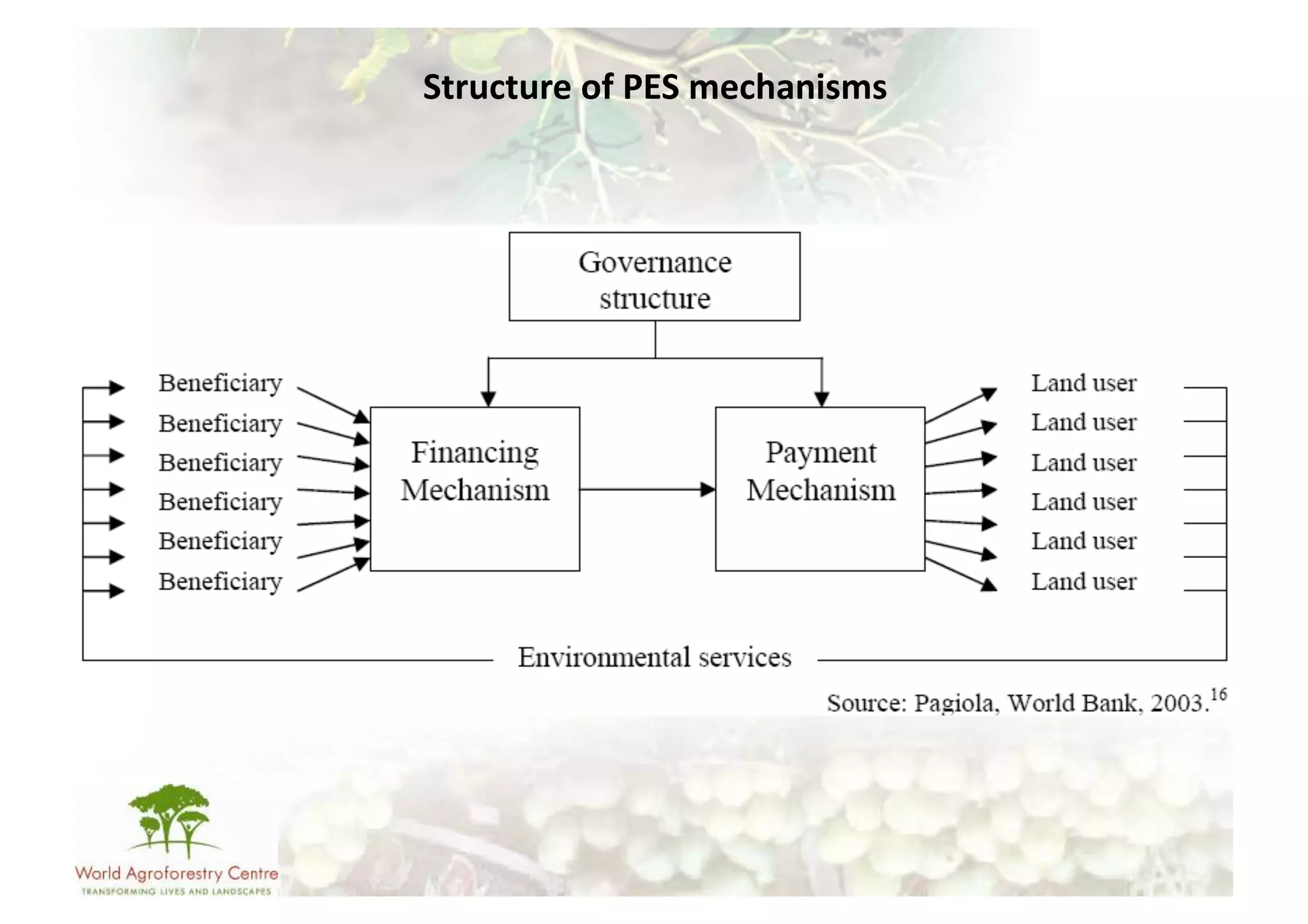
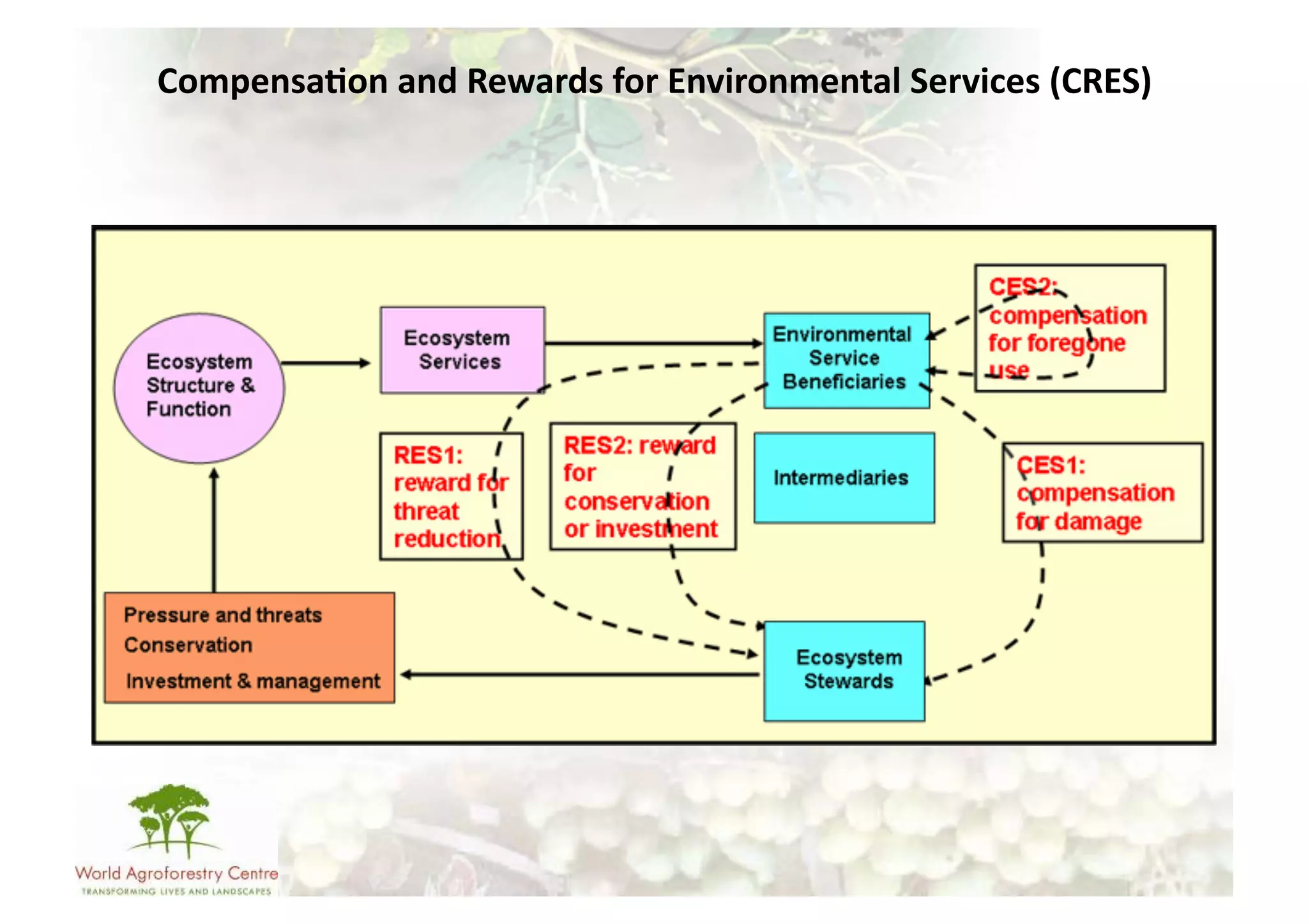
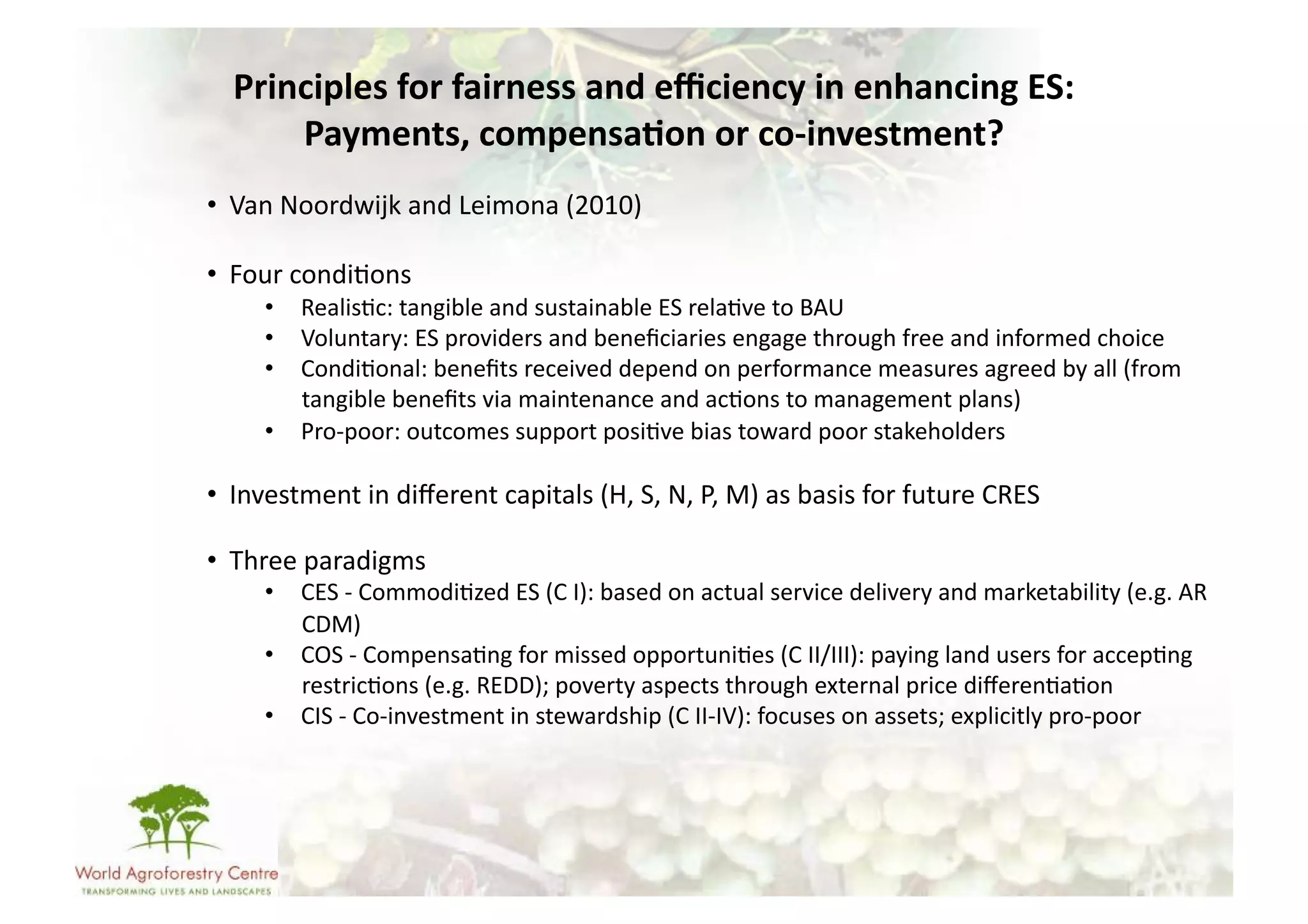
