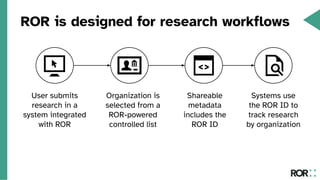
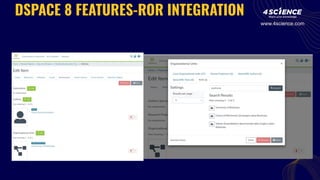
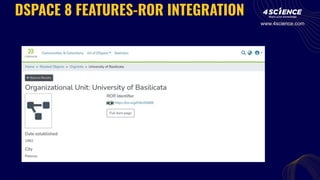
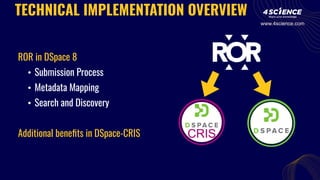
The document discusses the integration of the Research Organization Registry (ROR) into DSpace 8, enhancing metadata management for research organizations. Key benefits include improved data quality, discoverability, and interoperability, facilitating better connections between research outputs and their associated institutions. ROR is a sustainable, noncommercial initiative designed to streamline metadata exchange and support open science principles.