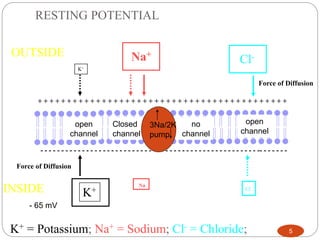
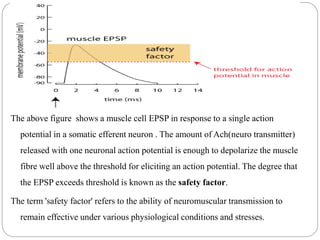
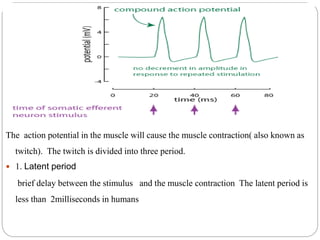
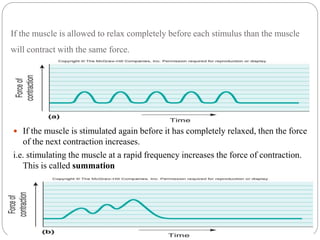
This document discusses neuron and muscle potentials. It begins by introducing muscles and neurons, explaining that muscles contract to produce movement while neurons transmit electrical and chemical signals. It then describes how neuron potentials arise from the electrochemical activity of neurons and the resting potential difference across the neuron membrane. When a neuron is stimulated, this polarity is reversed, generating an action potential. A similar process occurs in muscles - the action potential travels to the neuromuscular junction and causes the release of acetylcholine, generating a muscle action potential and contraction.