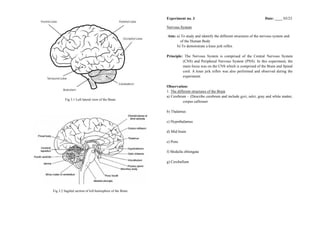
This document summarizes an experiment on the nervous system. It describes the main structures of the brain including the cerebrum, thalamus, hypothalamus, midbrain, pons, medulla oblongata, and cerebellum. It also describes the spinal cord as an elongated cylindrical structure suspended in the vertebral canal surrounded by meninges and CSF. Finally, it examines the knee jerk reflex, describing the reflex arc and sequence where a hammer hitting the patellar tendon causes sensory neurons to fire, sending a signal to the spinal cord and then back to the quadricep muscle, causing it to contract and straighten the leg.