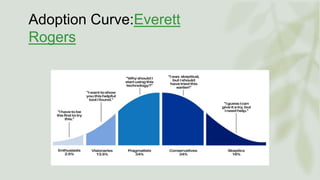
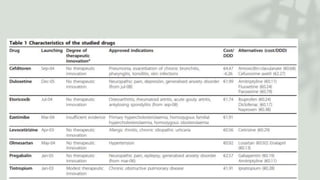
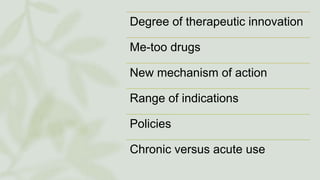
The document discusses the process by which doctors adopt new drugs, including the five stages of awareness, interest, evaluation, trial, and adoption. It describes different adopter categories from innovators to laggards and notes individuals differ in openness to new products. The rate of adoption for new drugs increases quickly at first then plateaus over time, and varies between family physicians and specialists. Characteristics like relative advantage and compatibility influence adoption rates.