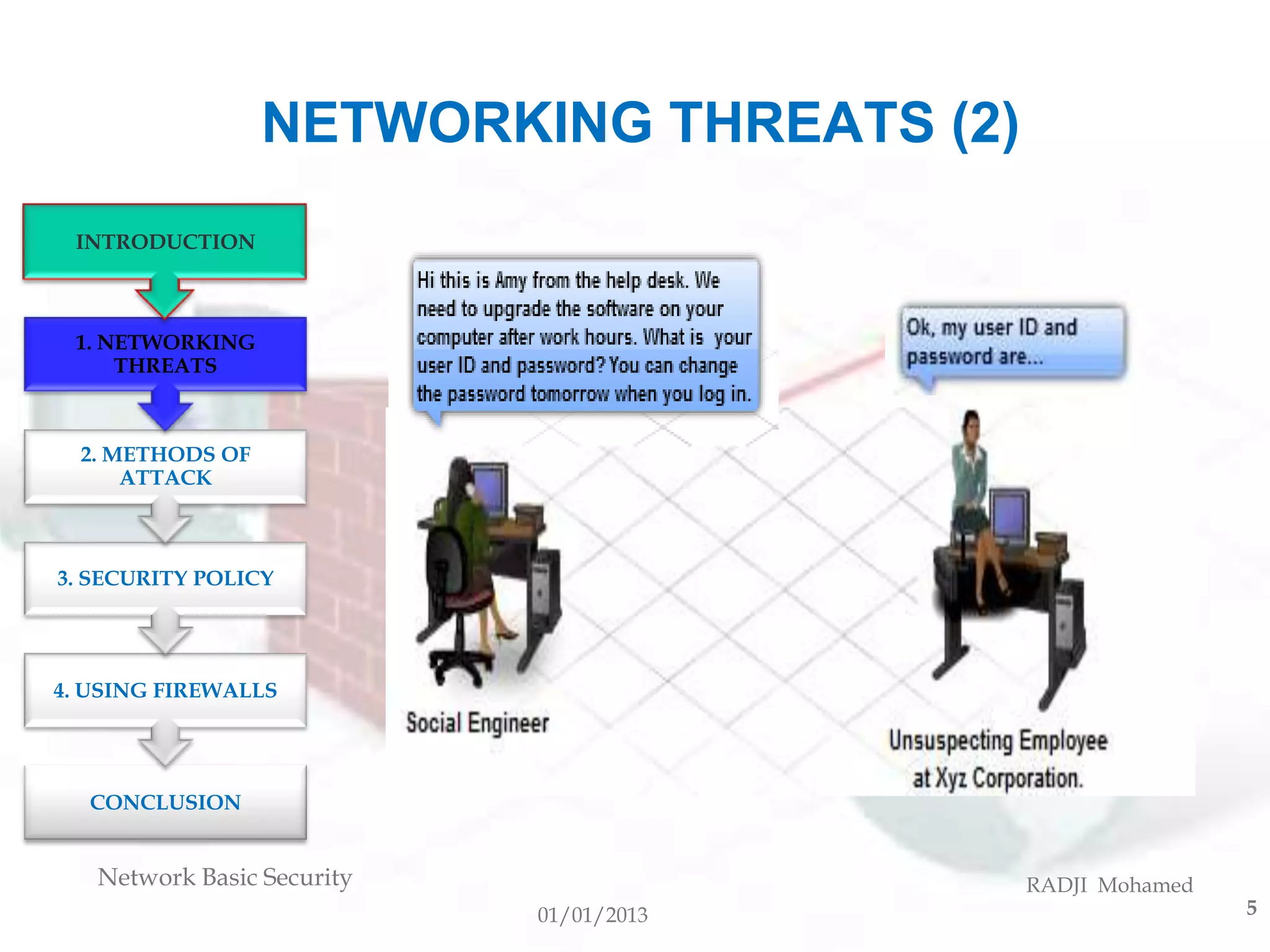
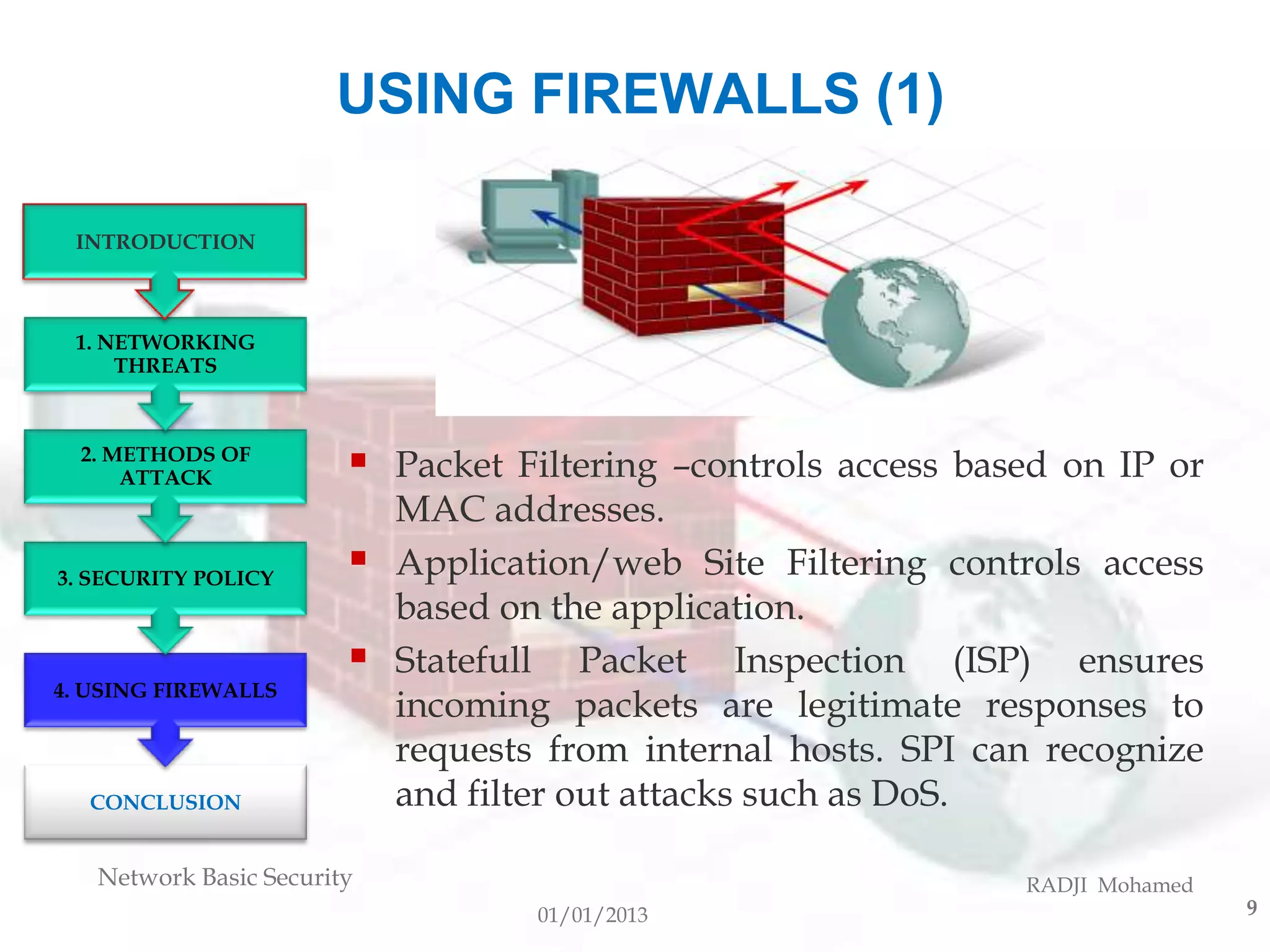
This document discusses network security basics. It covers networking threats like hackers and social engineering. Methods of attack include viruses, worms, and Trojan horses. The importance of security policies, keeping software updated, using antivirus software and firewalls are explained. Firewalls can use techniques like packet filtering, application filtering and stateful packet inspection to control network access and detect attacks. Finally, the document thanks the reader for their attention and welcomes questions.