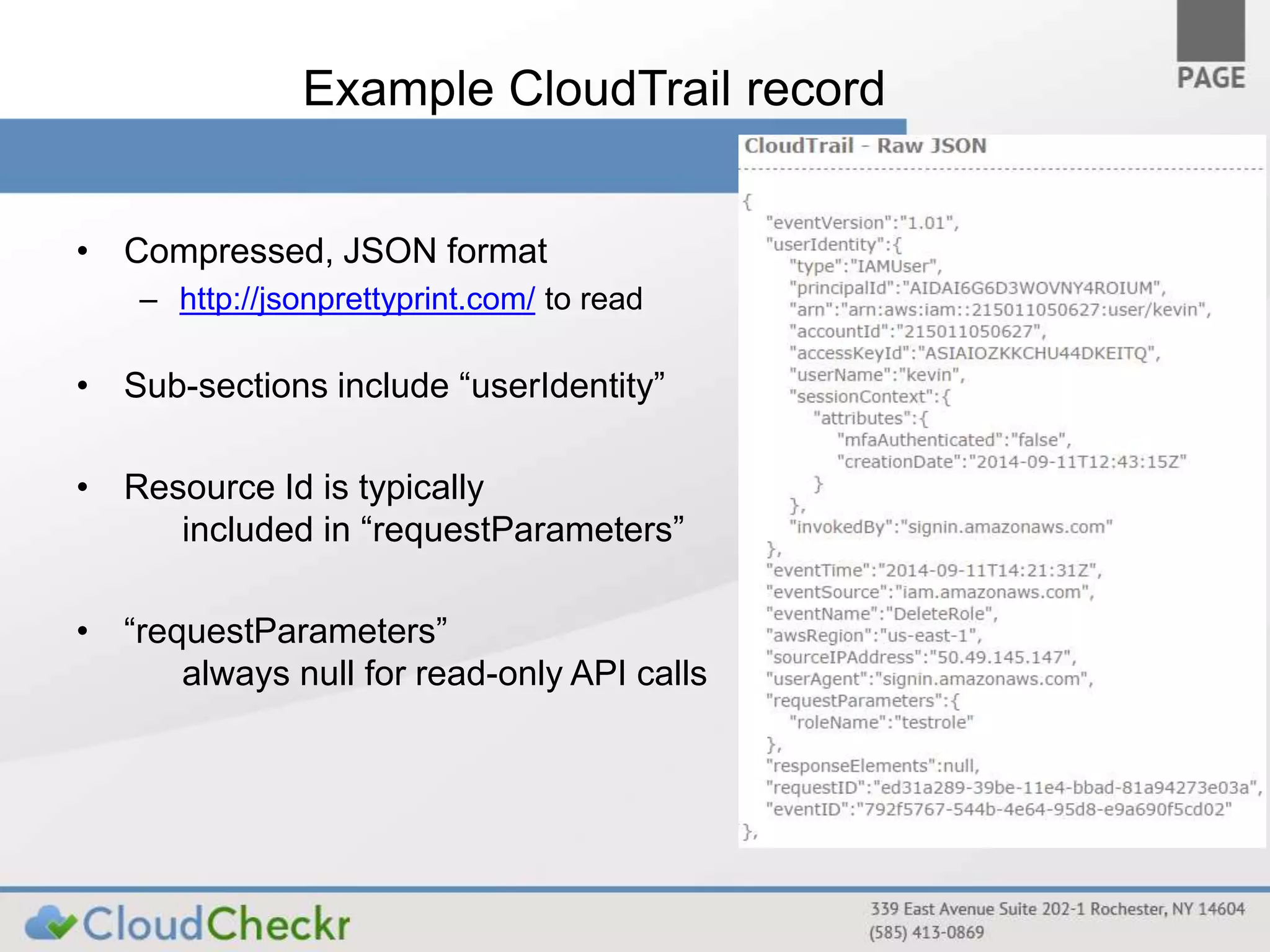
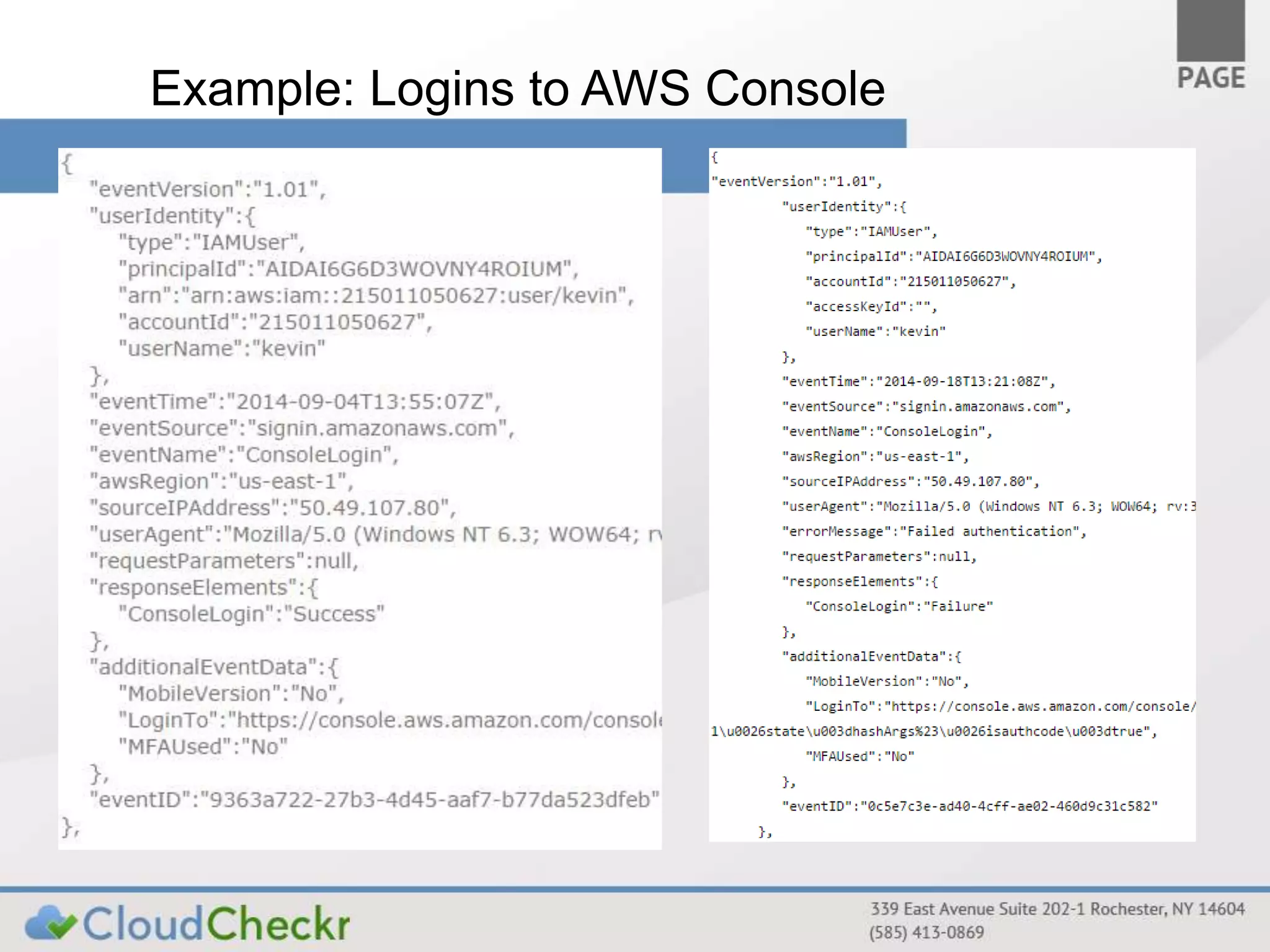
CloudTrail is an AWS service that records API calls across various AWS services, storing logs in JSON format in S3 buckets for near real-time monitoring of user and administrator activities. It does not replace logging at other layers and is primarily for tracking who performed what actions without detailed event explanations. Proper configuration and management of CloudTrail are essential for enhancing security and compliance, and recommendations include enabling it across all regions and considering best practices for log accessibility and tamper resistance.