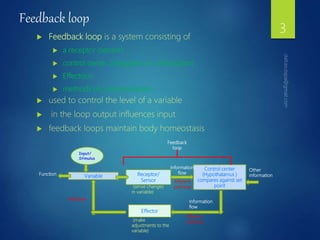
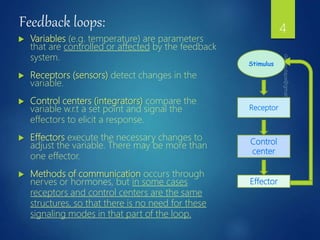
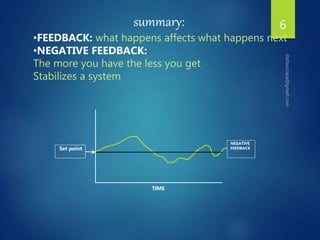
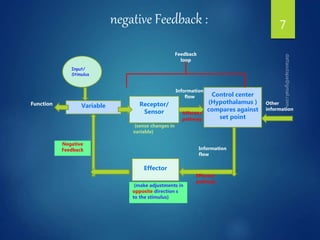
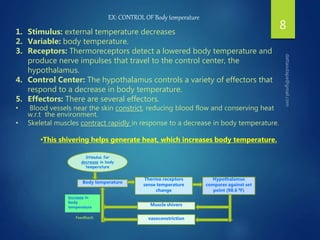
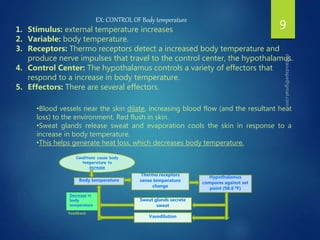
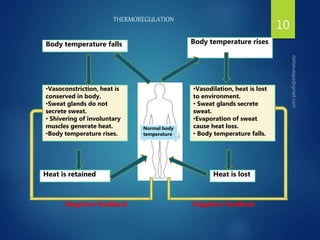
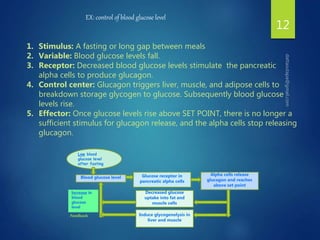
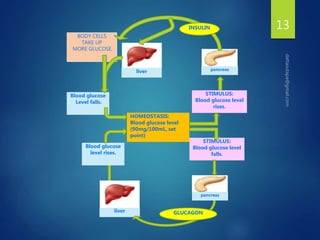
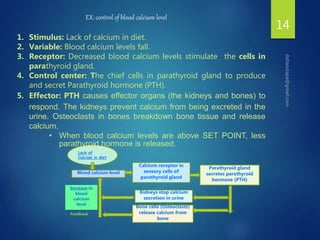
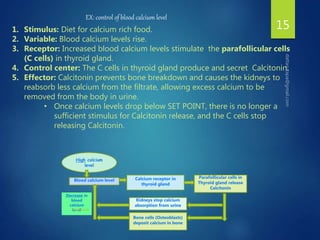
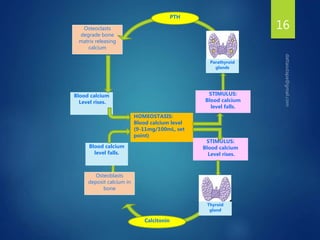
The document discusses physiological homeostasis through negative feedback loops. It explains that homeostasis refers to dynamic processes that maintain balance in internal variables like temperature, blood glucose, and calcium levels. Negative feedback loops work to stabilize these variables. They involve a stimulus, receptor, control center, and effectors. The control center compares the variable to a set point and effectors enact changes that oppose the stimulus in order to return the variable to the set point, maintaining homeostasis. Examples provided are control of body temperature, blood glucose, and blood calcium levels.