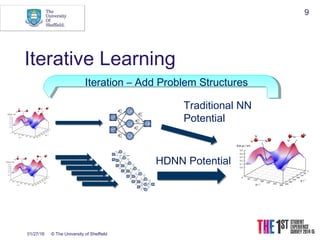
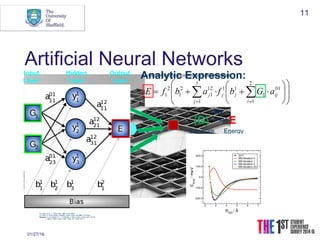
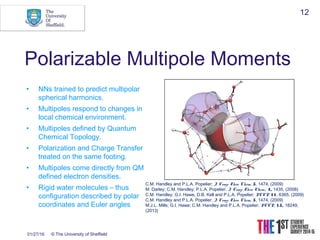
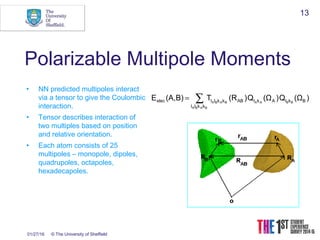
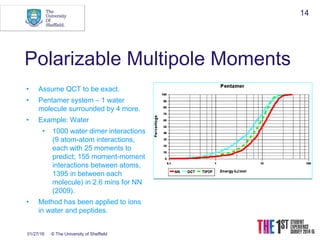
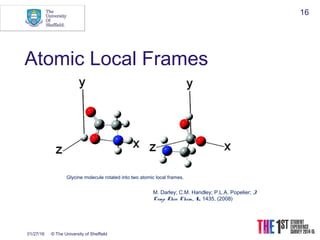
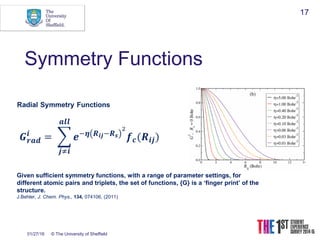
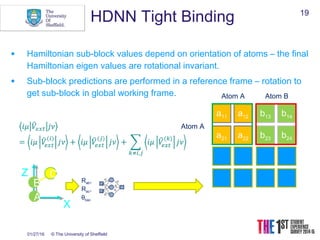
This document discusses using neural networks to represent potential energy surfaces for chemical simulations. It begins by introducing machine learning and how neural networks can be used for functional form discovery and interpolation. It then discusses limitations of traditional computational chemistry methods and force fields. Neural networks are presented as a way to achieve ab initio accuracy at a lower computational cost by training networks on ab initio data. The document outlines different types of neural networks that have been applied for this purpose, including those representing multipole moments and high dimensional neural networks invariant to translations and rotations. It concludes by discussing future directions, such as networks that better retain quantum information and more powerful machine learning methods.