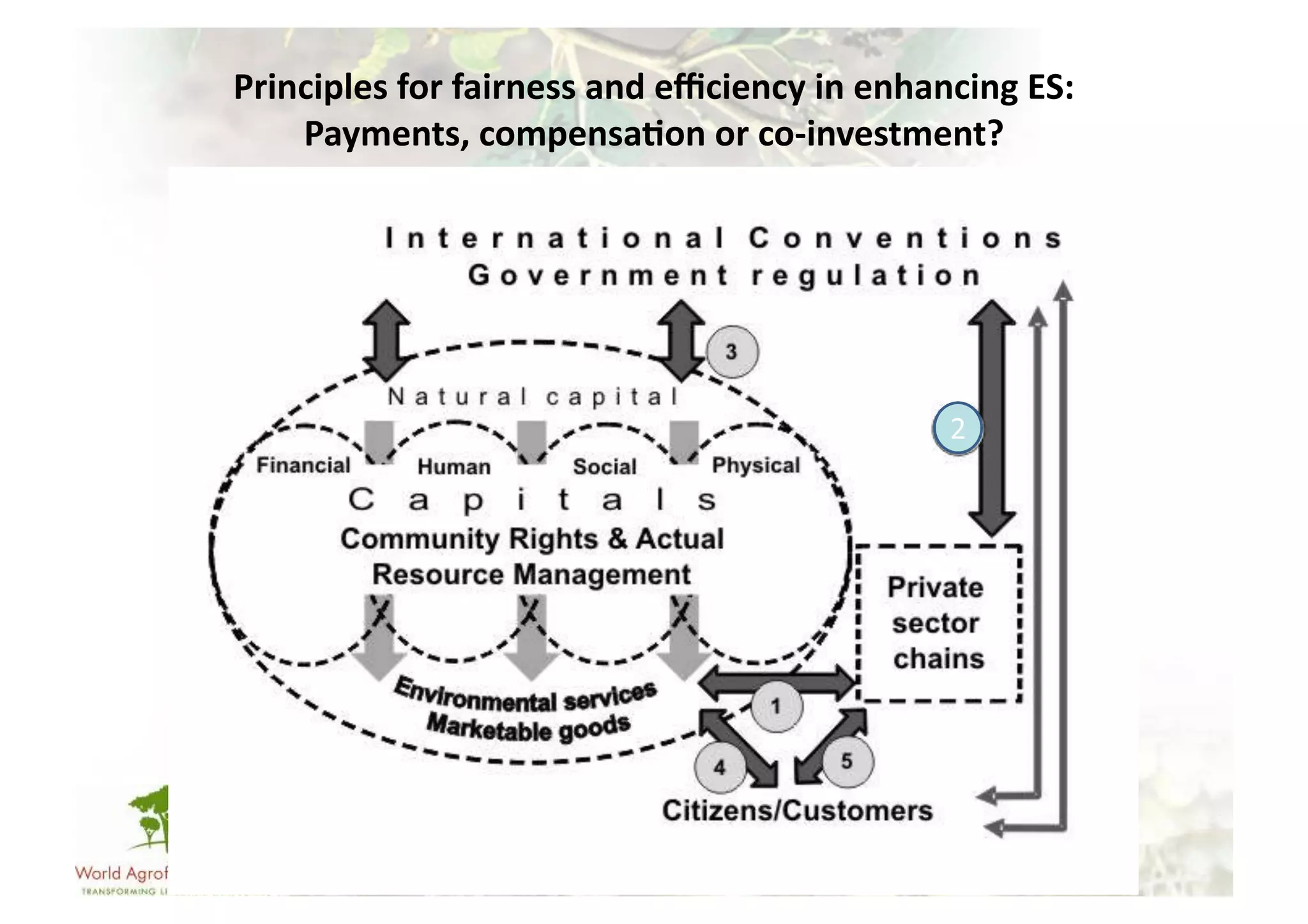
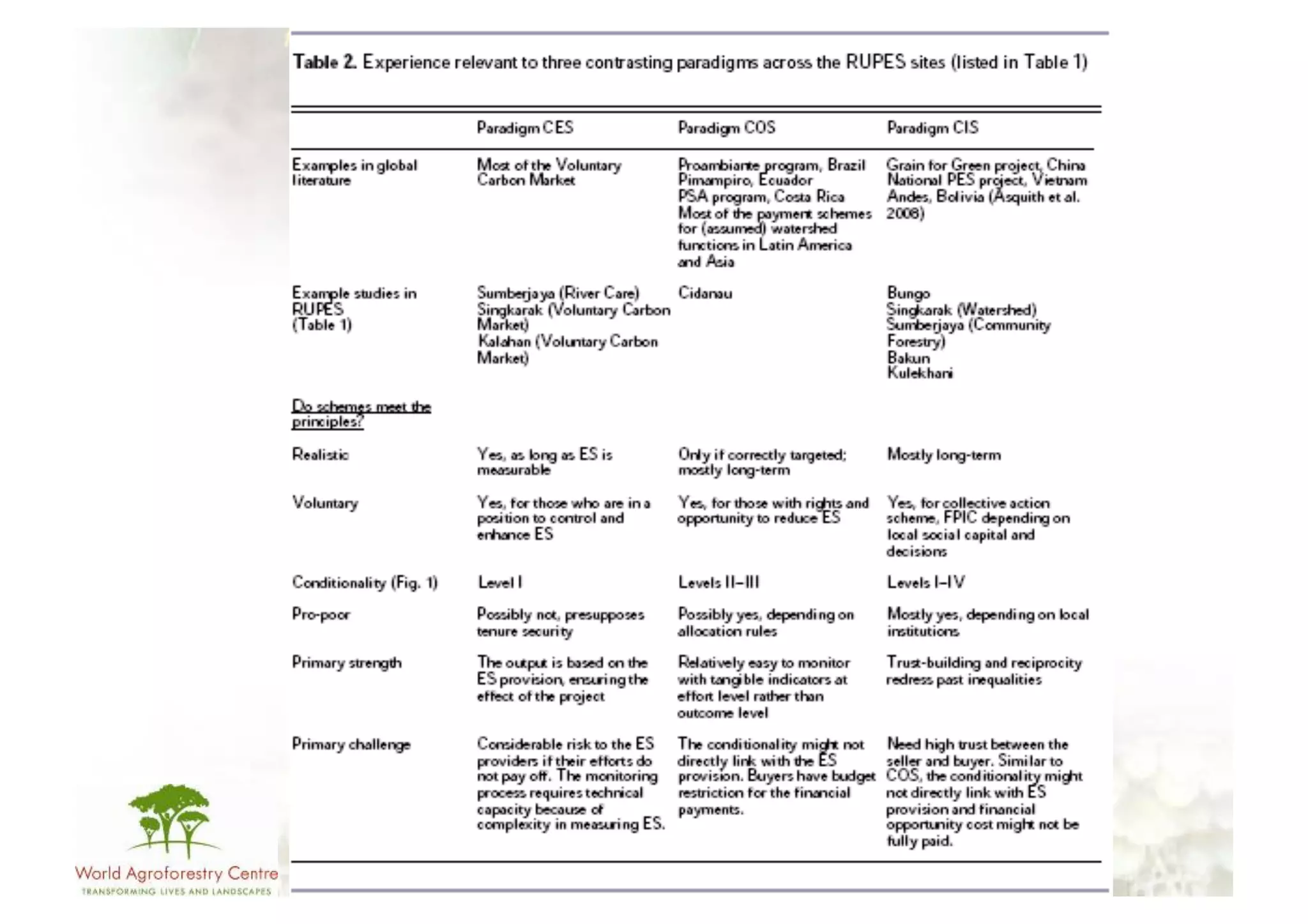
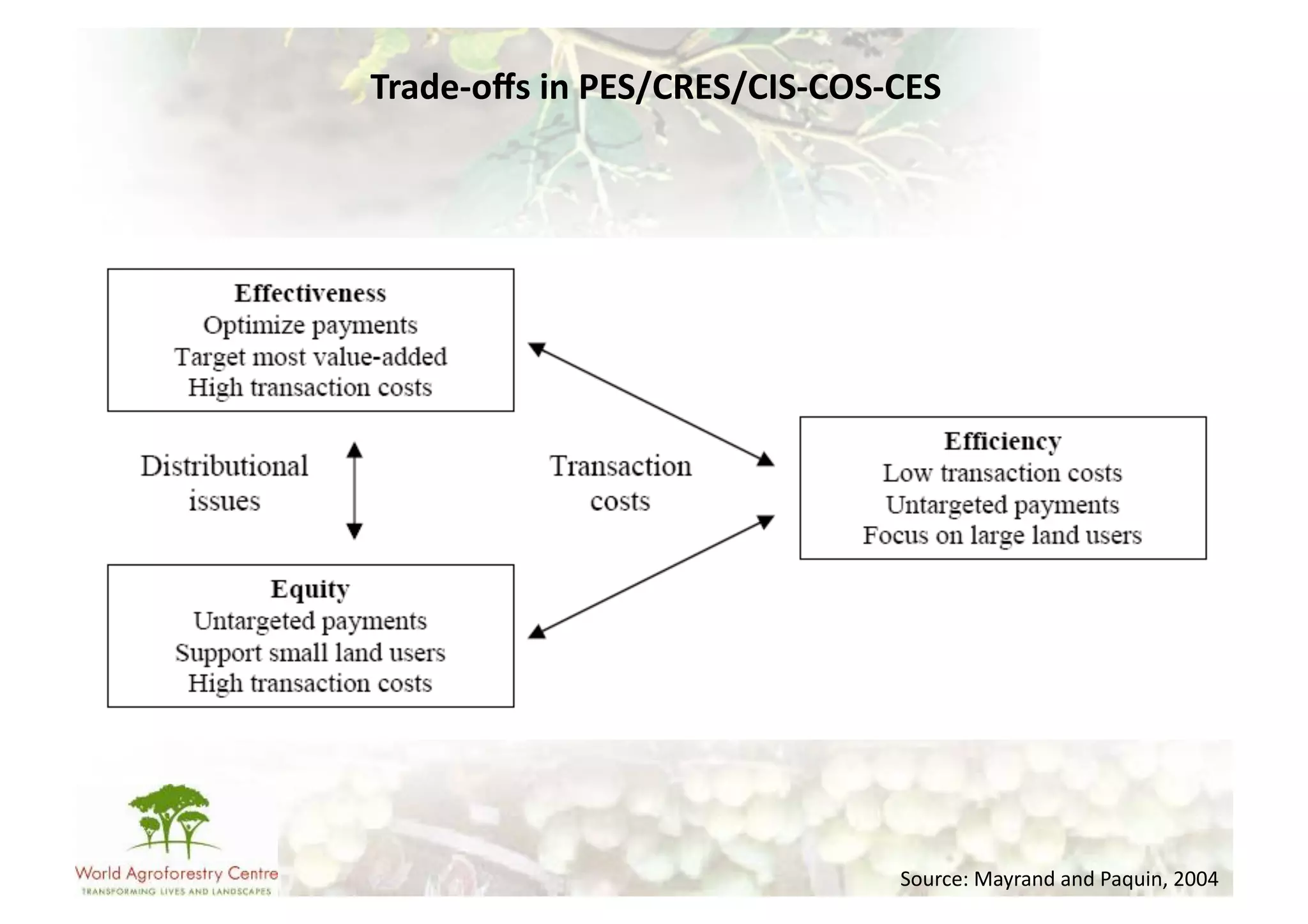
