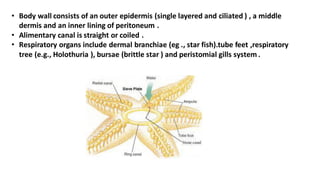
Echinoderms are exclusively marine animals with radial symmetry and calcareous ossicles that make up their endoskeleton. They have pentamerous radial symmetry as adults but bilaterally symmetrical larvae. Their defining feature is an ambulacral water vascular system that uses tube feet for locomotion and helps filter feed. Echinoderms have both indirect development through larval stages and undergo metamorphosis from bilateral larvae to radially symmetrical adults.