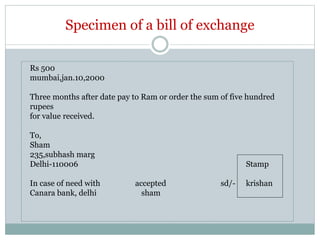
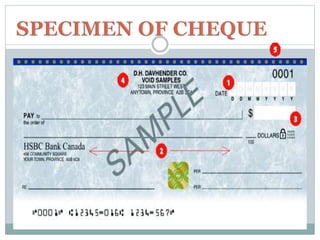
This document provides an overview of negotiable instruments, including promissory notes, bills of exchange, and cheques. It defines a negotiable instrument as a written document that can be transferred between parties in exchange for consideration. The key characteristics are that negotiable instruments are freely transferable, the holder's title is free from defects, and certain presumptions apply regarding dates, times, and signatures. The document outlines the essential elements and parties involved in promissory notes, bills of exchange, and cheques under Indian law. Sample templates and specimens of each type of negotiable instrument are also presented.