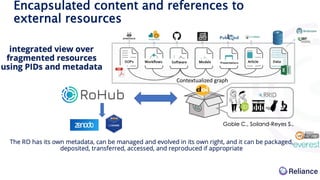
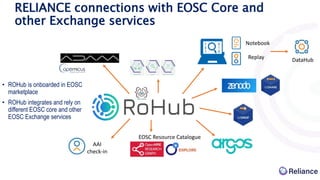
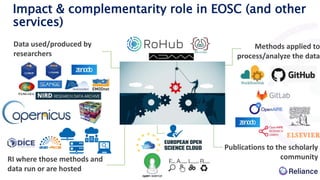
This document discusses Research Object Management Platform (ROHub) and how it supports open science through research lifecycle management in the European Open Science Cloud (EOSC). ROHub enables scientists to create and manage Research Objects (ROs) that encapsulate research outputs, data, code, and other materials, making research fully accessible, interoperable, reusable, and reproducible. It integrates with various EOSC services to allow users to publish and share ROs, access computing resources, and collaborate with other researchers. ROHub aims to facilitate open science practices across disciplines by providing tools for the entire research lifecycle from discovery to publication.




![Research outcomes and related resources
Each object has its own metadata and repositories
All are first class citizens and are required to make research FAIR
[source RO-Crate: A framework for packaging research products into
FAIR Research Objects]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rohub-general-final-240202083535-0b186117/85/RO-crate-FDO-ROHub-5-320.jpg)