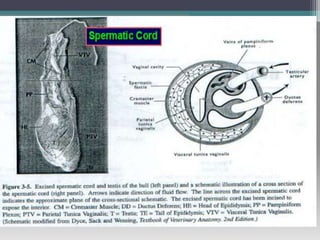
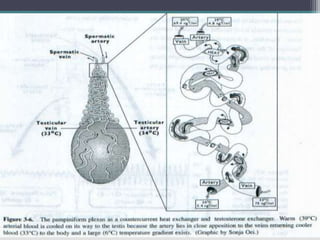
The document summarizes various mechanisms that regulate heat in the scrotum to maintain the optimal temperature for sperm production. It discusses (1) the tunica dartos smooth muscle and cremaster muscle that relax or contract to control proximity to the body, (2) the counter-current mechanism where the testicular artery exchanges heat with returning veins to deliver cooler blood to the testes, and (3) a lack of fat layer and abundance of sweat glands that enhance heat loss and keep temperatures lower than the core body. These combined mechanisms precisely regulate scrotal temperature for spermatogenesis.