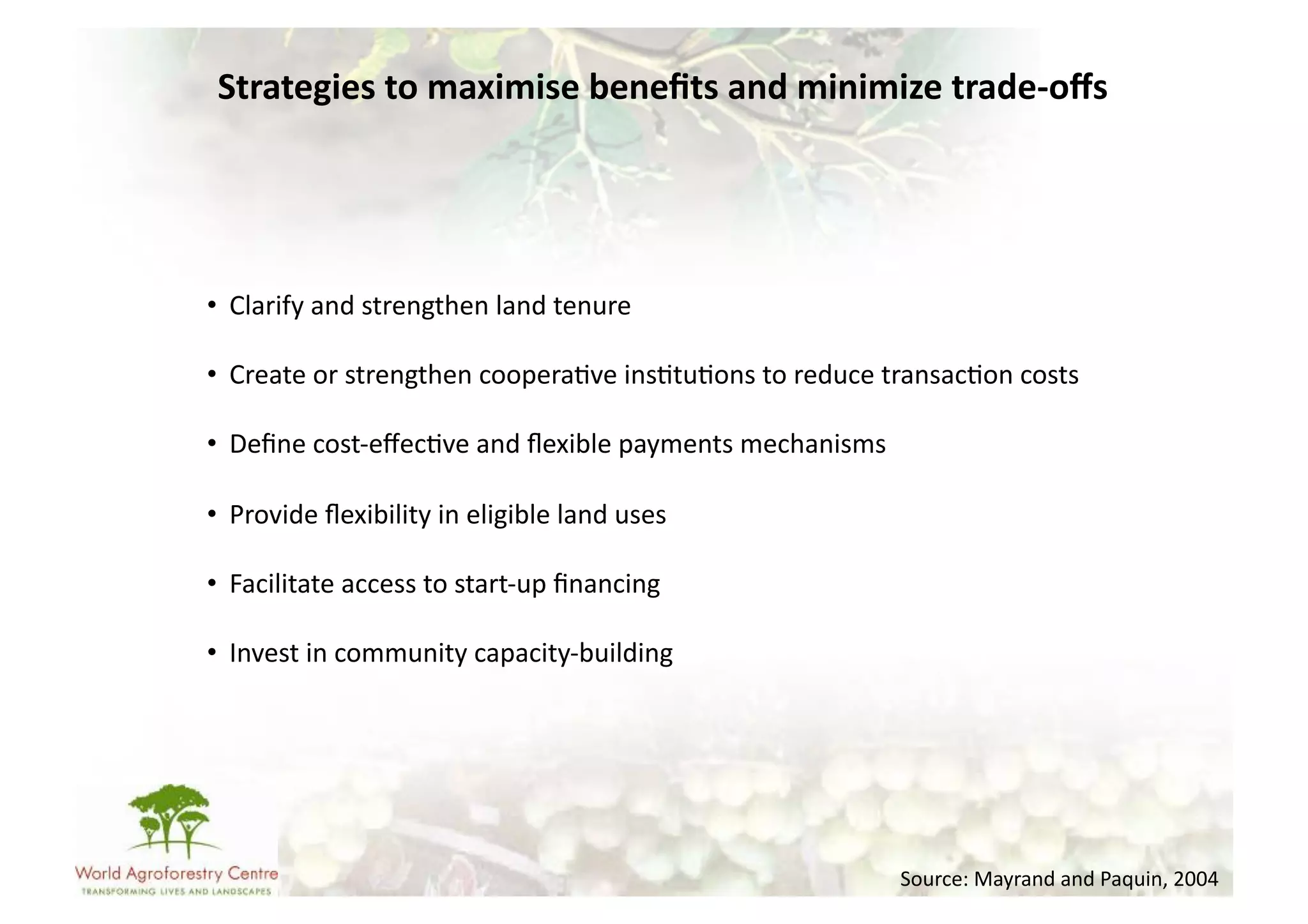
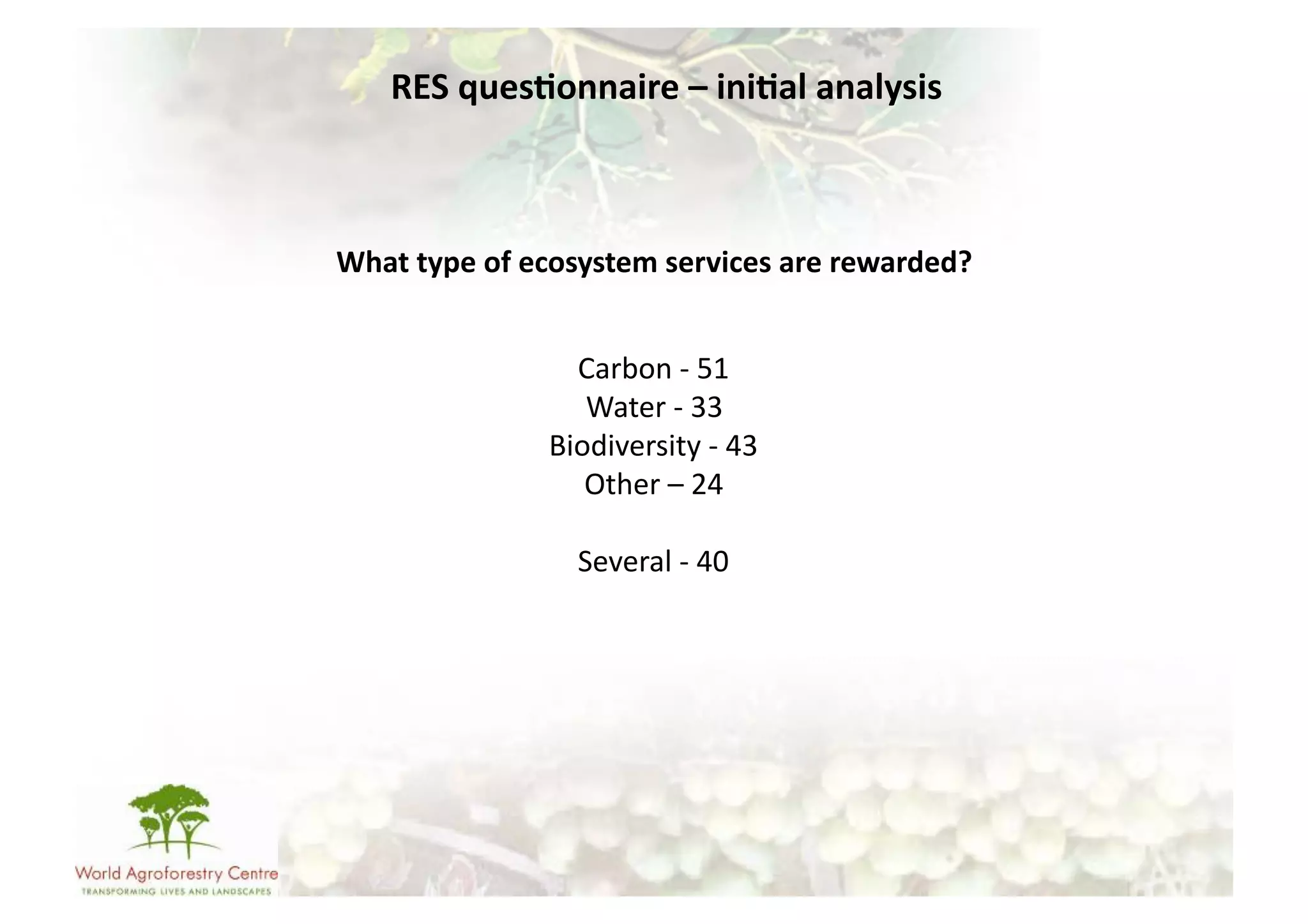
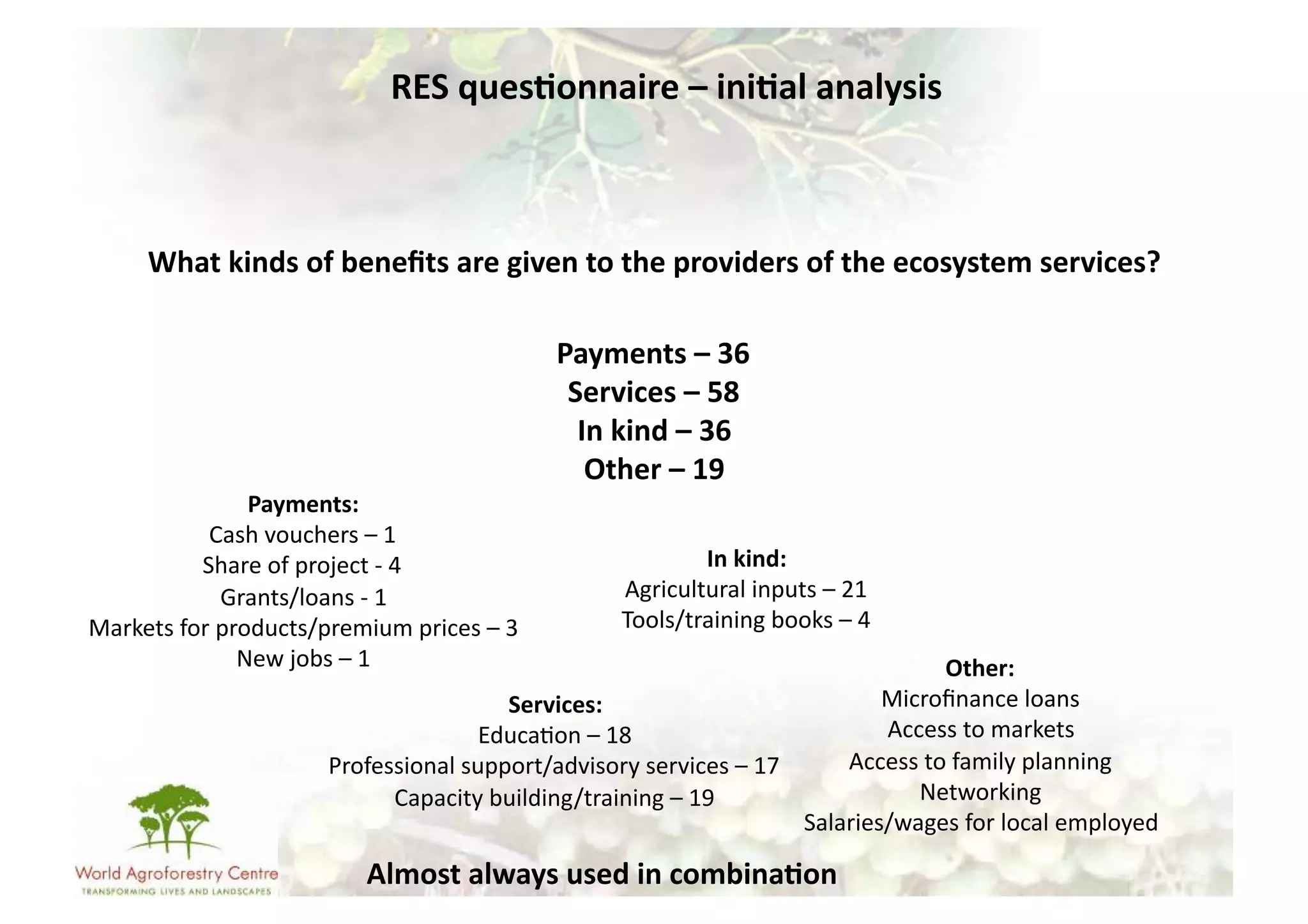
