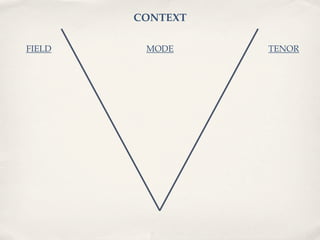
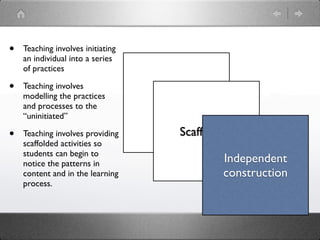
The document discusses various strategies and approaches for effectively teaching literacy skills to refugees and students, including scaffolding instruction, modeling practices, and developing metacognition through reflective thinking exercises. It also outlines different tutoring types, the context framework for understanding communications, and a teaching and learning cycle for developing literacy and language skills.











































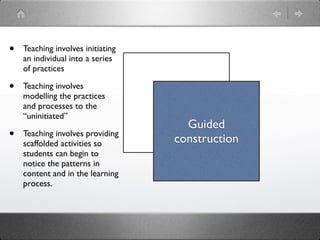

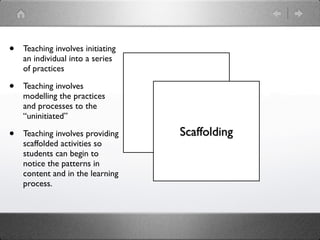
![The [student] as a novice is continually attempting to make sense of
new situations and to acquire the skills necessary to function in those
situations. The teacher’s role is to help the [student] by arranging tasks
and activities in such a way that they are easily accessible.
Intersubjectivity, shared understanding based on common area of
focus is seen by adherents of literacy engagement as a crucial
prerequisite for successful communication between teacher and
[student] (Verhoeven and Snow, 2001, pp. 5).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/newraslecture-120320032707-phpapp01/85/New-ras-lecture-48-320.jpg)