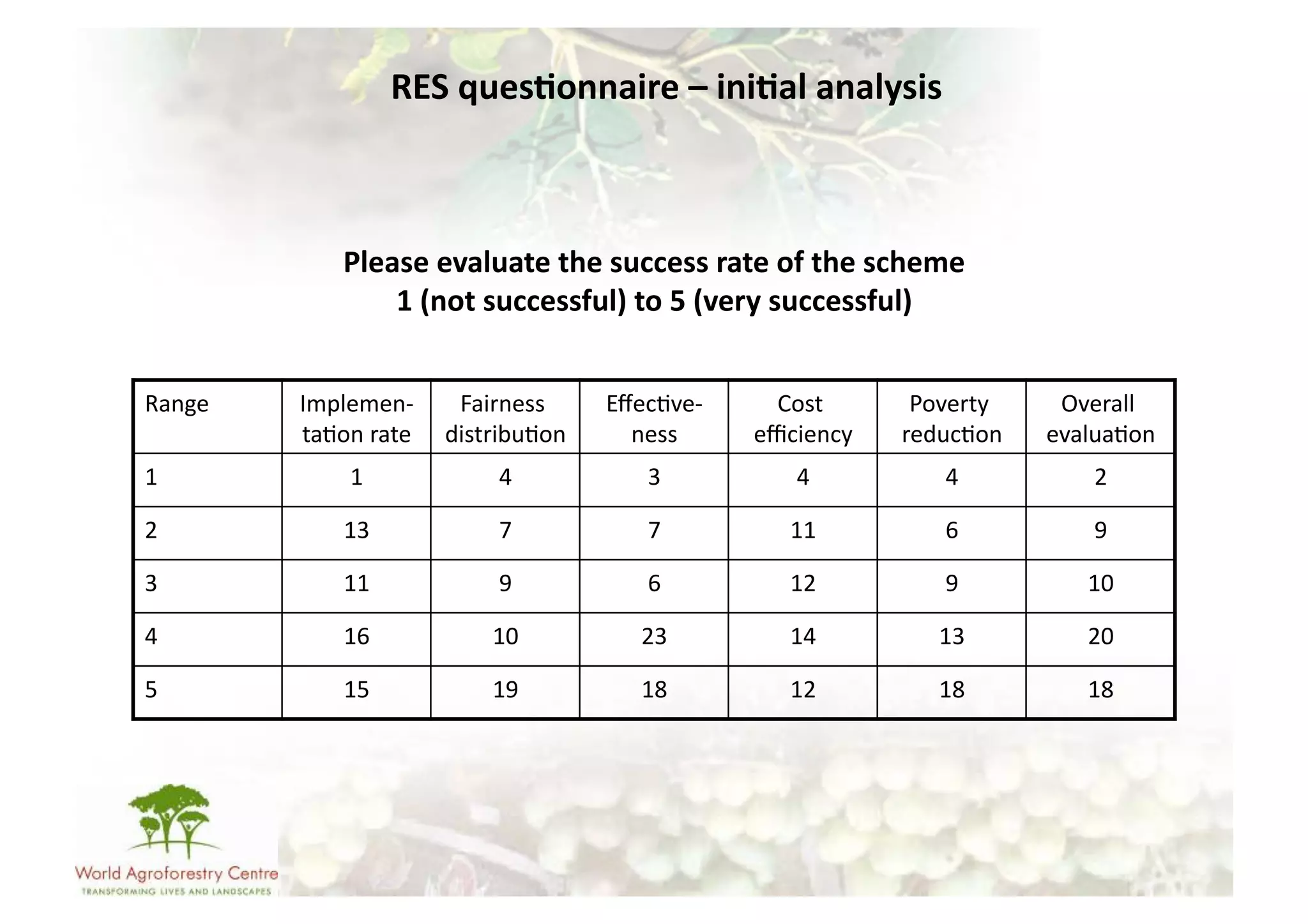
The document discusses climate change adaptation and mitigation through payments for environmental services (PES) in agriculture, focusing on criteria for successful schemes, stakeholder roles, and types of ecosystem services. It highlights strategies to maximize benefits while minimizing trade-offs, as well as the challenges and conflicts that can arise in implementation. The document emphasizes the need for flexible payment mechanisms, strong land tenure, and community engagement to enhance effectiveness and equity in environmental service rewards.